Grafting is a useful and necessary procedure aimed at propagating and breeding the desired varieties of fruit trees. Therefore, any gardener should know about the technologies of how to properly graft cherries onto cherries and not be afraid to put them into practice. Moreover, a grafted cherry can give its owner rich harvests of bulk berries much earlier in time than ordinary young seedlings.
Advantage of the method
So, the agrotechnical technology of grafting is represented by the possibility of transferring one fragment of a plant to another, for their fusion into a single organism, but with new features and properties.
The scion, the aboveground part of the tree with properties that influence the future quality of the fruit and harvest, is fused with its underground fragments, namely the rootstock, which affects the functional characteristics of the plant.
The advantage of the method lies in solving several problems at once, namely:
- The preservation of the varietal qualities of the tree being described, since seed propagation of certain varieties negatively affects the characteristics obtained from the mother plant;
- In forcing the harvest period. A grafted cherry is ready to bear fruit after just 2 years, while trees sprouted from a seed will take much longer - about 5-8 years.
- In the rejuvenation of plantings. Unproductive aged trees are pruned and then crossed with young cuttings.
- In increasing the resistance of plants to various types of diseases and negative environmental conditions. The so-called hybridization helps in merging delicate and vulnerable garden varieties with their hardy wild relatives.
- In combining the characteristics of certain varieties in a single representative.
- This is a factor in saving garden space, since shoots of a wide variety of cherry varieties can grow on one standard plant.
Important! Grafting can help save a damaged or even broken tree, but only if the plant's root system is alive.
Timing of vaccination
The most successful seasonal phases of cherry grafting are:
- spring periods, starting from March and ending in the first ten days of April;
- summer - from the second ten days of July to August.
However, based on horticultural experience, spring, at the peak of sap flow in trees, is the best period for grafting.
Summer, for grafting cherries with green cuttings, even at the moment the branches stop growing, is not the best period of time, due to the discrepancy between the cambial layers of the rootstock and scion.
In relatively warm weather, crossing can be carried out in the fall, but, in any case, the period of fusion will be completely completed only closer to spring.
In winter, fruit trees, when metabolic processes slow down, are in so-called hibernation.
Important! If the grafting technology will be carried out in summer conditions, watering the rootstock must be done ahead of time to speed up sap flow.
What trees can be combined with?
It happens that in the garden, apart from an old cherry tree, there is nothing fruit that could be grafted onto. And growing a new rootstock of the same variety is not only time-consuming, but also difficult, especially when there is no guarantee of grafting success.
But if a plum grows on a garden plot, then the crossing technology can be carried out directly on it. Moreover, this fruit tree is characterized not only by the strongest rootstock, but also by excellent adaptive capabilities.
Also, a cherry tree can be grafted onto fruit rootstocks in the form of:
- bird cherry;
- cherry plums;
- cherries;
- thorn.
The rootstock in the form of cherry plum has advantages - the crop is resistant to frost and has a well-branched and strong root system.
When crossing cherries, gardeners should know that merging them with cherries will go much faster, due to their excellent compatibility.
Step-by-step instructions for the procedure
For beginning gardeners, there are instructions for grafting cherries in one way or another.
Copulation
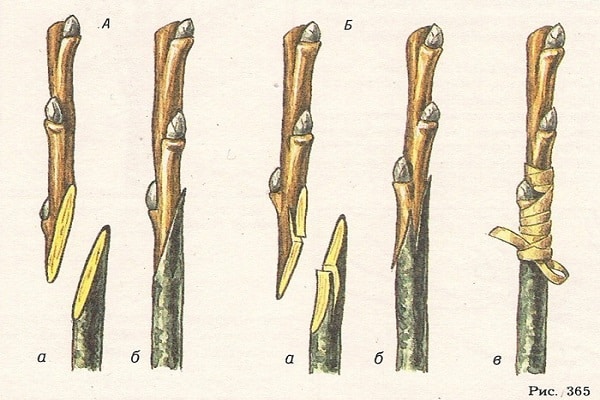
You can graft a cherry either using a cutting - the so-called copulation, or with a bud - in the form of budding.
