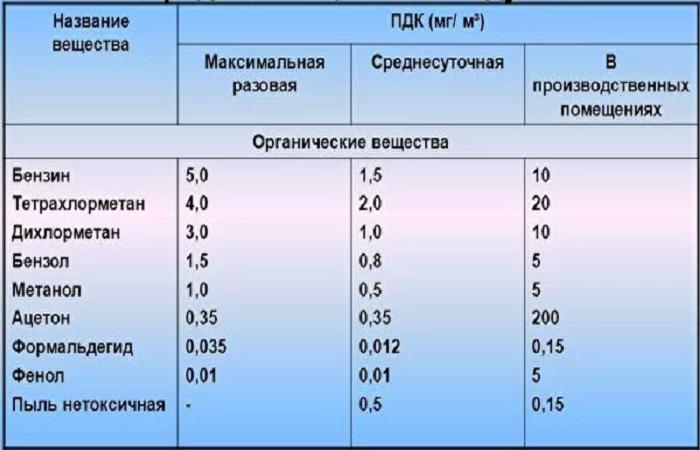
The content of toxic substances in the air, water and soil can negatively affect humans and animals. Sanitary regulations establish a set level, which is known as MPC or maximum concentration. Let's consider the classification of maximum permissible concentrations, how to determine the content of harmful substances and what precautions to take.
What is maximum permissible concentration
The term stands for “maximum permissible concentration”; it determines the volume of a substance that is concentrated in the measured object, and does not have a harmful effect on living organisms.This definition refers to the concentration of a chemical compound that, when exposed to a person every day and over a long period of time, cannot cause disorders or illnesses in him.
The permissible concentration is considered the main indicator of environmental regulation of harmful compounds in the natural environment. It is measured in milligrams per volume of medium: air, soil or water.
Classification
The amount of polluting components is measured in different quantities:
- in water – mg per cubic meter. decimeter;
- in atmospheric air – mg per cubic meter. m.
- in soil – mg per kg;
- in the air of the working area - mg per cubic meter. m.
The condition of animals and plant organisms may be affected by lower concentrations than accepted standards. Damage by certain substances, the content of which is an order of magnitude lower than normal, can cause partial or chronic growth retardation and a decrease in yield.
How to determine the PD value
The concentration of substances in the work area should not lead to health problems or diseases detected by research methods, provided that workers inhale air during the working day, that is, 8 hours. For industrial facilities, the MPC indicator is accepted equal to 0.3 of the MPC of the work area.
For example, the maximum permissible concentration of ethylbenzene, which is used in the manufacture of plastics and rubbers, in ordinary air is 0.02 mg/m³, the maximum is 150.0 mg/m³; average daily – 50.0 mg/m³.
In the atmosphere of cities and villages, the accepted norms are different. Two indicators are determined separately – daily average and maximum. At the maximum permissible concentration, the substance should not smell, and it should not irritate the eyes when exposed for 20 minutes. The average daily maximum concentration limit is determined by exposure to the measured object for 1 day; during this time it should not have a general toxic effect.
When determining the maximum permissible concentration in a work area, the impact on adults and healthy people is taken into account; when identifying this indicator for the population, the impact on people of any age and gender, health status, who live in this area is taken into account. Therefore, for the same compound these indicators can differ many times.
To determine the maximum content of substances in water, there are different standards for fishery reservoirs, for drinking water and for cultural and domestic purposes.
Maximum permissible concentrations of polluting compounds in the soil are determined taking into account their chemical origin and toxicity, as well as the characteristics of the soil. Since the properties and composition of the soil are very different, the accumulation of compounds in the soil does not occur quickly, microorganisms modify the incoming substances, there are no exact standards for permissible concentrations.
Precautionary measures
Those working in hazardous enterprises must be provided with personal protective equipment for the skin and respiratory organs, special clothing and safety footwear. Enterprises must have: regular laundry, dry cleaning, places for drying work clothes and safety shoes, decontamination of clothes and additional PPE.
MAC is considered the main environmental standard for environmental quality indicators.The standards for the main toxic compounds are recommended by health authorities for measurement in air, water and soil, in products and feed.
It has been established that many toxic substances, which are harmless to humans at the observed concentrations, cause great damage to nature, which is why the standards for permissible concentrations are constantly decreasing.