Most people don't see much difference between bees and wasps, and that's wrong. Although they belong to the same species, insects differ significantly in their structure and lifestyle. Unlike bees, which feed on nectar and pollen, wasps are predators that hunt small insects and do not disdain food waste. How else do insects that look similar at first glance differ, we will look into the details further by studying the structure of an ordinary wasp.
Origin of the species and description
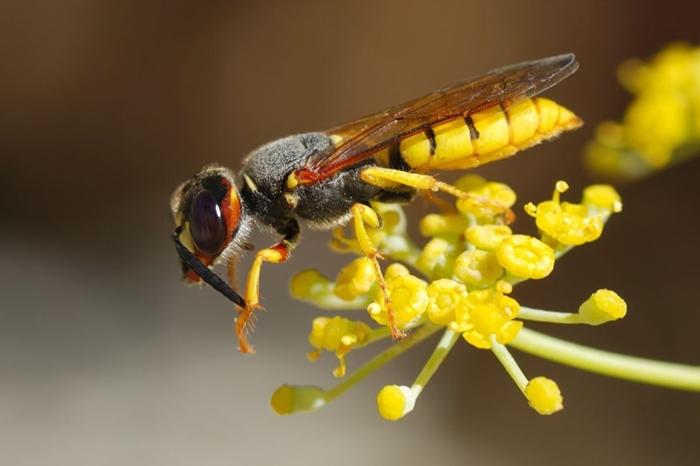
Unusual representatives of the fauna, due to their huge eyes and appearance, resemble alien creatures from science fiction films.Wasps are bright representatives of the order Hymenoptera insects. Since scientists are still debating which species the minke whales belong to, they have been combined with all stinging insects, except bees and ants, and are considered representatives of the suborder of stalked bellies.
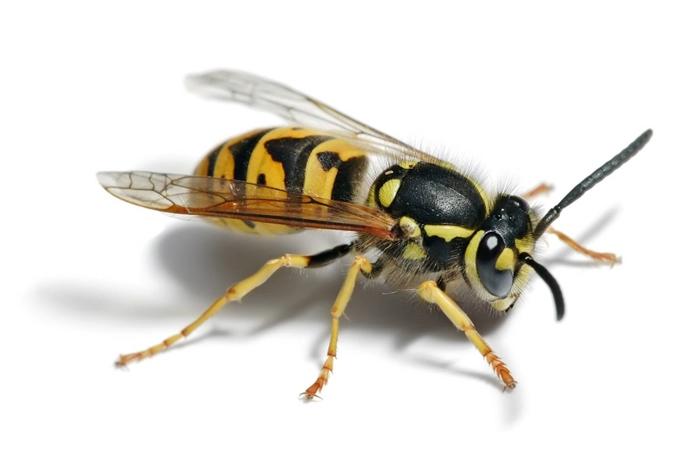
There are many varieties of wasps, differing mainly in their size and color. But the structure of insects is the same.
- Females are always much larger than males. The size of the female ranges from 1.8 to 2 cm, the size of the male – from 1.2 to 1.5 cm. In latitudes with tropical and subtropical climates you can find species of insects up to 5.5 cm in size.
- The color of most varieties is bright, which in nature means increased danger or toxicity. The body of insects is painted in contrasting stripes and spots of black and bright yellow. Rainbow wasps and solid black individuals are also found in nature.
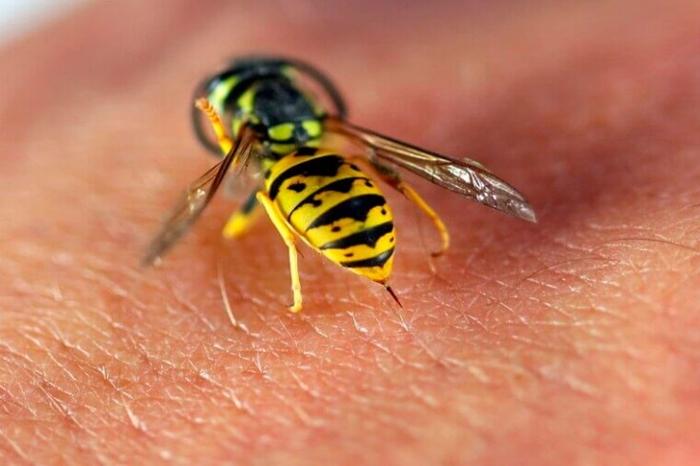
- A special organ produces poison, which when bitten can cause severe allergic reactions. Wasp stings are very painful and can be felt for several days. In some cases, they are accompanied by swelling of internal organs or increased body temperature. After receiving a bite, it is recommended to take a long-acting antiallergic drug.
