The defeat of bees by infectious diseases is a common phenomenon that causes significant economic damage to beekeepers. To successfully combat bee sac brood, it is important to correctly diagnose the disease and begin treatment in a timely manner. To prevent the death of a significant number of bee colonies, regular disease prevention is carried out.
What is sacbrood?
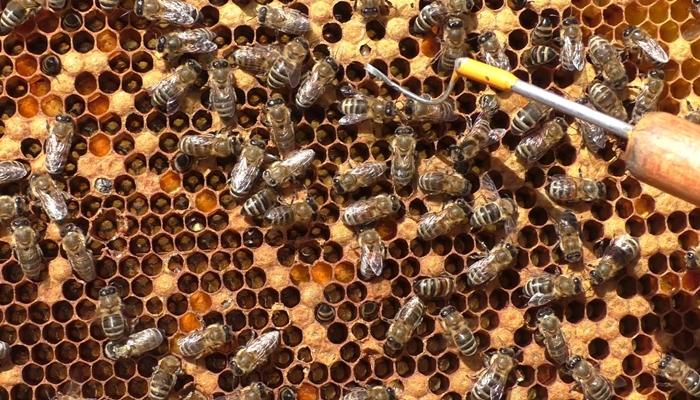
An infectious disease of bee seal brood caused by a virus is called sac brood. It is noteworthy that adult bees do not suffer from the virus, but they can carry it.The disease affects larvae (drones, queens and worker bees) 2-3 days old. Since the duration of the incubation period is 5-6 days, adult larvae die in the pupation phase.
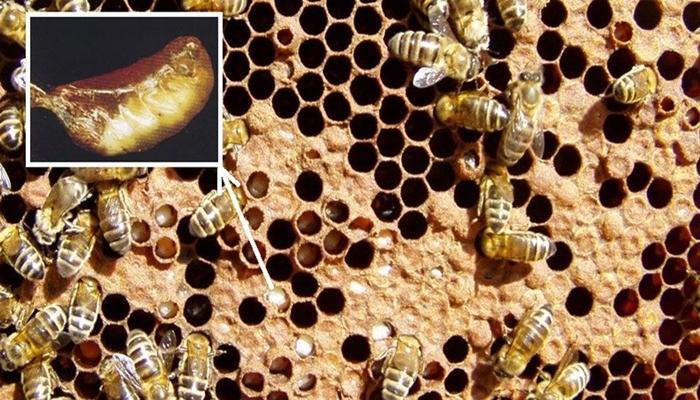
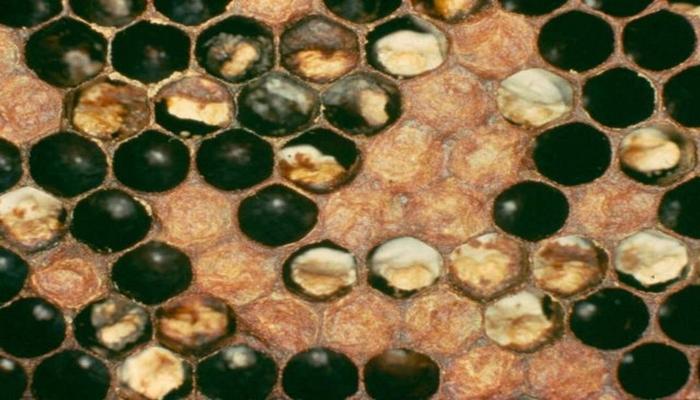
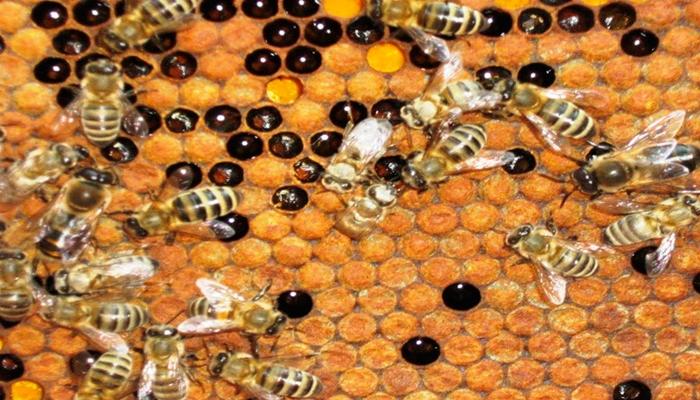
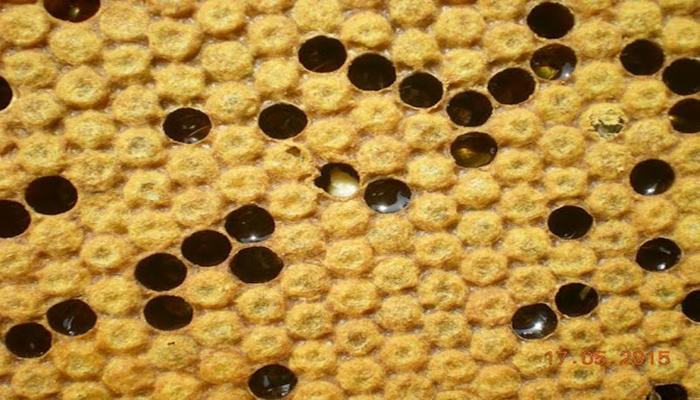
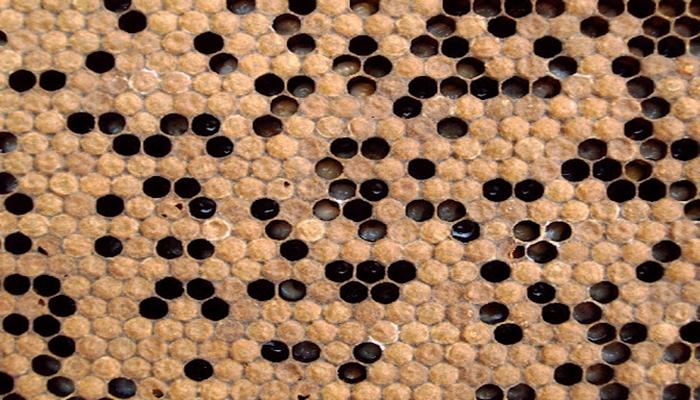
Cells with larvae affected by the disease acquire a dark shade. Wax honeycombs exhibit a mottled appearance because dead larvae can be found anywhere.
Causes and signs of the disease
The virus emerges and spreads in late May and early June. The causes of the disease can be different:
- damp cool weather;
- placing hives in shady, damp areas;
- wandering bees that carry the virus;
- Poor insulation of hives and lack of nutrition significantly weaken bee colonies.
Characteristic signs of the disease: mottled color of the honeycombs, corpses of larvae lying on the dorsal side are located along the cells, flabby appearance of the affected larvae. Features of sac brood are the absence of a putrefactive odor and a peculiar viscous mass, which is usually present when removing the corpses of larvae.
The causative agent of the disease is a neurotropic virus, which is localized in the cytoplasm of bee brain cells.
Diagnostic methods
It is impossible to unambiguously determine the diagnosis based on the external symptoms of the disease, since the signs of infection may be similar to European and American foulbrood. To eliminate diagnostic errors, a sample is examined with parameters of 10x15 cm. Modern laboratory methods: polymerase chain reaction, chemiluminescence, enzyme immunoassay. As a rule, the final test results are known after 10 days.
Treatment options
