Sometimes rotten fruits are suddenly discovered among the red and juicy apples. Many gardeners are concerned about what to do if apples rot on the tree. It is not difficult to find means that will help preserve the crop from spoilage.
The main causes of rot
The cause of apple rot is considered to be fungal diseases. In addition to fruits, they damage leaves and young shoots.The disease mainly spreads on trees whose fruits have seeds and seeds. Fungal spores are carried by the wind from one tree to another, exposing it to fruit rot.
Signs and characteristics of apple rot
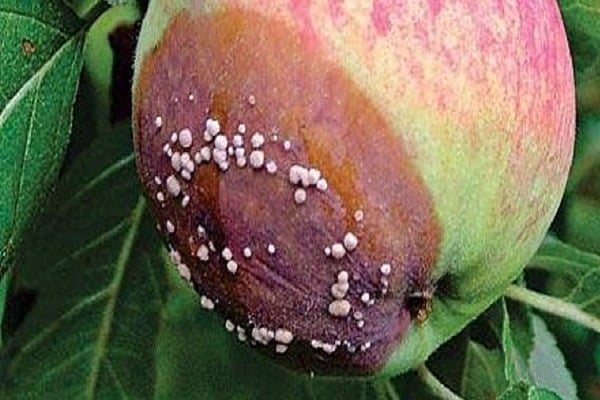
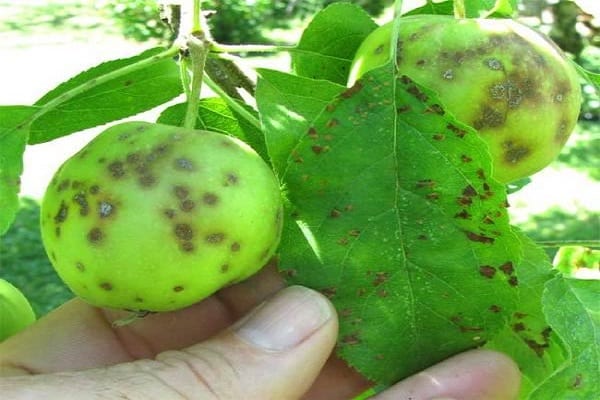
Fruit rot is unmistakable when apples become covered with brown spots that eventually spread throughout the fruit.
Signs of rot are the following changes:
- fruits do not grow and are damaged by worms;
- the quality of the fruit pulp changes: it loses its elasticity;
- brown spots form on apples;
- the blackened formation begins to increase in size and gradually occupies almost the entire surface of the fruit;
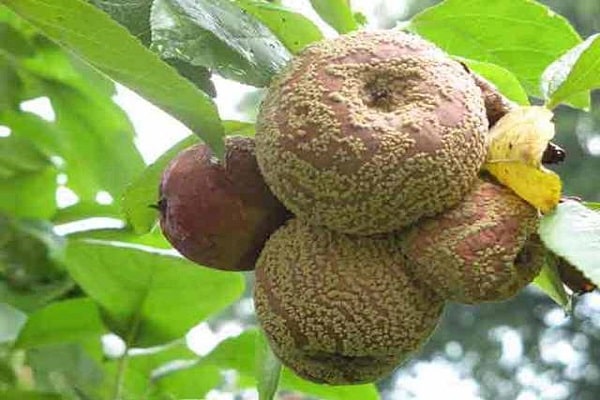
- on the surface where the apple rots, gray conidia are formed;
then it completely rots while on the branch, infecting nearby fruit trees; - a large number of ripened fruits, due to this there is an increase in the number of affected apples.
It was noticed that rotten fruits on apple trees are most often found in summer varieties. The fungus is very difficult to destroy because it tolerates frost well, and in the spring it will again begin to spread to other fruit trees, damaging young shoots.
Another reason for the active origin and spread of the fungus is too dense planting of trees. Even if you fight, the treatment will only last for one year if there is a neighbor’s garden nearby who does not cultivate his apple trees.
