Bees in apiaries live in adapted houses and are looked after by a beekeeper in winter and summer. Sometimes you can notice not only “domestic” individuals, but also wild ones. A wild wasp hive is characterized by a complex design and has certain features. A novice beekeeper needs to become familiar with the nuances of construction, materials, and the life processes of the family.
How to find a wasp's nest
Determining the location of a “wild” hive can be difficult because wasps make homes in secluded places.You can find a wasp nest by carefully inspecting the buildings on the site (residential building, utility buildings, etc.) and trees.
Attention! Insects constantly fly over the territory in search of food. People's places of residence attract them with the opportunity to enjoy various foods (fruits, those containing sugar, even leftover meat products).
If after inspection you are unable to find a wasp nest, you can try to track the flight direction of the insects:
- choose an open place;
- leave food in a visible place (something sweet, fruit, maybe sugar syrup to feed the bees);
- determine in which direction the insects carry food.
If there are a lot of insects on the site, it means that the wasp’s home is nearby. Once discovered, you will need to follow certain safety rules. Details in the next video.
Where do they build their nest?
Young queens choose habitats so that there are supplies of food and building materials nearby. Wasps make homes in different places. For example:
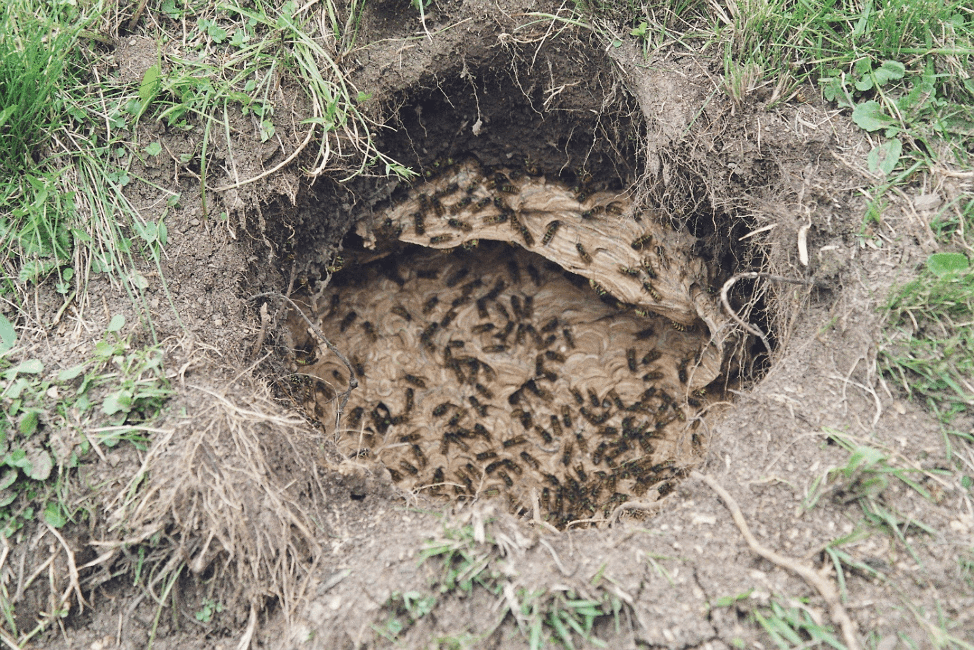
- underground (often in the burrows of various small animals - mice, moles, if they are abandoned by their owners);
- in hollows and branches (old trees are selected, sometimes dried out or, conversely, with a thick crown);
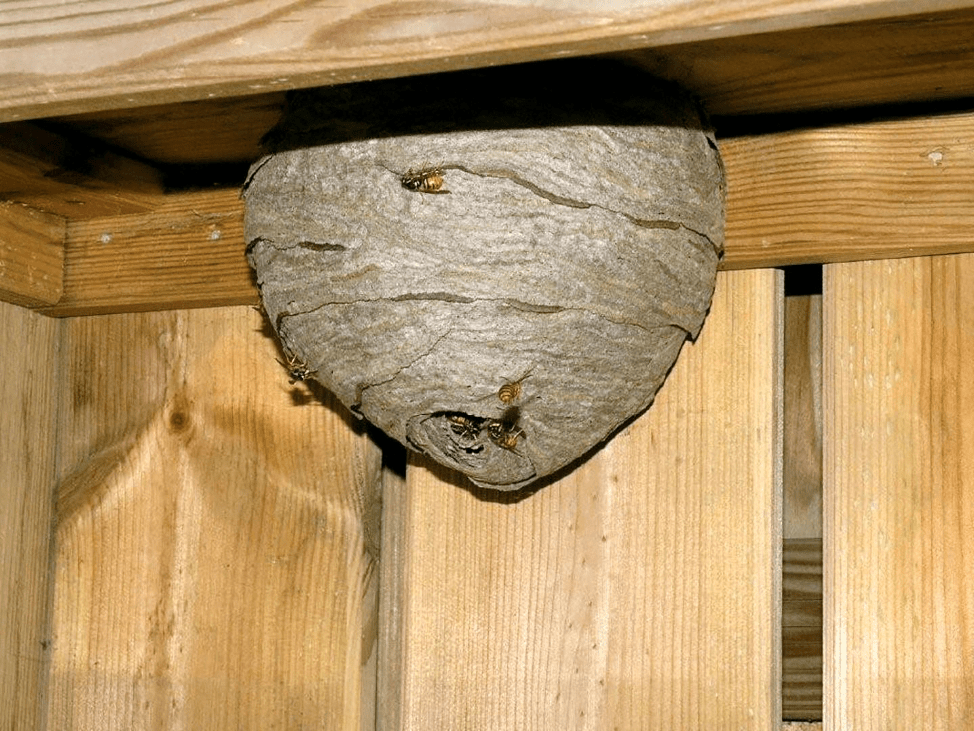
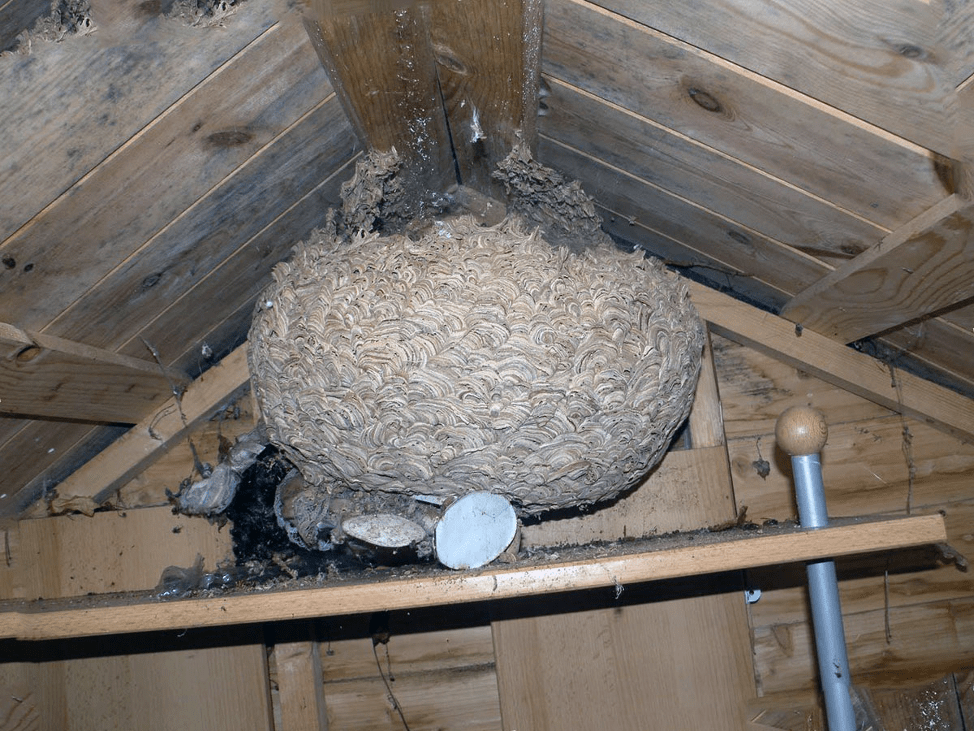
- in hard-to-reach places of houses (attics, basements, balconies);
- inside old stumps;
- abandoned bird houses and nests.
There were cases of arranging hives in the grass and on stones. The location is determined by the female, after which the workers begin construction.
Attention! In nature, wasps are beneficial - they destroy pests and carry out pollination. In a developed area or apiary, they can become quite dangerous for humans, animals and domesticated bees. It's easy to anger insects.
