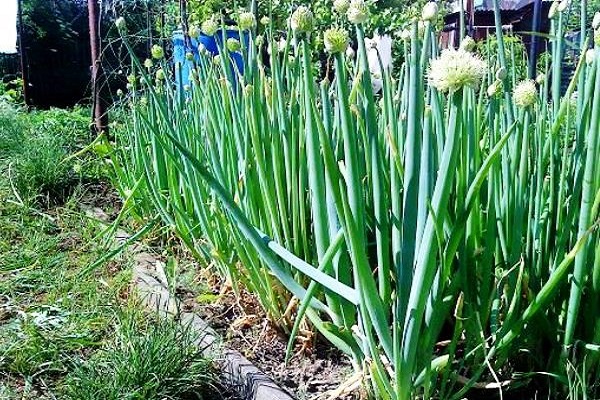
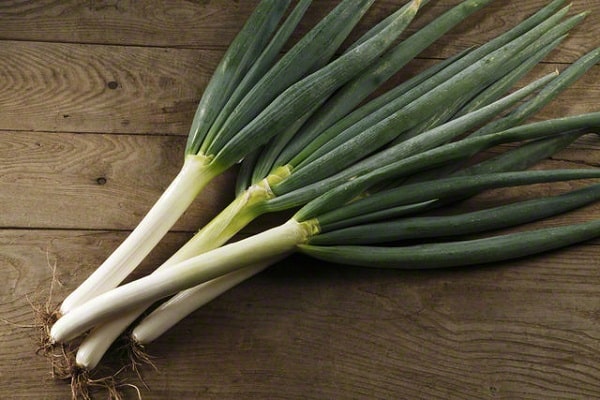
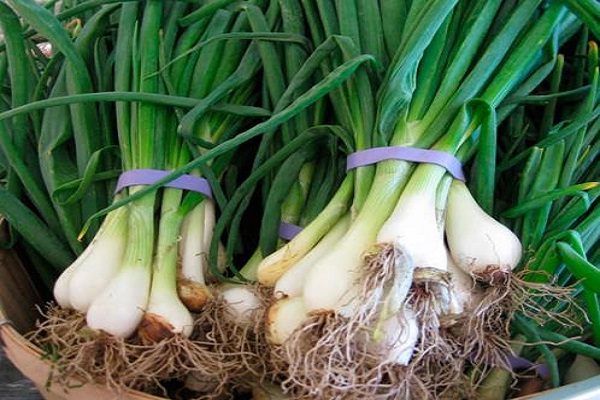
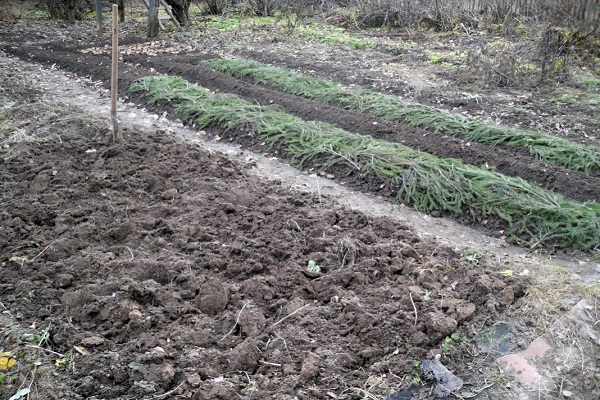
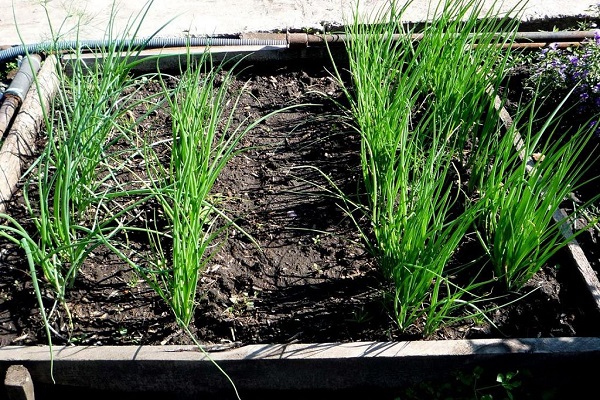
In April, the human body craves vitamins and garden herbs, and here the onion comes to the rescue, replenishing the reserves of essential elements. A herbaceous plant came to us from Asian countries and gained popularity among residents of even the northern regions. The crop is valued for its endurance and ability to withstand spring frosts. The plant is an unpretentious species, because it is grown for its juicy green leaves, and the size of the bulb does not matter.
