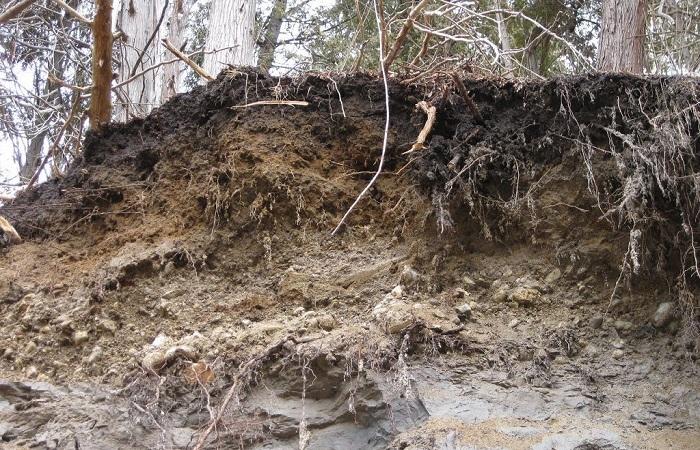
The formation of soil took many thousands of years. Initially, the planet had a mountainous landscape. However, under the influence of minerals, its geology changed. Gradually the properties of the substance improved. This occurred under the influence of plant residues, fallen leaves, and microorganisms. So what does such a thing as soil mean? This term refers to a natural body that appears as a result of the interaction of organic and inorganic nature.
What is soil?
Soil is a natural body that is formed as a result of the transformation of the surface layers of the Earth under the influence of soil-forming factors. It includes soil horizons that form a profile and is characterized by fertility.
A special science, soil science, studies the composition of soil. Soil is also mentioned in other disciplines - in biology, geography, and soil science. The properties of the earth are of interest to agronomists and geologists.
History of the term
Before the appearance of the works of V.V. Dokuchaev, soil was considered as a geological and agronomic concept:
- In 1839, this term meant rock in the form of a sheet. It was called a bed or sole.
- In 1863, the following definition appeared in V. I. Dahl’s dictionary: soil – earth, foundation.
- In 1882, this term began to refer to the top layer of the earth.
In 1883, the definition was created by the famous soil scientist V.V. Dokuchaev. He considered the soil as an independent natural body that is formed under the influence of soil-forming factors. The scientist included soil, climate, vegetation, relief, and age. He clarified that soil is a function of parent rock, climate and organisms, multiplied by time.
Composition and properties
The soil includes several fragments that are present in it in different proportions. These include solid, liquid, gaseous and living parts. The amount of organic matter and living organisms decreases from the upper layers to the lower ones.
So, the earth contains the following parts:
- Solid is the main part of the soil. Its basis is considered to be mineral components that are of lithogenic origin. These include fragments of primary minerals formed as a result of weathering of secondary ones.This part also includes organic matter, including plant and animal remains and special humus components.
- Liquid – This part is also called soil solution. It is water that is present in the soil with gases and dissolved organic and mineral substances. The composition of soil moisture depends on the characteristics of the soil formation process, climatic factors, and plants. Soil solution provides an important medium for the movement of chemical elements and moisture to plants.
- Gaseous - this part is also called soil air. It fills the soil pores unoccupied by moisture. In total, the volume of soil pores can reach 25-60% of the total. This composition is unstable. It changes frequently throughout the year and even the day. Air penetration into the soil is of great importance for root respiration of crops.
- Living - this part includes soil microorganisms and animals.
Specifics of education
The process of soil formation is divided into primary and anthropogenic. Initially, its structure includes humus and minerals. Then the voids are filled with air, and microorganisms settle there, which, after death, decompose and organically enrich the soil, improving its characteristics.
Basic properties
Fertility is considered the key property of soil. It affects other parameters. These include the following:
- Absorption capacity. Plants absorb nutrients from soil solutions. However, for this they must be unconcentrated. If there is an excess of salts, the plants will starve.
- Water permeability.Water enters the soil under gravity and surrounds the particles. In this case, the indicator depends on the structure of the soil. Thus, sands include large particles, and therefore water easily gets into them. At the same time, water is absorbed into clay elements with difficulty.
- Moisture capacity. The closer the layer of moisture is to the soil particles, the more it is retained by the earth.
- Air capacity. In dry soil, air fills all the wells. Some of the air attracts soil particles. He is called absorbed. In this case, the air that is in large pores is considered free. For normal plant development, the soil must be constantly ventilated. This helps restore oxygen supply.
- Soil heat. Its soil receives sunlight. The internal structures also emit a small amount of heat.
- Relative density. From it you can determine the ratio of the mass of the solid phase of the soil to the mass of the same volume of water at a temperature of +4 degrees.
- Porosity. This term refers to the total volume of all pores between solid particles of the earth.
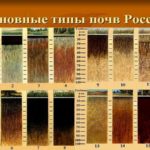
Types of soil
The most common is the genetic classification of soils. According to this gradation, there are the following types of land:
- Normal - corresponds to soil areas. Examples of such soils include gray, podzolic, desert-steppe.
- Transitional - these include carbonate and above-ground swamp soils.
- Abnormal - this group includes ash, swamp, alluvial lands.
Based on their mechanical composition, the following types of soils are distinguished:
- sandstones – have a light and loose structure;
- sandy loam - also considered light, but contains a lot of clay components;
- alumina - are heavy soils in which silty rocks predominate;
- loams - considered the most optimal variety for gardens and vegetable gardens;
- limestone - have a very poor composition;
- marshy - need careful cultivation.
Based on organic composition, the following types of soils are distinguished:
- tundra - found in areas saturated with moisture;
- podzolic – concentrated in the forest zone;
- gray forest - include many nutrients and a thick humus layer;
- chernozem - ideal for agriculture;
- chestnut - are found in dry steppes and contain little humus;
- brown - located in dry steppes and adjacent to chestnut;
- gray soils - localized in foothill and low-mountain areas;
- solonetzes, solonchaks, solodi – do not have their own natural zone;
- red soils and yellow soils are found in the humid subtropics.
Meaning in nature
Soil performs important functions in nature:
- stores energy - without it, plants cannot carry out the process of photosynthesis;
- affects the composition of the atmosphere and hydrosphere;
- regulates the density and productivity of living organisms;
- converts surface water into groundwater;
- is a source of substances for the formation of minerals;
- is a habitat;
- is a planetary membrane;
- protects the lithosphere from excessive erosion.
Soil is an important object that is of great importance for the normal course of natural processes and human activity. The formation of soil depends on many factors that affect its properties.