During construction, wasps can chew through wood and other coverings.But the greatest danger is posed by wasps that organize nests underground. When females begin to reproduce, they dig burrows closer together. This leads to the fact that the garden plot (apiary or land under the house) is strewn with wasp nests, which turns out to be unsafe for the owner. In addition to plant nectar, such insects use pollen, small midges that died in the web of individuals. Some benefit - they destroy pests.
What building material is used?
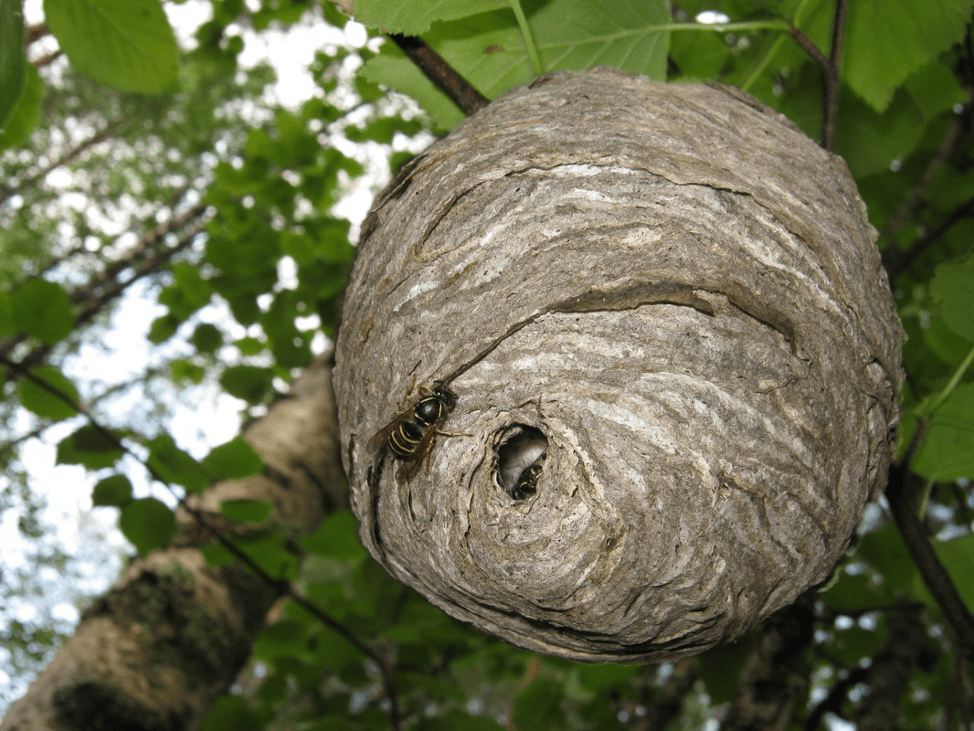
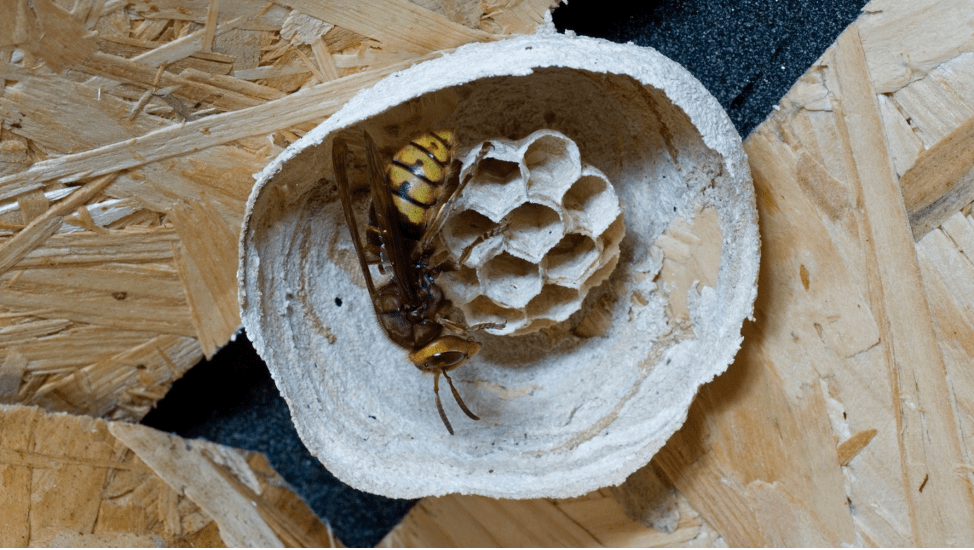
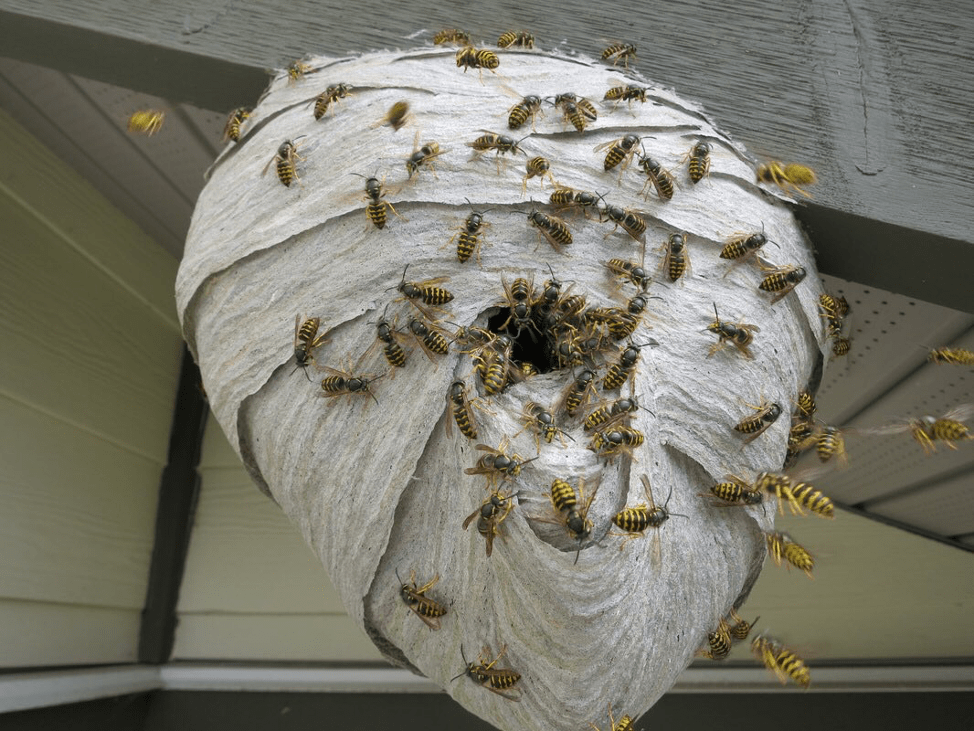