- What is onion batun?
- Preparatory procedures at the site
- Choosing a landing site
- Good and bad predecessors for onion
- Planting onions in the garden
- Preparing seeds before planting
- Seed sowing pattern and depth
- Timing of sowing seeds
- Care and cultivation of onion
- Watering mode
- Weeding and loosening of rows
- Fertilizer application
- Diseases and pests
- Harvest
- Forcing onion greens in winter
What is onion batun?
The herbaceous plant is classified as a perennial, although annual species of the vegetable are also found.
The roots of the batun are a complex bulb from which leaves emerge that look like a pipe. That’s why another name for the batun is the fiery onion. The green leaves reach two centimeters in diameter and up to thirty to forty centimeters in length. Each daughter branch has five to seven leaves.
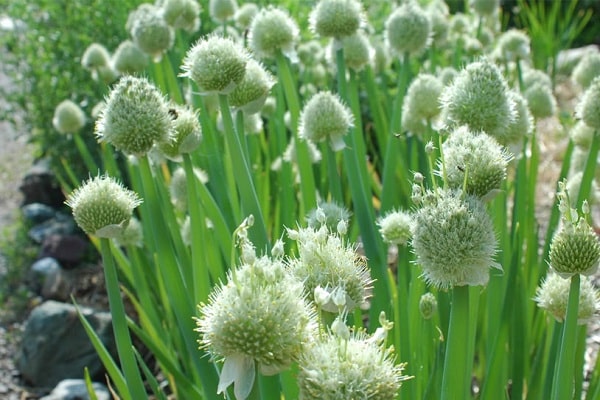
Among the shoots during the growing season, a dense stem appears, at the end of which there is a ball consisting of many small white flowers. They emit a scent that attracts insects to pollinate the plant. Soon the flowers turn into seeds. Growing batun onion from seeds is used more often than propagating the crop by vegetative means.
A variety of the crop is multi-tiered onion, which is divided into Chinese, Russian and Japanese types. All subspecies differ in the volume of green mass, degree of branching, and pungency of taste. There are early-ripening and late-ripening varieties of batun.
The advantage of growing crop varieties is that onions:
- produces large yields of green mass;
- contains twice as much ascorbic acid in the leaves;
- ripens earlier than everyone else;
- resistant to vegetable diseases.
Without the spring, the diet loses many vitamins and microelements that are so necessary for a person at this time.
Preparatory procedures at the site
It is worth preparing a bed for planting perennial onions in the fall, when the harvest from the garden is harvested.
Before digging the area, add a bucket of compost for each square meter. The earth requires wood ash as a source of phosphorus; 150 grams is enough.
Depleted soils are fed with ammonium nitrate, superphosphate (25 grams each), and potassium chloride (15 grams). It is better to dilute the mineral complex in ten liters of water and pour it over the area.
In the fall, the composition of the soil is also checked, determining the pH level. For a perennial crop, acidity is needed closer to neutral, 7.0 - 7.3 units. If the soil is acidic, then add slaked lime or sprinkle with dolomite flour, embedding it in the bed.
All that remains is to dig up the soil or plow the area to a depth of eight to ten centimeters. After harrowing, the ridges are marked, leaving space for planting onions on greens.
It is worth choosing an early variety of batun, which will ripen in April.
Choosing a landing site
The place for the culture is chosen based on the fact that the plant needs a site where:
- there is no stagnation of water;
- fertile soils;
- loamy or light sandy loam soil;
- there is partial shade or sun.
Although the herbaceous plant loves moisture, prolonged rains will lead to swampiness of the low places where it grows. perennial onion batun. This is especially dangerous in March, when groundwater lying close to the surface floods the beds with the plant.
Good and bad predecessors for onion
Since the plant needs fertile soils, they choose areas where vegetables grew that are suitable for the crop as predecessors.
Planting of batun onions is organized where white and Chinese cabbage, potatoes, and tomatoes grew. The herbaceous plant feels good after radish, radish, dill and celery. You can plant batun where beans grew, since after legumes the soil is saturated with useful substances. Vegetables and herbs are harvested in the fall, and the beds begin to be prepared for planting onions.
