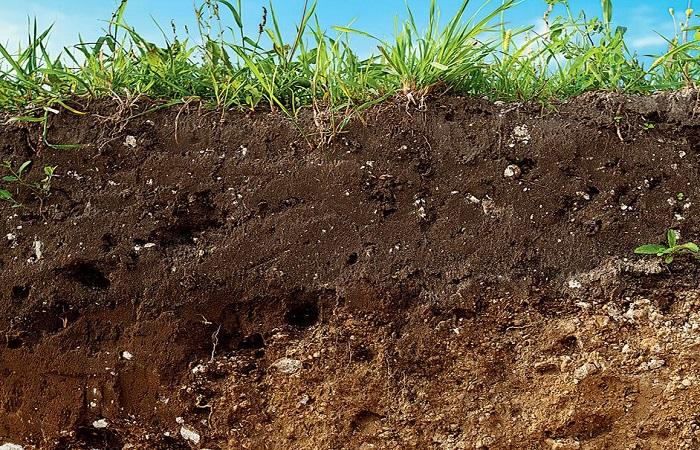
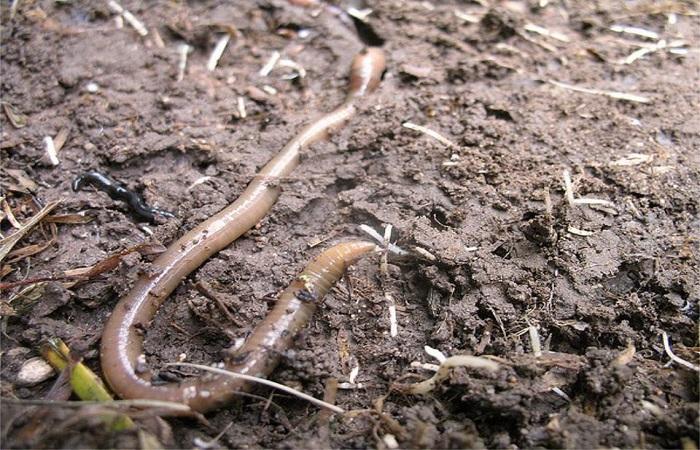
Soil is a natural heterogeneous body with a complex structure. It includes a number of components. There are several phases of soil, each of which has certain characteristics. Their ratios differ depending on the type of soil. Different proportions are also possible, taking into account the soil horizon of the same land.
What phases does soil consist of?
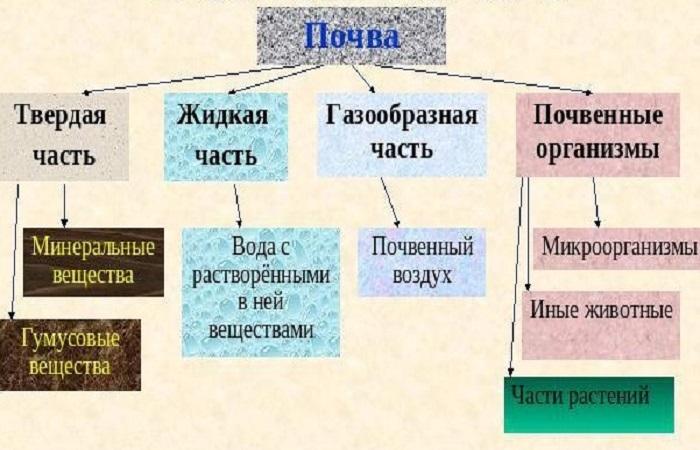
There are several components of soil, each of which has certain features and characteristics.
Solid
This soil phase includes the following components:
- mineral part – it accounts for 90-99.5%;
- organic matter – 0.5-10%.
The mineral part is understood as fragments or fragments of primary rocks and minerals. The soil structure also includes secondary substances. These include newly formed minerals, salts, oxides and other elements that are formed during weathering and soil formation. Mineral components include all ash substances.
The organic part is the remains of plant and animal microorganisms. The structure of these elements also includes products of decomposition and neosynthesis. The main part among them is humus.
Almost 93% of the solid phase of the earth consists of: oxygen, aluminum, iron and silicon. 4.6% are calcium and potassium, and 2.5% are the remaining components. Moreover, nitrogen is present only in the completely organic part, while oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur and carbon are present in both mineral and organic components.
Liquid
This phase is also called soil solution. It is a solution that includes minerals and gaseous substances that are soluble in water. This phase is considered the most active and dynamic. Plants absorb useful elements from it well and interact with fertilizers and ameliorants.
The soil solution contains cations and anions. It also contains water-soluble organic substances and gases. Ions enter the soil solution from the solid and gaseous phases, fertilizers, and ameliorants.
Gaseous
This phase is the result of the interaction of atmospheric air and gases that are produced in the soil. It contains more carbon dioxide than atmospheric air. This figure is 0.3-1% or even 2-3%. In this case, the soil is characterized by less oxygen.
This soil element is considered more mobile. Moreover, this is influenced by many conditions - the amount of organic component, climate, vegetation characteristics and many other factors.
With a sufficient level of oxygen in the soil, favorable conditions are created for the activity of aerobic microorganisms. Moreover, its deficiency is favorable for anaerobic bacteria, which are considered pathogenic for plants.
The amount of soil air is in dynamic equilibrium with the liquid phase. The more water it contains, the less air volume. Gas exchange in the soil structure occurs constantly due to the decomposition of organic substances, microorganisms, and respiration of the root system of plants. This is also affected by individual chemical reactions.
As a result of gas exchange, the above-ground air is enriched with carbon dioxide, which provokes an improvement in the conditions for photosynthesis. When the substance interacts with water, a slight acidification of the soil solution is observed.
As a result, individual mineral substances of the solid phase are converted into a form accessible to plants. In this case, an excess amount of carbon dioxide provokes a deficiency of oxygen and leads to the appearance of anaerobic conditions. This is due to excessive moisture and compaction of the soil.
Oxygen deficiency in the soil leads to a halt in the growth and development of microorganisms and disrupts the absorption of nutrients.
Live
It is also called soil biota. It includes the organisms that inhabit the soil. These include bacteria, fungi, algae, worms, and protozoa. All these elements have a significant impact on the development of cultures.
The influence of phases on plants
All soil phases closely interact with each other, forming a single bio-inert system - soil. The most favorable proportions between solid, liquid and gaseous elements are 50:35:15% of the total volume of soil. Soil phases closely interact with each other and have a significant impact on the development of cultivated plants.
Soil phases are considered important parameters to consider when practicing agriculture. To grow plants successfully, it is important to take into account the ratio of the various components.