Moniliosis
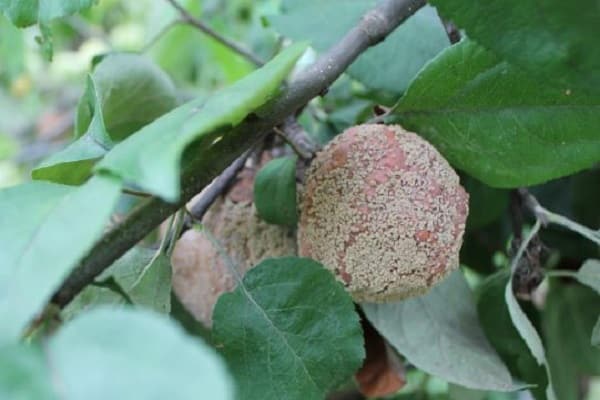
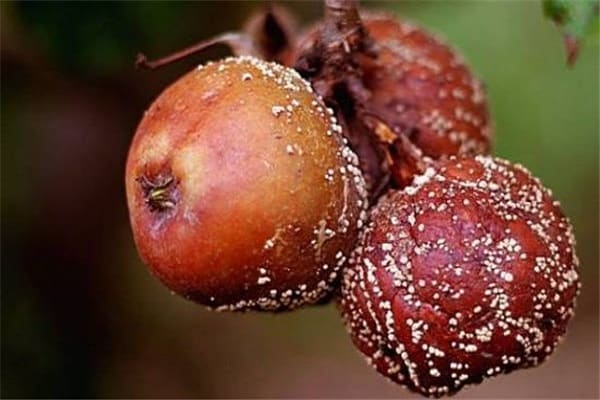
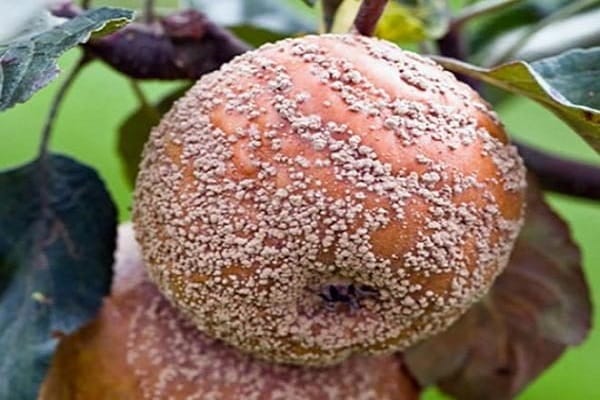
The disease of fruit trees, moniliosis, is caused by fungi, as a result of which the apples rot from the inside. Most often occurs when spring is cold and rainy. Spores falling on apple trees have a detrimental effect on them. The biggest blow comes during flowering.
Fungal microorganisms penetrate trees through the bark.After a two-week incubation period, the flowers turn brown and gradually begin to dry out. Whitish, sometimes gray pustules containing fungal spores appear on the stalks and leaves.
They most often begin to be carried by the wind, affecting more and more trees. When fungal spores get on an apple, the fruit becomes soft, changes color from green to brown, and has an alcoholic odor.
Fruits infected with the fungus fall, but may sag until winter. High air humidity and temperatures above +15 °C are considered favorable conditions for the development of the disease.
Chlorosis
When the supply of nutrients to apple trees is disrupted, the disease chlorosis develops. It is recognized by the changed color of the leaves. They become pale, may turn yellow, and dark, rotten spots of various sizes form on them. At the same time, the veins of the leaves remain the same rich green color. It is believed that apple trees lack iron, but not in all cases:
- When yellow leaves form at the top of the shoots, this is an indicator of iron deficiency.
- The pale leaves at the bottom of the branches indicate insufficient nitrogen content.
- If the leaves turn pale in color, located in the center of the shoots, this indicates that they did not receive enough potassium.
- When the leaves are covered with spots, it means there is not enough manganese and magnesium.
It is possible to correctly find out the cause of the disease only when it has just begun to manifest itself, after which it will be useless. The fruits will rot inside.