You cannot plant a perennial crop after carrots, cucumbers, and garlic. Spores of pathogenic fungi remaining in the soil will cause vegetable diseases.
Planting onions in the garden
So how to grow onion from seeds easier, then you need to decide on the timing of sowing. After all, this can be done not only in spring, but also in autumn. They also choose another time for sowing the plant.
The rules for planting onions include:
- preparation of beds and seed material;
- choice of planting density;
- care of planted material.
Both perennial and annual types of batun are grown by seeds. In one place, a perennial crop can grow for seven years without losing its beneficial qualities. For annuals, the planting site is changed annually, without leaving it in the same area.
Preparing seeds before planting
Onion propagates both by seeds and vegetatively. But preference is given to seeds, since when they are planted, the varietal qualities of the vegetable are preserved.
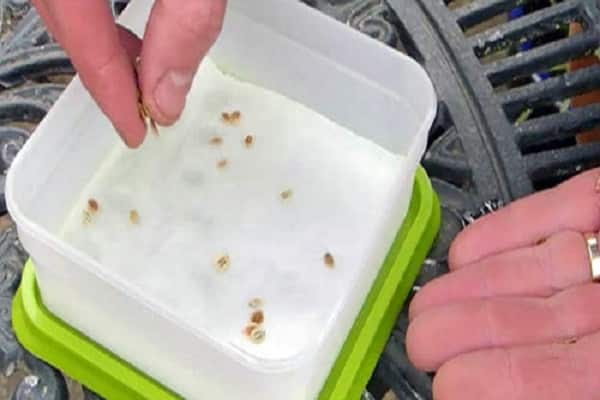
Seed germination is slow, so before sowing in the ground, planting material is soaked in cool water and left for a day. It is worth changing the water twice. After hardening, the seeds are dried.
To speed up the emergence of seedlings, place a bag of nigella in a solution with complex fertilizers. A warm solution of potassium permanganate will protect the seed from the action of pathogenic microorganisms.
Thanks to proper seed preparation, onion sprouts will appear within a week or ten days.
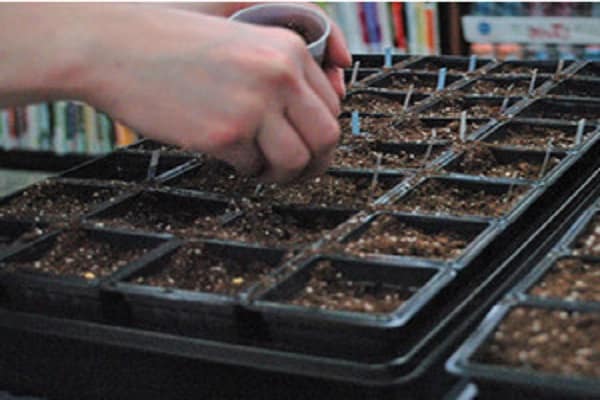
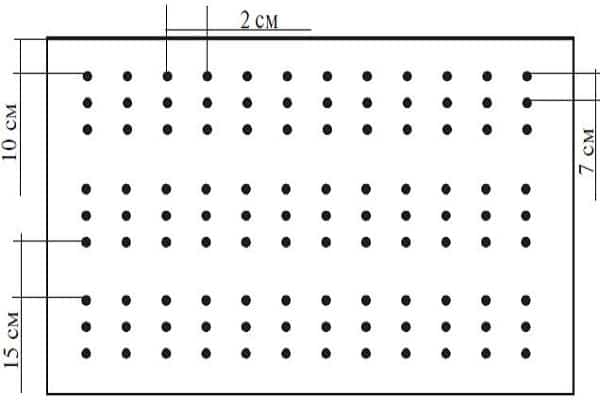
Seed sowing pattern and depth
The method of planting a perennial plant is a two-line tape method. A gap of seventy centimeters is left between the tapes. The distance in the row should not be large, because the bulb does not form, so 10–15 centimeters is enough. The planting norm is considered to be 1.5–2.0 grams per square meter. In cold weather, the density increases to three grams per square meter.
The grains are buried 2–3 centimeters into the ground.The crops are sprinkled with a layer of mulch. After the seeds are buried, the soil is slightly compacted, and after a week the beds need to be loosened.
Timing of sowing seeds
Annual plant varieties are planted as soon as the snow melts, in the first half of March. In Siberia, sowing time is the end of March.
