To prevent onion diseases from causing significant damage to the crop, you need to know preventive measures, rules of cultivation and care, as well as methods and means of combating them. Knowing the description of onion diseases, you can carry out the correct treatment.
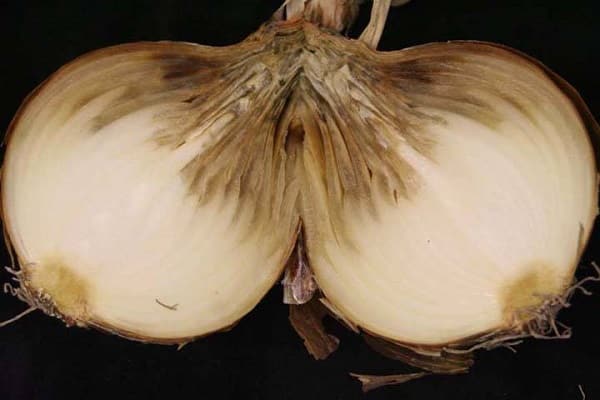
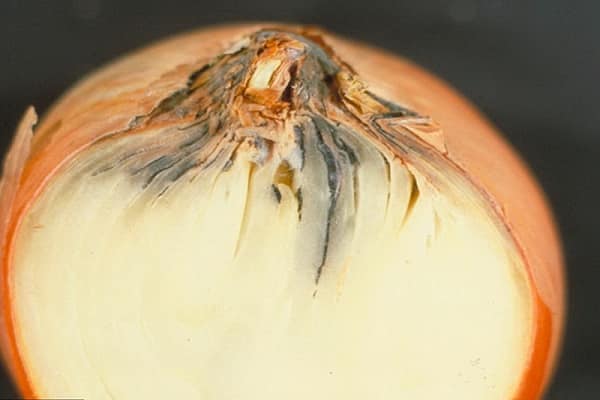
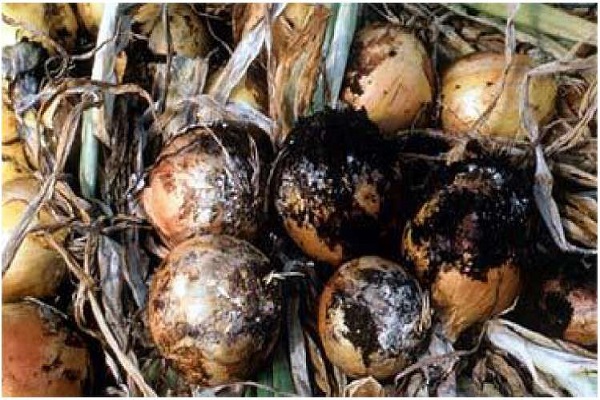
Neck rot of onions
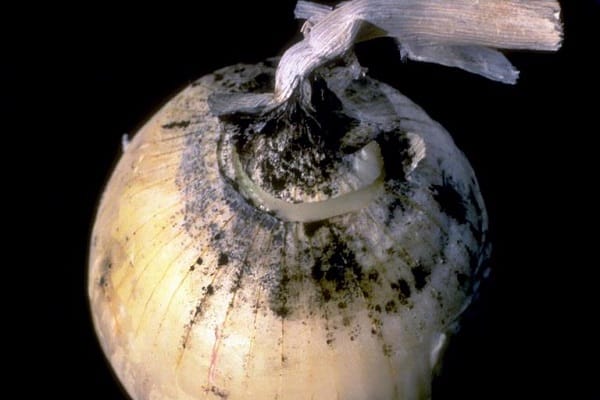
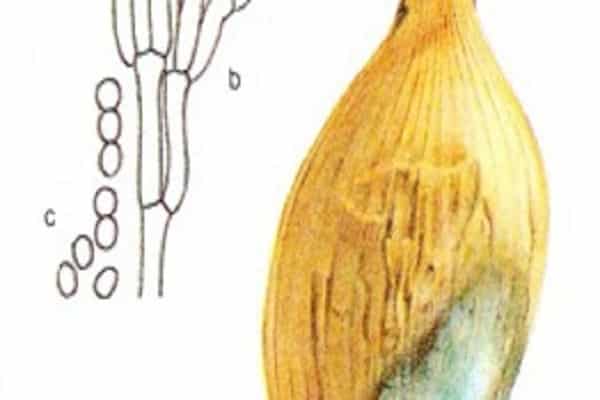
The causative agent of cervical rot is a fungal infection. Often the disease affects unripe bulbs or crops that have been in wet soil for a long time.