Most often, the infection begins to appear in late spring or early summer.It is advisable to treat families that are weakly and moderately affected. If the degree of damage is significant, then the family is destroyed. Abundant summer honey production can dampen or even stop the spread of the disease. However, virus activity increases in late summer or next spring. It is recommended to use medications to treat the disease.
"Baktopol"
To treat bees, strips are hung between frames in the middle of the streets for 2-3 weeks (in places where insects are most concentrated, at the rate of 2 strips per 10-12 frames). Advantages of the drug: wide spectrum of bactericidal action, lack of toxicity for bees, does not affect the development and productivity of bee colonies.
Precautions when using "Baktopol": after finishing work with the drug, you need to wash your hands with soap, honey can be pumped out and eaten 3 weeks after treatment.
"Rivanol"
A drug that exhibits antimicrobial activity is added to the syrup at the rate of 1 g per liter of syrup.
Feeding is done in the evenings (3-4 times, with a five-day interval).
Hyperimmune serum
For preventive and therapeutic purposes, hyperimmune serum obtained from rabbits or horses is used. The drug is available in the form of a transparent liquid of a dark or light straw color. To prepare the remedy, add 80 ml of whey to a liter of sugar syrup.
Method of treatment: 150-200 ml is given three times per bee street, with an interval of 5 days. The advantage of whey is that it promotes the formation of stable immunity to diseases.
Prevention
Only ensuring decent living conditions for bees will prevent the emergence and spread of a viral infection:
- there must be enough food for all families;
- Insect nutrition must include vitamin and protein supplements;
- only strong bee colonies are kept in the apiary;
- hives are inspected regularly, especially during damp and cool spring weather;
- Dry, well-lit areas are selected for placing the hives.
In the spring after wintering, equipment is thoroughly cleaned and disinfected (metal objects are heated with a blowtorch, honeycombs are treated with hydrogen peroxide (3% solution)).
Sac brood of bees, depending on the geographic location of the farm, may appear in late spring or early summer. During the summer honey planting period, the manifestations of the disease disappear, but the infection does not completely disappear. Therefore, it is important to pay attention not only to therapeutic measures, but also to preventive ones.