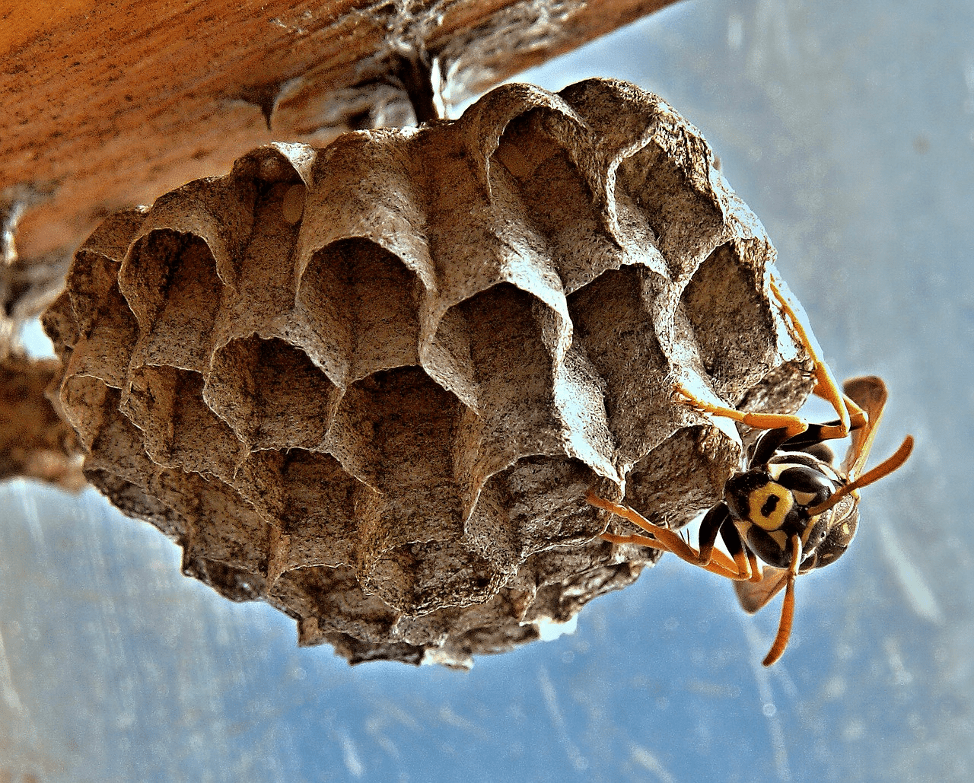
The finished wasp house is impressive - it is a smooth structure on the outside and with a complex structure on the inside. Family members are arranged in a certain way. The color of the material from which the walls of the dwelling are made is gray, reminiscent of paper or cardboard (this is why insects are called “paper insects”). Processing process:
- the wasp lands on a tree and secretes a small amount of corrosive secretion;
- the top layer of wood liquefies;
- With its jaws, the insect scrapes off the soaked piece and transfers it to the desired place;
- At the construction site, the material is chewed again and spat out onto the site.