A characteristic sign is softening of the neck of the bulb, its thinning and rotting. A gray fluffy coating and an unpleasant odor appear.Gradually, the plaque turns into small black grains that merge with each other. If you do not start fighting the disease, plaque covers the entire bulb.
If you plant infected bulbs, then in the future the feathers will grow weak and pale green. The inflorescences do not reach the ripening stage, become covered with mold and the heads drop down.
The main agrotechnical measures to combat the disease are:
- For planting, you need to choose fungus-resistant varieties;
- after harvesting, the site is cleared of all waste;
- weeding and watering the beds are carried out carefully, without damaging the feathers;
- do not overdo it with nitrogen fertilizers;
- You need to harvest in dry weather, drying the collected bulbs for at least two weeks;
- The leaves of the harvested onions do not need to be cut too short; it is recommended to leave a stump of 3–4 cm.
- Only whole, large and dense heads, without damage, are selected for storage;
- It is advisable to treat planting material with special solutions.
If neck rot of onions has already appeared, chemical control measures will help. Treatment with fungicides such as Tigam, Benlat, Fundazol helps. During the formation of the heads, the beds are watered using the drug Effecton. For foliar treatment, you can use a solution of copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture.
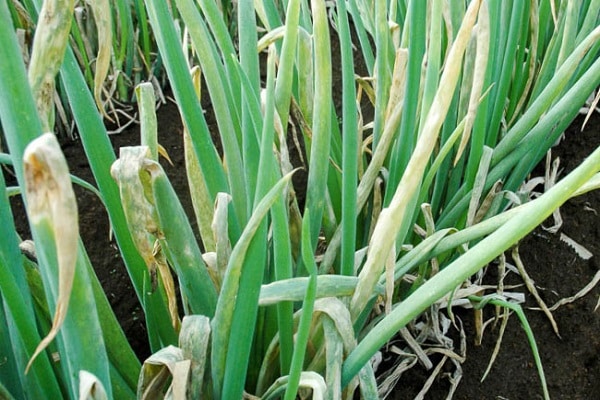
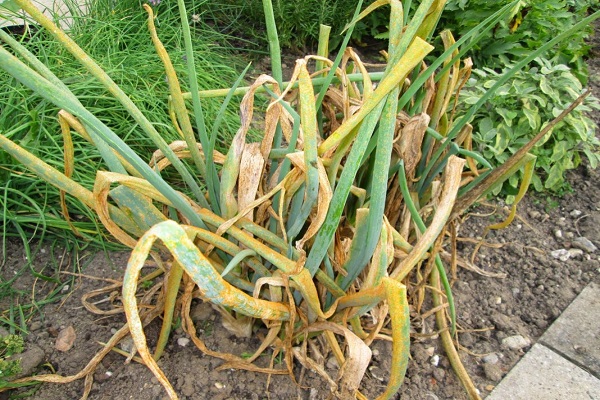
Downy mildew
The fungal disease downy mildew spreads favorably after prolonged rains or when watering rules are not followed. The affected feathers of the vegetable look sluggish, drooping, and lose color saturation. Gradually, the leaves become covered with brown-yellow spots, dry out and the plant dies.
Onion pests, such as aphids and whiteflies, contribute to the spread of infection.They spread spores to healthy plants, and the disease quickly gains momentum.
Preventive measures to combat the disease are:
- vegetable beds need to be weeded;
- In the fall, they begin to prepare the land allocated for planting onions: they dig up, apply fertilizers, and disinfect;
- seedlings can be sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux mixture;
- in rainy, cool summers it is useful to treat vegetable beds with biological products such as Fitosporin, Planriz, Gamair.