You can postpone planting seeds until the summer. But they sow so that the vegetable has time to grow before the cold weather. When you plan to sow onions in June, the vegetable will ripen in May.
But when you want to plant a batun in the fall, for the winter, then they select the weather so that the plant does not freeze, sprouting ahead of time.
The green mass is harvested depending on the time of sowing. Autumn planting will allow you to collect succulent feathers only in mid-summer.
Annuals are valued for the large amount of feathers they produce during the growing season. But perennial varieties do not require constant planting. The batun was planted, and in the second year they began to trim the leaves. Useful foliage is collected twice during the season.
Care and cultivation of onion
You definitely need to know about caring for and growing batun onions. After all, without following the rules of agricultural technology, a vegetable plant may die. You will have to be careful about growing the batun. Growing features include common activities that are performed regularly. Planting vegetables requires:
- glaze;
- feeding;
- loosening.
Although leafy vegetables rarely get sick, you also need to be able to free them from infections and pests.
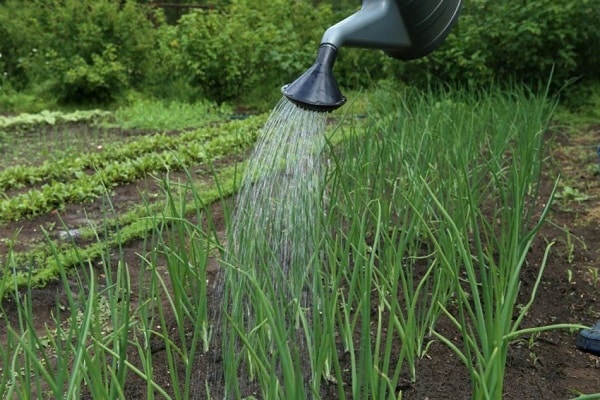
Watering mode
For garden plants, soil moisture is important during the growing season. After the first shoots appear, water generously to speed up leaf growth. If the area for the vegetable is selected correctly, there will be no stagnation of moisture. And the young greens will be served on the table in two weeks.Every three days, water ten liters of liquid per square meter of plantings. During the rest period, the frequency of moisturizing is reduced. To get a good harvest of green leaves, watering should be done in moderation.
Weeding and loosening of rows
For a full growing season, monitor the planting density of the trampoline. Thinning is included in the agricultural technology of vegetables. Excess plants are removed, leaving a distance of six to nine centimeters.
Loosening of row spacing is carried out after each watering, removing the top crust. The depth of loosening should not exceed three to five centimeters, so as not to damage the roots of the plant.
During the dormant period, onion care is not stopped, freeing the beds from weeds. Shooting occurs constantly in culture. Therefore, there is no need to panic about what to do if the batun bow goes into the arrow. If the seeds are not needed for sowing, the arrows are cut off. But when all the stems start to shoot, this indicates a lack of moisture in the soil.
Fertilizer application
Like any plant, the batun requires feeding during the growing season. Soil fertility is important for the growth of green mass. The vegetable is planted in soil fertilized with organic and mineral complexes. The first feeding is carried out with mullein infusion in a ratio of 1:8 or bird droppings in a ratio of 1:20. In the future, it is worth eliminating fertilizers containing nitrogen. Includes nutritional complexes with potassium and phosphorus.
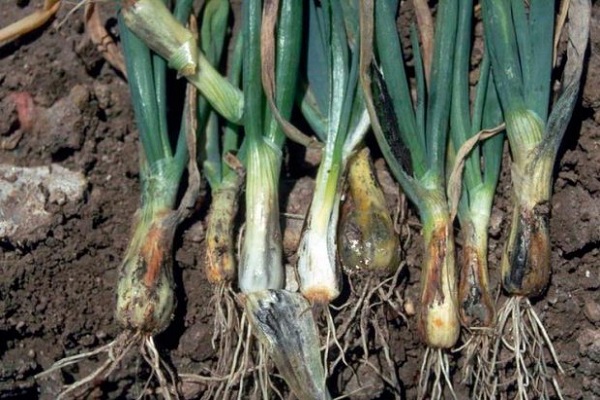
Diseases and pests
By the appearance of the plant, it is determined whether the onion has been exposed to disease or not. The leaves begin to turn yellow, wither, and become covered with brown spots. The result of the disease is drying of the aerial part or rotting of the neck. And the infection must be fought immediately. An experienced gardener knows how to deal with plant pathologies. Control measures include:
- spraying with fungicidal agents such as Fitoverm;
- removing diseased plants from the garden;
- treatment with preparations containing copper.