After this, the wood is given the desired shape. The material dries in a few seconds, and thanks to the secretion secreted by the insect, it becomes sticky and strong.
Construction process
After fertilization, the young queen decides on the location of the building. The wasp hive is built in the following stages:
- work starts in early spring;
- the uterus produces a small amount of adhesive substance, attaches it to the selected location of the base and pulls it out - a small leg is formed, on which the insects then begin to build honeycombs;
- During the first 30 days, the initial generation of worker individuals is hatched and becomes the builders of the wasp’s home. Attention! After this, the queen is removed from the hive construction process. The queen’s task is to breed new individuals and increase the number of insects in the wasp’s house. Only workers are engaged in construction; 10 individuals are enough to start work;
- on the first cells, the next rows of honeycombs are built up - the wasps cannot hesitate, the next generations of working individuals appear one after another;
- The shape of the future bee home gradually emerges - insects build honeycombs in the shape of a bowl, gradually rounding, leaving a small hole in the center.
The honeycombs are arranged in several rows. Upon completion of construction, the queen frees up a small space inside, eliminating several initial parts. Peculiarities:
- externally, the wasp's nest resembles a gray cocoon;
- the shell is thin, more like paper (because it is made from soaked wood);
- the outer part is formed from long soft plates.
For the construction of some elements, recycled material is used, which remains after the destruction of internal honeycombs and partitions.
What does the nest look like from the inside?
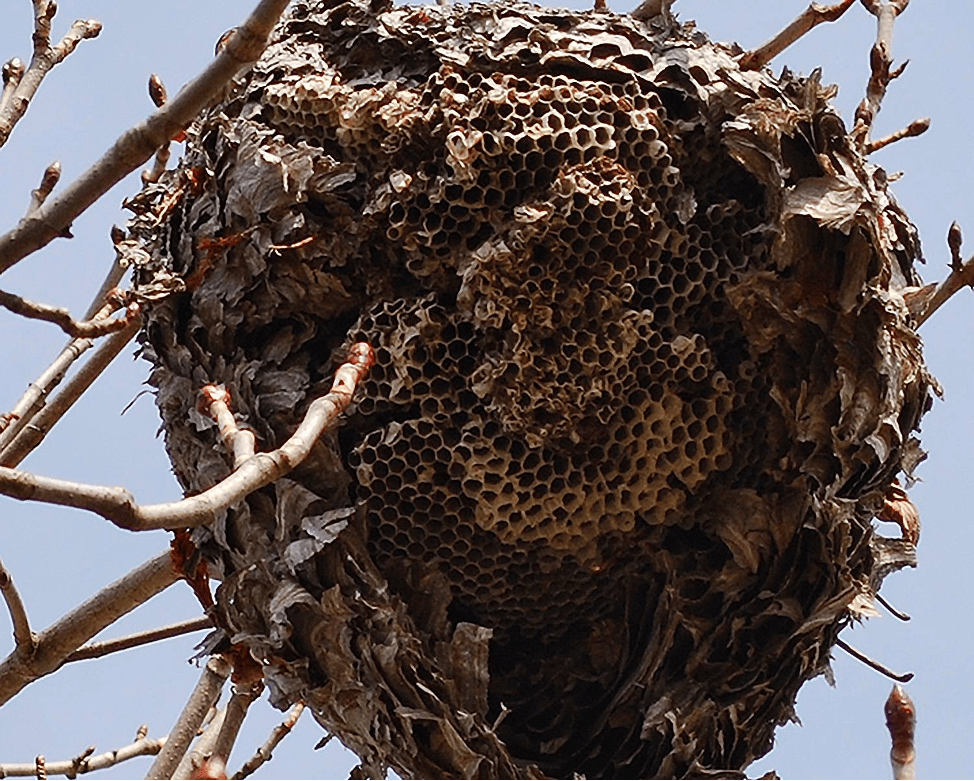
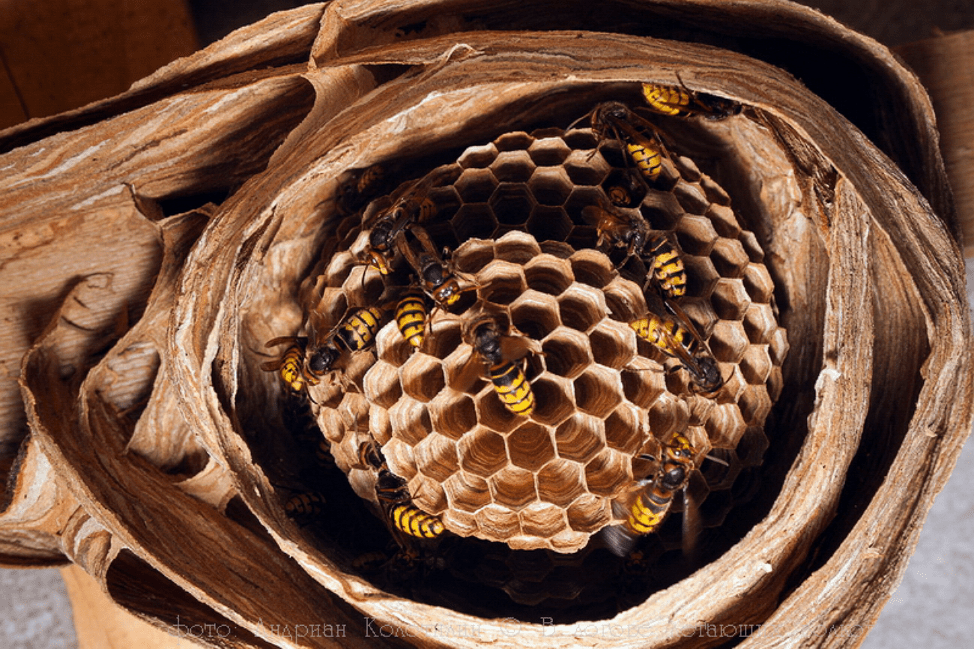