To disinfect the soil, you can use a solution of copper sulfate, Fitosporin, Alirin, Gamair, Baikal-Em. You can treat onions to remove powdery mildew with such products as Thanos, Ridomil, Vectra, Topaz.
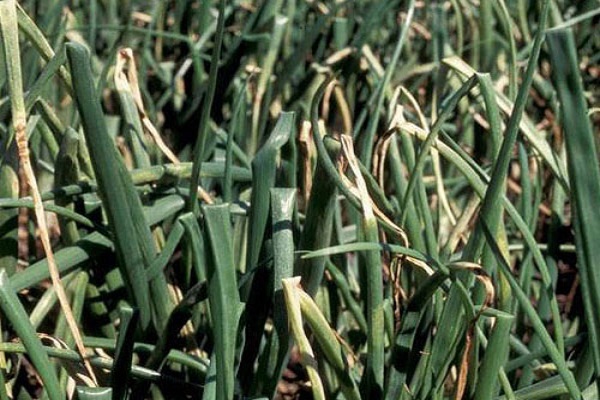
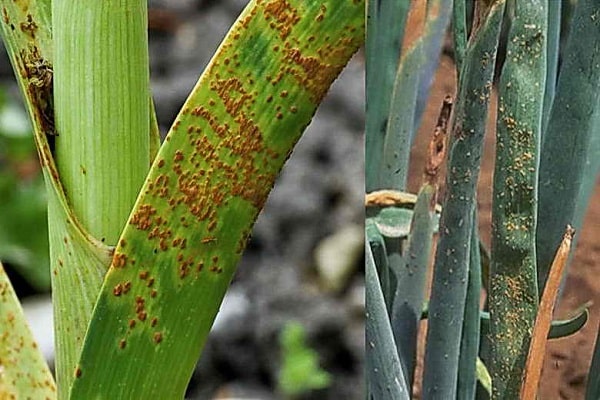
Onion rust
Signs of infection by the fungal disease rust include wilting, drying and yellowing of the leaves. The bulb is formed in small sizes and is poorly stored. Orange-yellow or brown-reddish tubercles appear on diseased leaves. Gradually the feathers begin to die off.
Fungal spores tolerate cold well and overwinter on plant debris. That is why it is recommended to remove the remaining tops from the garden at the end of the growing season. The development of rust is also promoted by cool, rainy summers, too dense plantings and an excess of nitrogen in the soil.
What to do if the feathers become coated and other signs of rust appear? Most often, the disease develops at the end of summer, so it is important to inspect your plantings daily. If a problem occurs, you need to stop watering the beds and applying nitrogen fertilizers. Damaged stems are cut off and removed away from the site.
If signs of disease are detected, the vegetable crop should be treated with fungicides. Folicur, Ordan, Topaz are considered effective.The drug Hom, Tilt or simple Furacilin cope well with the disease.
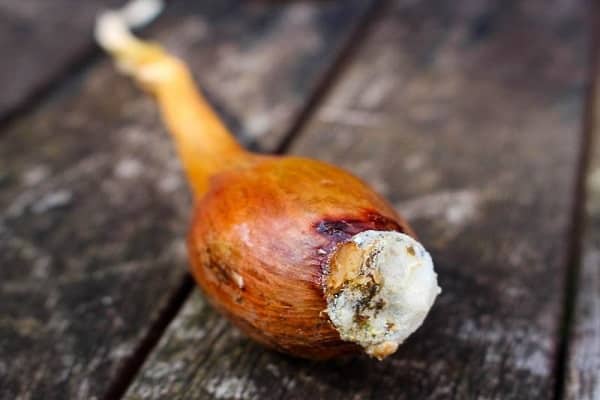
Fusarium
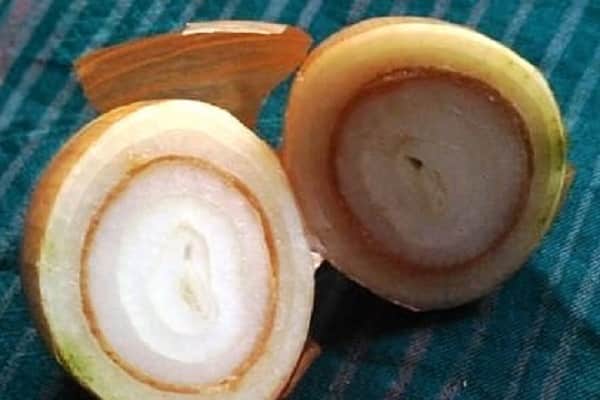
Common onion diseases include the fungal disease Fusarium. The appearance of the first signs is indicated by yellowing and wilting of the leaves. Initially, the tops of the feathers are affected, gradually rotting spreads along the entire length of the leaves. Often the bulb itself rots. It becomes watery, softens and smells unpleasant. A pinkish fungal coating forms on the bottom of the bulb.