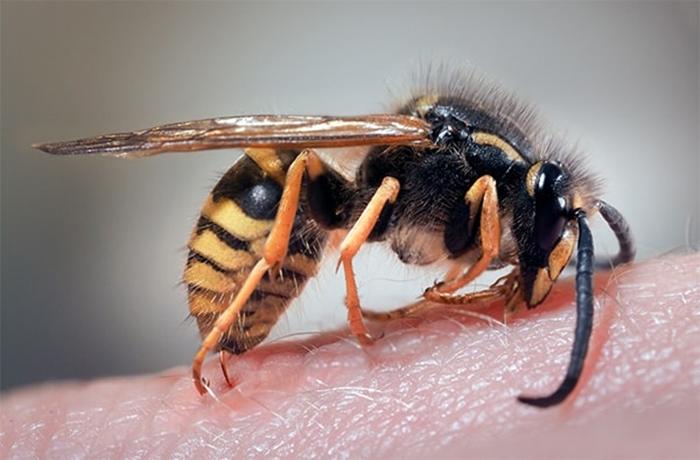
Just like bees, the structure of wasps suggests a sting. If in honey-bearing workers it is jagged and remains at the site of the bite, and the insect dies, then in the wasp the sting is smooth and can be used by one individual several times.
Wasps rarely attack first and become aggressive in the following cases:
- protect their nest;
- trying to defend their prey;
- react negatively to sudden movements and strong odors.
Poisonous minke whales are capable of producing a small amount of honey, which they feed themselves and feed their future offspring.The taste and consistency of this product are significantly different from the usual bee honey. Aspen nectar is characterized by a less sweet taste and thicker consistency.
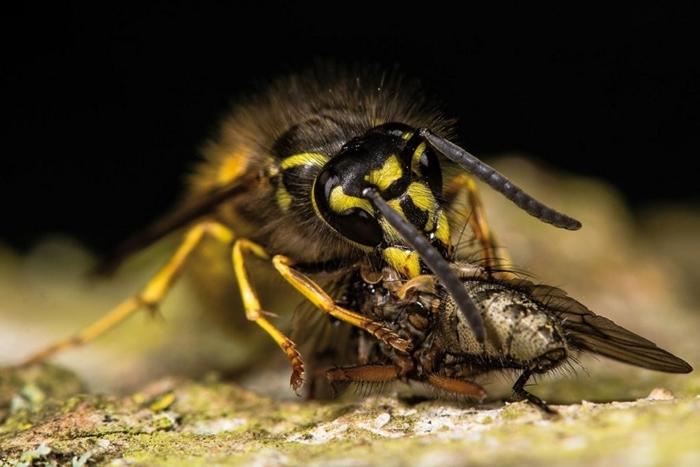
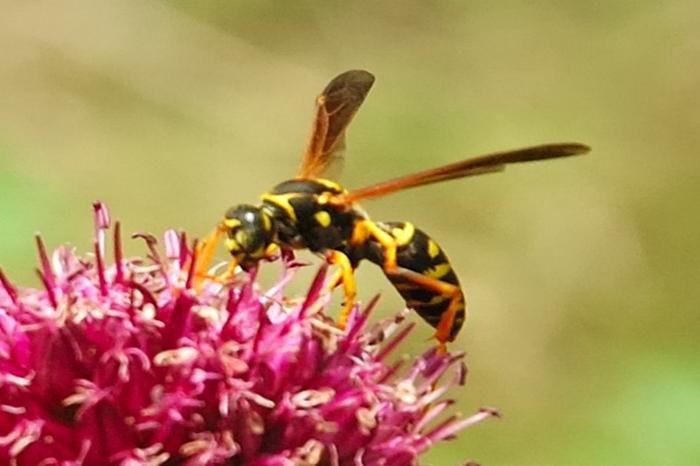
Thanks to their hunting skills, wasps are an important layer for flora and fauna. Stripes actively exterminate harmful insects and their offspring, thereby saving the harvests of various crops. Wasps are also good pollinators for fruit, vegetable, cereal and berry plantings.