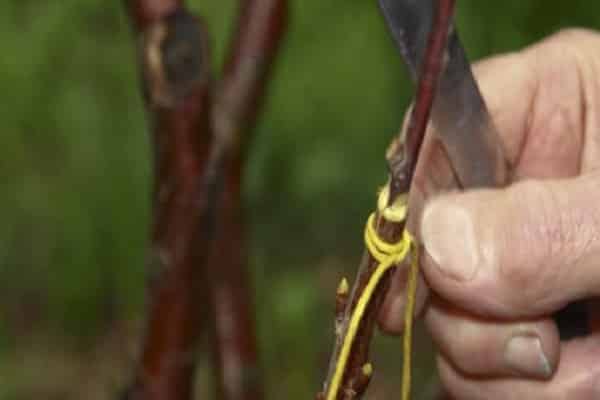
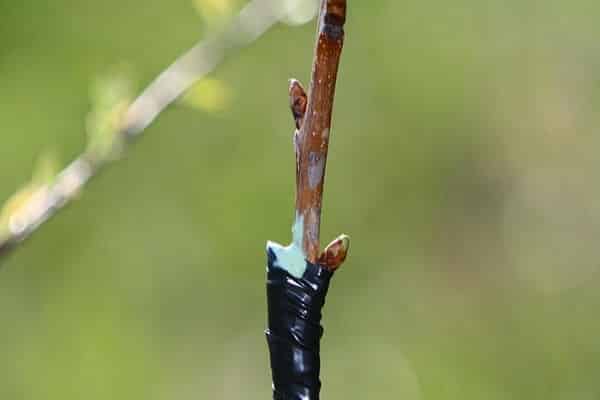
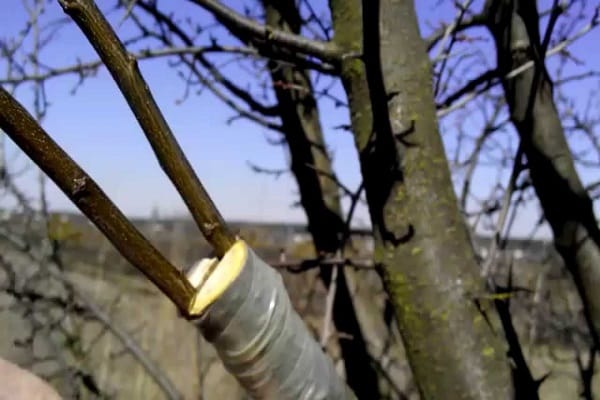
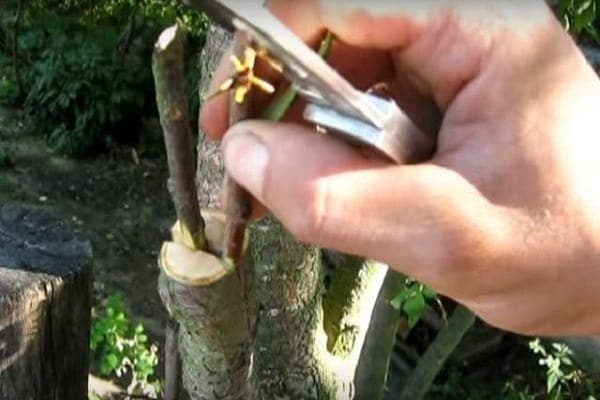
Copulation is suitable for twigs of the same size, with the most suitable diameter being 1.5 centimeters. Sections must be made at the ends of both the scion and the rootstock. The size of the cut should be within 3-4 centimeters.
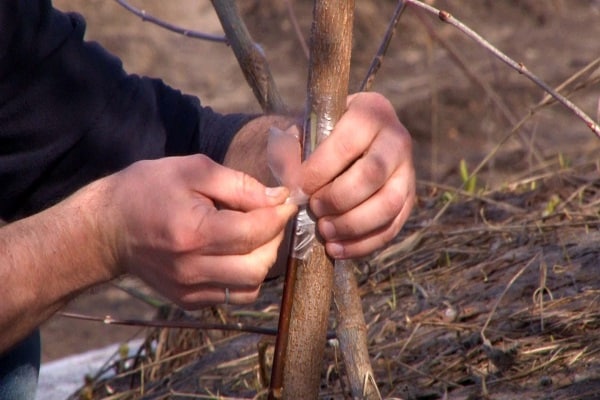
After such preparatory work, both sections must be connected, so that the cambial layers have the same area. Wrap the junction with a special material, in the form of, for example, a film, or carry out a special treatment using the so-called garden varnish.
Important! To protect the future tree from possible infection, mandatory treatment of the wound surface of the plant with special antibacterial agents is recommended.
For the bark
In order to properly graft a cherry tree onto the bark, and before the peak of sap flow, it is necessary to first free the rootstock from the branches. Then prepare cuttings for it - from 2 to 4 pieces, with transverse sections at the ends.