Provoking factors are excess moisture in the soil, untimely harvesting, poor-quality planting material, and too dense planting.
Proper preparation of soil and seed material is considered preventive control measures. It is recommended to treat the soil with copper sulfate or a preparation such as Iprodione. Disinfection of planting material is carried out with a solution of the drug Fitosporin, Quadris or Fundazol, which can be soaked in a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
If signs of disease are detected, it is necessary to remove the affected plants from the garden and burn them, and treat the remaining vegetables, for example, with Fitosporin.
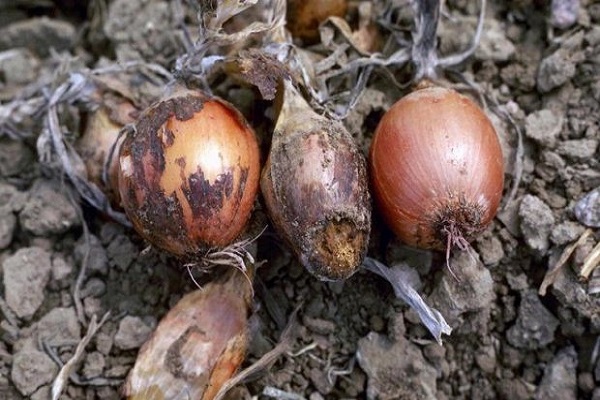
Bacterial rot of onions
Bacterial rot penetrates into the wounds that form on the leaves during weeding or watering. The first signs of rot infection become noticeable on the leaves. Light spots first appear on them, then they increase in size and reach the neck. After rains, watering or dew, bacteria penetrate deep into the soil to the onion head.
Unlike bulbs that are affected by onion bottom rot (fusarium), the heads with this disease may look healthy. But when you cut it, you can see that the core is completely rotten. Gradually, rotting spreads from the center to the edges of the head.
Prevention and control of the disease consists of observing the following rules:
- It is not recommended to plant onions in the same place for several years in a row;
- After harvesting, you need to remove all plant debris from the garden;
- all work in the garden bed must be carried out carefully, without damaging the onion feathers;
- monitor the regularity of watering; from the moment the bulb is formed, it should be moderate;
- loosening the soil slows down the spread of the disease;
- apply fertilizers in accordance with the standards (excess nitrogen causes infection activity).
Vectors of infection are pests such as onion fly, spider mite. Therefore, preventive measures should also be aimed at pest control.
To prevent bacterial rot from appearing in the planting material, it is kept for several hours in a solution of formaldehyde or potassium permanganate. Then dry well in the sun. Suspicious bulbs are treated with antibiotics. A mixture of tetracycline and streptomycin is suitable.