In medicine, wasp venom is used to make ointments and various drugs that have an anti-inflammatory and tonic effect on the human body.
Interesting! In South American countries, there is a species of honey wasp called Polybia Occidentalis. The first mention of healing aspen nectar dates back to the ancient Mayan tribes.
Anatomy of a wasp
The structure and lifespan of female and male individuals differ. The main function of males is to fertilize the queens, after which they die.
The lifespan of males is about 14 days.
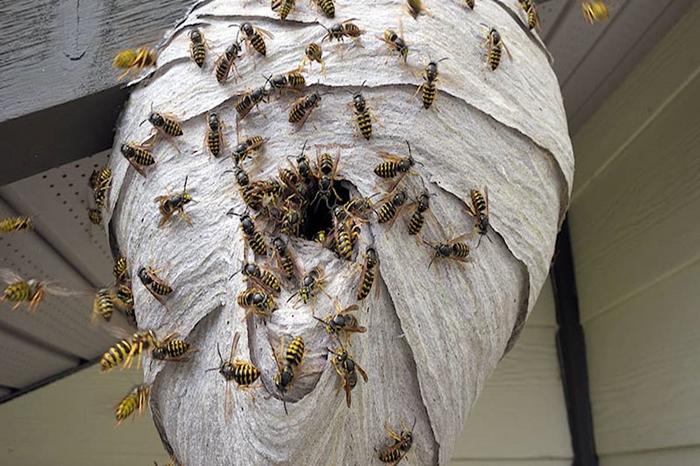
Queens, in addition to reproducing offspring, search for and improve the nest. The lifespan of the uterus is about 1 year, it ends with the onset of cold weather.
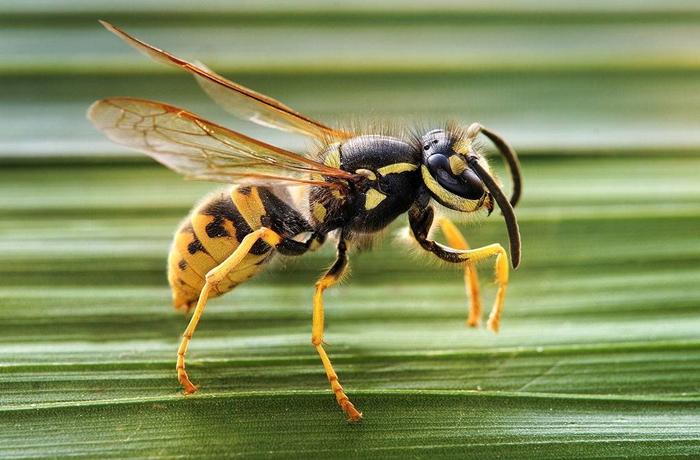
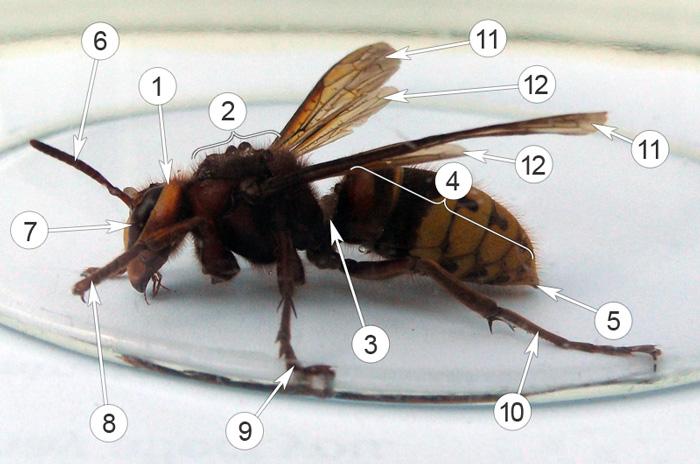
The main parts of the wasp's body are the abdomen, head and thorax. On the head there are eyes, a mouth represented by well-developed jaws, and antennae. There are 6 pairs of legs and 4 wings attached to the chest. The abdomen consists of special scales and ends with a sting. The sting, in turn, connects to a special gland that produces poison.
Important! The structure of the mouthparts directly depends on the type of wasp. In predatory individuals they are more powerful and well developed.Wasps that feed on flower nectar and pollen have jaws designed for liquid food.