Afterwards, process the rootstock using a hacksaw and strip it with a knife. Make five-centimeter cuts on the bark along the base, into which insert the scion tightly, cut to cut.
Important! Work on cuts in the bark must be carried out using a sharp knife to prevent possible damage to the wood itself.
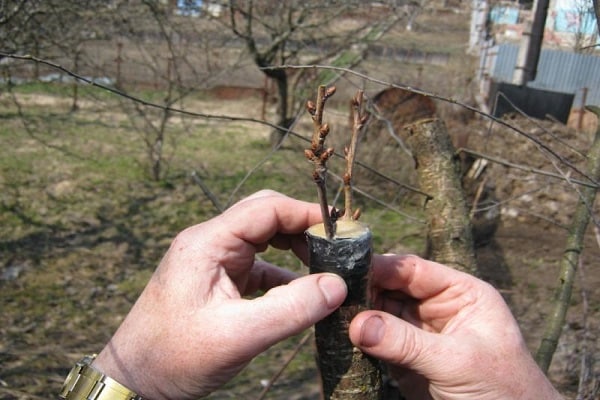
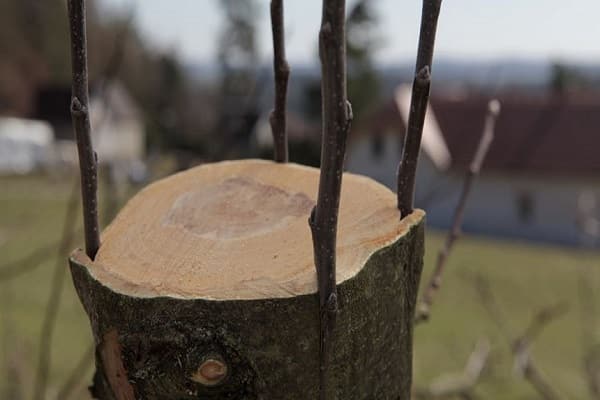
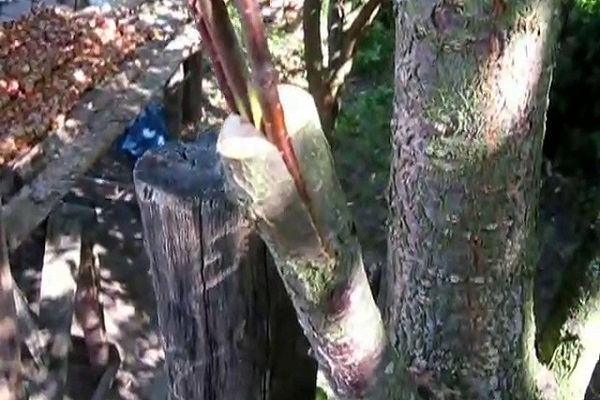
Into the cleft
The method of crossing trees must be carried out before the onset of the growing season.The preparatory step for grafting is the process of cutting down knots - on a young tree, work begins with an indentation of about 40 centimeters from the beginning of the branching of the trunk, while an old plant is processed by increasing this distance to a meter.
The grafting is carried out following the instructions below:
- the base of the cutting with several buds is cut with a knife into a so-called double wedge;
- the rootstock is cut down to the required height and then trimmed;
- using a knife, split the rootstock exactly in the middle;
- a scion is inserted into the split so that its bark coincides with the bark of the rootstock. If the thickness of the plant allows, then up to 2 cuttings at a time are buried in the splitting area;
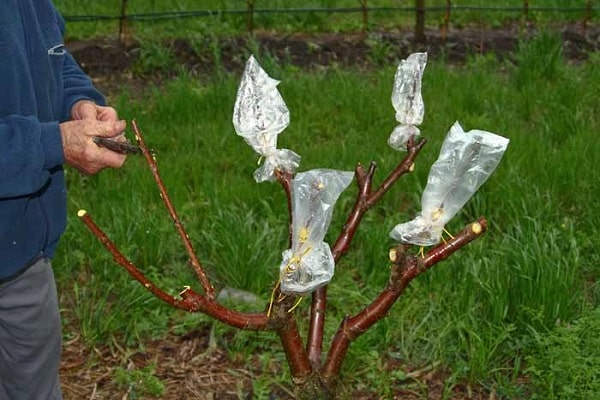
- The grafted area of the tree is wrapped with twine, polyethylene or treated with garden pitch.
In comparison with other methods of crossing, grafting cuttings into clefts is due to the best survival rate.
Half-split
The advantage of this grafting method is that it causes little damage to the trees.