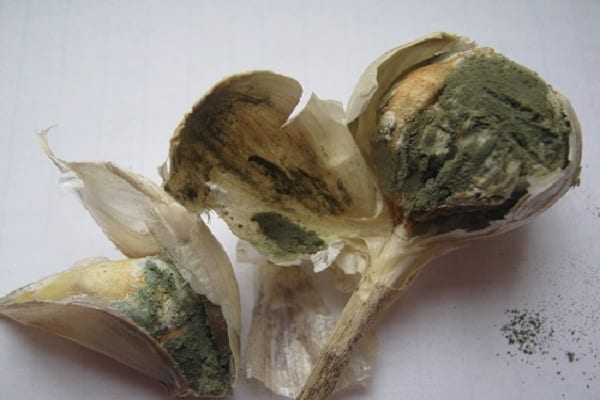
Green mold rot
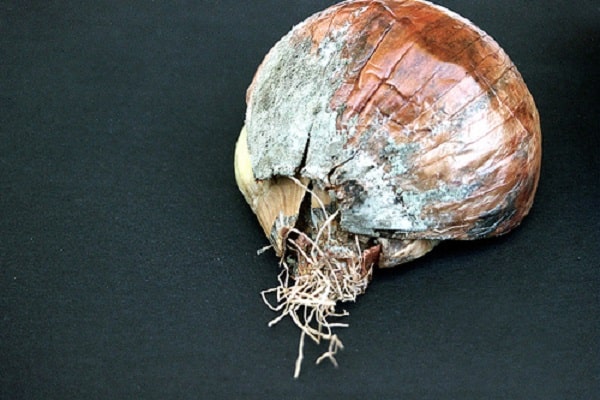
Green mold rot affects already harvested crops during storage. The onion skin dries out and becomes covered with green mold. The main reasons are: damage to the bulbs during harvest and high humidity in the room where the crop is stored (more than 70%).
Onion pests often cause the development of the disease. Even in the beds, they introduce infection into the plant, and under favorable conditions, pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively develop, leading to rotting of the crop.
Watery brownish spots appear on infected bulbs near the bottom. After some time, an unpleasant smell of mold appears from them, and a greenish coating is observed under the scales.
Preventive measures include careful drying of the crop and compliance with all requirements for its storage. The room should be dark, cool (about +3 degrees) and not damp. Preliminary disinfection of the place for onion storage.
It is recommended to select bulbs in advance for planting next year. Advice: remove the seed material for storage in another place. Check it periodically and get rid of diseased and damaged bulbs in a timely manner.
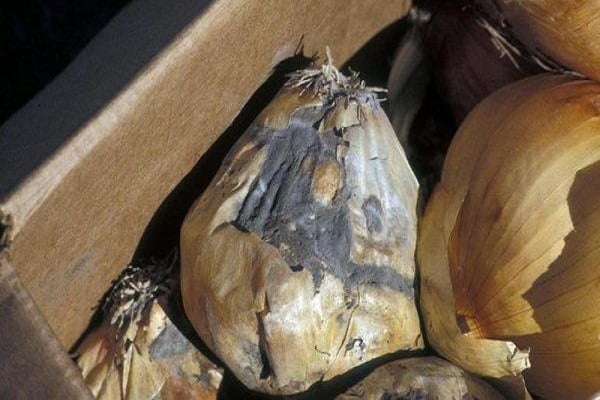
Black mold rot
Fungal disease black mold rot is a problem mainly of already harvested crops that have been put away for storage. Diseased bulbs become soft, rot, become deformed, the scales dry out and become covered with a black coating. But you can notice signs in the garden. Fungal spores infect leaves when they are wet for more than 7 hours.
The development of the disease is provoked by improper storage conditions. Black mold on onions develops in musty, damp rooms where there is high humidity, large temperature fluctuations and poor air ventilation. The disease is provoked by insufficiently well-dried crops after digging out of the soil.
The protective measures are:
- when loosening and weeding the soil, care must be taken not to damage the leaves, otherwise the wound may become a site of infection;
- The harvested crop should also be protected from damage;
- maintain low air humidity and low temperature in the room;
- remove old plant tops from the garden bed;
- Since onion pests cause disease, there is no need to allow them to appear in the garden.
Harvesting must be done in a timely manner. You cannot remove unripe or overripe onions. It will be poorly stored and there is a high risk of developing various diseases.