Scab
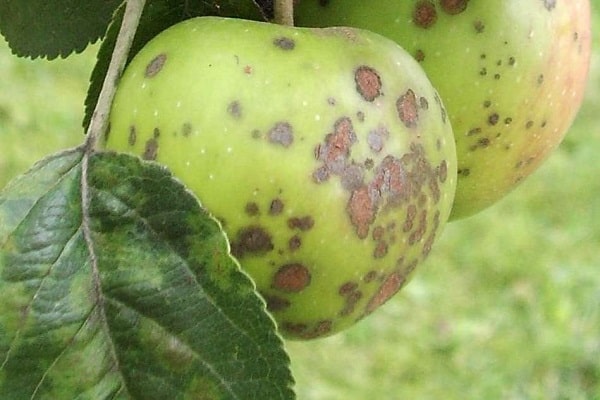
Scab is a fungal disease. It begins to show its activity during rainy and damp weather with frequent fogs. As soon as spring comes, fungal spores penetrate the bark and young shoots into the apple tree. They begin to spread throughout the tree.
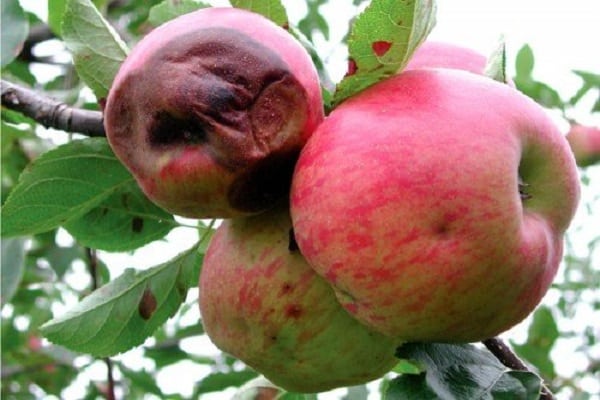
The disease affects the harvest and can also destroy young trees. Scab is easily recognized. Initially, yellow spots begin to appear on the leaves, gradually they turn brown, then turn black, leaving cracks.
First, young leaves located at the ends of the branches become diseased. The disease gradually spreads to apples. First, small spots and cracks appear, gradually they, merging with each other, occupy the area of the entire fruit.
Old and young apple trees are at risk. Especially if they are densely planted, the weather is damp and rainy. The fungus is well preserved in winter in fallen dry leaves. In the spring, when examining the foliage, if there are dark tubercles on them, it means that there are fungal spores that begin to ripen and are carried by the wind throughout the garden. Infected trees appear diseased and may freeze in extreme cold in winter.
Flycatcher
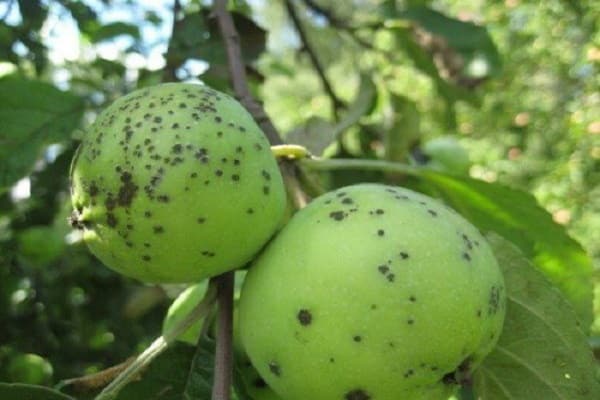
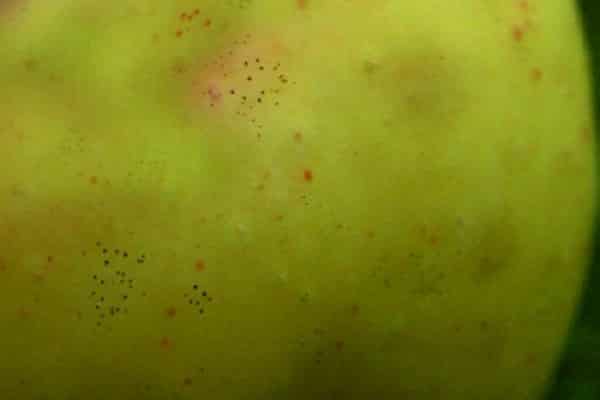
The fly beetle disease occurs due to the introduction of fungal spores into apple fruits. When examining the fruit, you can see that it is covered with small dots that resemble fly excrement. But this is easily recognizable, because these dots are not erased, no matter how hard you try.