The wasp hive amazes with its well-thought-out internal structure. If you disassemble the bee's home, you will find the following:
- the honeycombs are lined up vertically, creating a kind of floors;
- every 4-6 rows insects leave a small space;
- Cells of honeycombs are lined up in one direction - down and in the selected direction.
The empty dwelling can be seen in cross-section - there are eggs in the center, and the queen is located, on the sides of the wasp there are “paper” walls of the floors. The internal sections are stronger than the external ones because they are built from small chips (the size is such that insects can carry them away). It is noteworthy that wasps form separate “rooms” for the queen, food, larvae and other things. A clear example of the internal structure of a wasp's nest in the video.
Number of wasps in one hive
Aspen families grow in different ways - some hives are no larger than the size of an apple, others reach significant sizes. A small swarm will grow slowly, so insects will not be able to rebuild quickly. Tens of thousands of insects can coexist in large houses at the same time, sometimes the number of individuals reaches a million.
Families grow thanks to working insects. There are most of these in the hive; they gather around the queen and begin construction, without stopping it, as long as there is opportunity and food.
Attention! In wasp families, in addition to worker wasps and the queen, there are also females and males. Such individuals are smaller in size; male insects have long antennae, but no sting.
Wasp nests pose a danger to humans, bee families and the site. The beekeeper needs to know how to find and destroy a family. It is useful to familiarize yourself with general information - what a hive is built from and what it looks like from the inside, how many individuals there can be.