Head
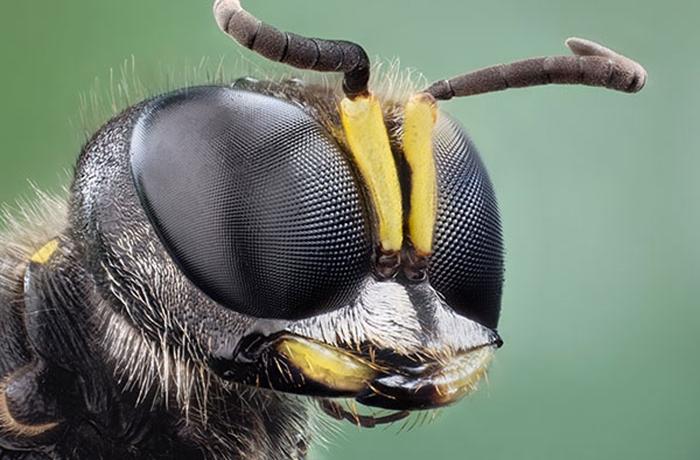
The head of insects is large with a noticeable expansion in diameter. The head contains complex eyes, antennae and mouthparts.
The jaws are powerful and can develop both for gnawing type and for receiving liquid food. In this case, the lower part of the mouthparts changes and becomes suitable for collecting nectar and pollen.
Eyes
The complex structure of the visual organs allows wasps to expand their viewing angle to 180 degrees. In addition to 2 large, bulging eyes, insects have 3 more microscopic ocelli, located in an equilateral triangle between the main organs of vision.
The eyes are made up of microscopic facets, each of which is responsible for a piece of visual information. As a result of this structure of the eyes, wasps see the image in the form of a mosaic, which consists of a huge number of small pieces. Insects are sensitive to light and can distinguish images in the range of up to 300 Hz. For example, in humans this range does not exceed 50 Hz.
The main eyes are located in special recesses and are strengthened by round cuticles and are characterized by complete immobility.
Interesting! Additional eyes, located in the center of the head, have a pupil, similar in structure and appearance to humans.
Mustache
Above the eyes, minke whales have long antennae in the form of thin cords or stalks. They consist of many articulated compartments fastened together.Such compartments are called segments, and their number can reach up to 60 on each antenna, which is one of the sense organs of insects. It is with the help of such antennas that wasps receive basic information about the world around them.
Legs and paws
The limbs of minke whales are characterized by a complex structure. Insects have 3 pairs of legs, consisting of a coxa, femur, tibia and tarsi with 5 segments. The legs of insects are adapted for movement on any surface. Some species of minke whales have special organs on their lower limbs for collecting pollen.
Breast
The thoracic region of striped predators also consists of many segments tightly connected to each other. The anterior and part of the thoracic region are poorly developed, the main load falls on the middle of the chest.
Basin
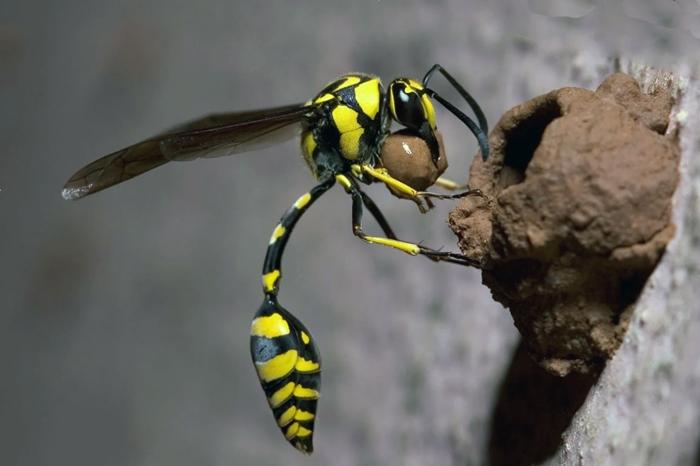
The coxa, or wasp waist, helps the insect fold its body in half. This feature is necessary for minke whales in the process of hunting and obtaining building materials for arranging a nest.
Abdomen
The abdominal part of the body consists of 6 or 8 segments, tightly fastened together. The back of the abdomen turns into a sting, which is the main reproductive organ of insects. It is in it that fertilization of eggs for future clutches occurs and there is a gland that produces a toxic substance.
Wings
The wings are membranous, mostly transparent in color. Along the edges of the wings there are microscopic hooks that hold their surface together during flight. The front pair are larger in size than the hind wings. When at rest, they fold along the body of insects.