Cuts must be made on the side of the rootstock, namely:
- stepping back about 3 centimeters from the end of the cut;
- use a hatchet to split, but not completely;
- Insert the cuttings into the cut so that their tissues are in close contact with each other.
The scion is harvested using the same method as for complete splitting.
Into the corner cut
Grafting in a similar way is carried out with branches with a diameter of about 2 centimeters.
To begin with, an angular notch is made using a knife located 3 centimeters from the edge, where a cut is made to a depth of 6 millimeters, at an angle of 30. Moreover, the same cut is made in the other direction, but of a different size, about a length 6 centimeters.
The cut at the lower tip of the cutting is made diagonally, in accordance with the cuts made on the rootstock. The fusion site is wrapped with a special film.
Into the side cut
This method involves a cut made along an oblique line, with an indentation of 20 centimeters from the base of the branch. Moreover, the length of one side should be one centimeter longer than the other. The cutting intended for grafting is cut into a wedge, the sides of which should also have a difference of 1 centimeter.
After such preparation, the shoot is inserted into the cut and wrapped with protective film.
By the bridge
Grafting using the bridge method is used for fruit trees damaged by hares in winter.
The scion is placed in a circular pattern along the diameter of the trunk. The tips of the shoots are distributed slightly below or above the wound. Damaged areas are cleaned down to healthy wood tissue. Then cuts are made along the edges. The tips of the shoots are cut obliquely.
Initially, the graft is introduced into the incisions located below. Afterwards, the cuttings are bent into an arc and inserted into the cuts from above. The joints are wrapped with twine.
Care after vaccination
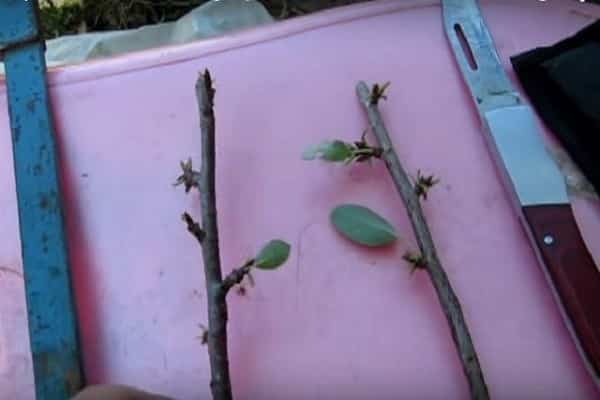
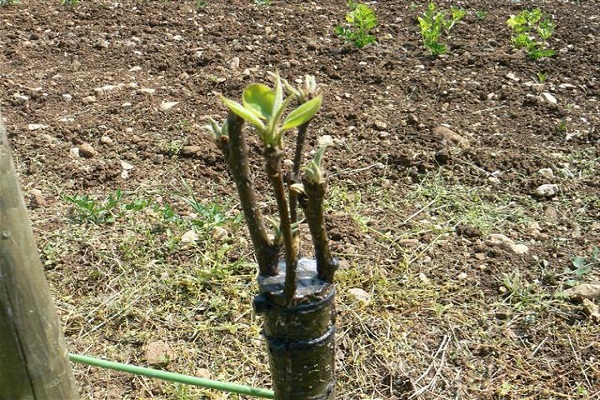
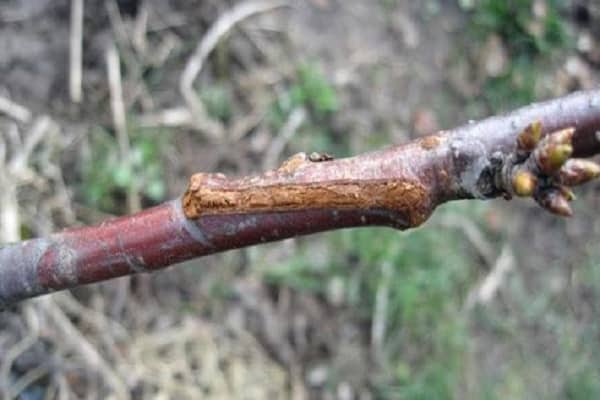
It will become clear whether the graft has taken root or not in a month. A positive result will be indicated by the scion buds and their growth.
At the end of the grafting process it is necessary:
- Strengthen the branch with a special tire - for strength and protection of the scion from windy weather.
- The remnants of the grafting film should be removed after a certain period of time, but it is more advisable to leave everything as it is until next year.
- Supply the area near the rootstock with fertilizers containing nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
A careful approach to grafting with the choice of appropriate technology is the key to the success of the crossbreeding goal, and the first time.