The plant rarely gets sick, but the appearance of pests must be monitored carefully. The onion fly, moth, and weevil are especially fond of planting vegetables. Insects and larvae feed on the sap of the plant, gnawing inside the leaves. You can save yourself from pests with insecticidal agents, as well as by treating plants with mustard solution (one tablespoon per 10 liters of water), infusion of potato tops (a kilogram per bucket of water).
Diseases and pests will bypass the onion bed if you follow crop rotation, planting pattern and frequency, and loosen the soil.
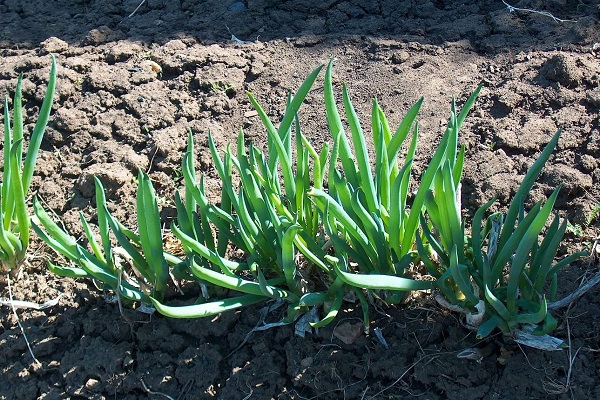
Harvest
To harvest the first vegetable harvest, plantings from the second year of life are taken. Although you can cut off the leaves after a month has passed from the date of sowing. The green mass is completely removed in the fall before winter, but no later than a month before the onset of frost.
Next year, cut it when the onion appears in the spring and reaches a height of 20 centimeters.
Cut the stems closer to the surface of the ground. The leaves are sorted, tied into bunches and wrapped in film. Store the leaves in the refrigerator. The dug up bulb can also be placed at the bottom of the refrigerator without removing the leaves. The green color of the stem is used to decorate salads and sprinkle dishes.
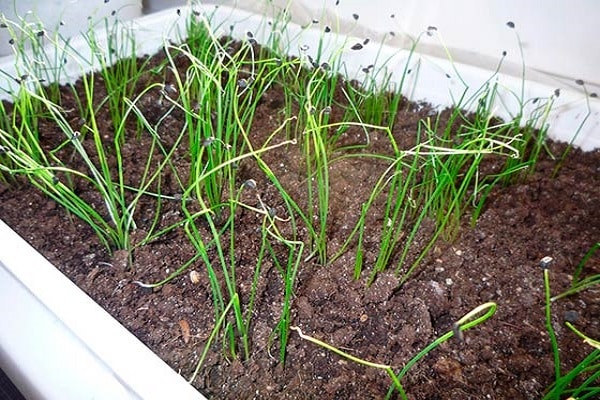
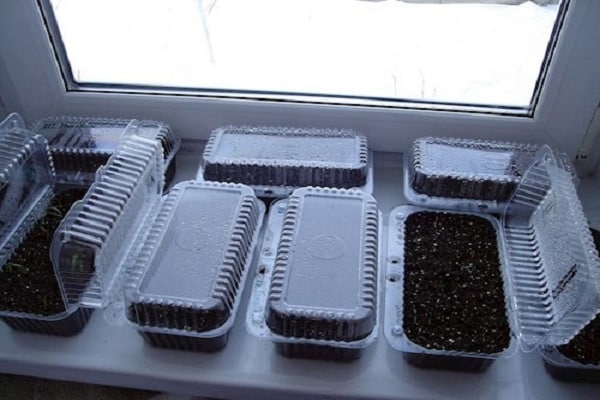
Forcing onion greens in winter
In autumn, when to plant onions It’s too late for the vegetable garden; it’s grown on the windowsill. In October, mature stems are dug up. The operation is carried out carefully, trying not to damage the roots, without removing the earthen lump from them. For plants, choose containers with drainage holes. A layer of pebbles or crushed stone is placed in them, then nutrient soil.
The diameter of the container is selected to be five to seven centimeters wider than the clod of earth on the roots.Forcing onions will be successful if the plant is provided with an air temperature of 18–20 degrees and a humidity of 80 percent. In a month, healthy greenery will appear on the window. In the spring, when the soil warms up to five degrees, the plant is returned to its place, in the garden.