Black dots are considered the reproductive organs of the fungus; spores mature in them. As soon as their ripening ends, they begin to fly around the garden with the help of the wind, infecting new trees and fruits. These fungi are especially active when the weather is damp, rainy, there is frequent fog, and dew falls in the morning. Infection occurs especially quickly in dense plantings, where due to poor ventilation there is high air humidity.
This mushroom is safe for humans, so there is no possibility of infection.You can eat apples that have black dots on them, these fruits store well, the only thing is that their presentation is lost.
Ways to fight diseases
There are many ways to combat fruit rot.
Control and treatment measures include:
- carrying out preventive measures;
- digging the soil and treating it with copper sulfate;
- fertilization;
- treating trees with special chemicals;
- compliance with the rules of planting seedlings.
When the first signs appear on trees, they should be treated.
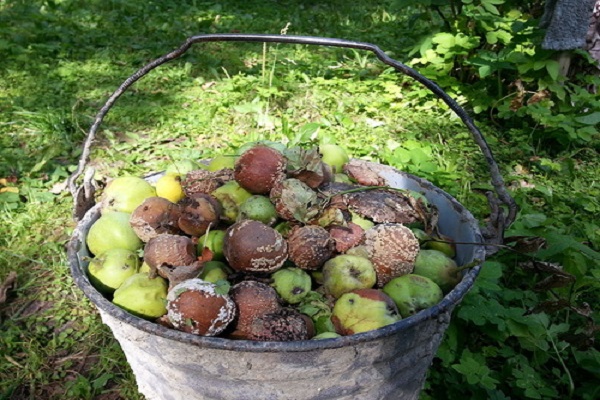
What to do with rotten fruit
As soon as signs of rotting of the fruit tree, as well as completely rotten apples, are discovered, you should definitely get rid of them. Remove them from the apple tree, otherwise other fruits will become infected.
Preventive actions
It is easier to prevent the development of a disease than to treat it later.
To prevent further development of fungal diseases and the formation of rot on fruit trees, it is recommended:
- In the fall, remove all fallen leaves and burn them, trim off damaged branches.
- In early spring, treat the trunks of apple trees with lime and a fungicide.
- When planting, maintain distances between seedlings to avoid crowding. It is necessary that there is good air circulation between the trees.
- Do not injure trees. If this happens, then the wounds must be immediately treated with garden varnish, since they are the entrance gate for fungi.
- When pruning diseased branches, cut off some healthy tissue.
- Remove all fruits from the apple tree; they should not be left to overwinter on the branches.
- Conduct spraying apple treesso that they are free from pests.
- In the fall, be sure to dig up the soil around the apple tree trunks. It is advisable to apply fertilizer during autumn digging.
- Before pruning apple tree branches, treat the tools with an antiseptic.
It is advisable to plant trees that are resistant to fungal diseases and various pests.
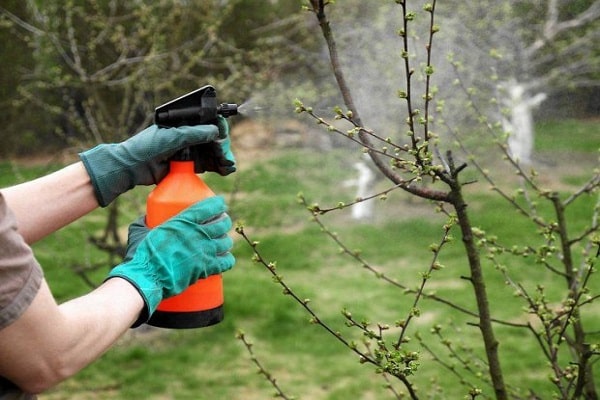
Spraying with specialized products
To prevent various diseases, it is recommended to spray apple trees using chemical protective agents. First, trees are treated before apple trees bloom.
The following drugs are used:
- "Mikosan-V";
- "Horus";
- Bordeaux mixture;
- "Meters";
- colloidal sulfur;
- "Strobe";
- "Abiga Peak";
- "Agricola";
- "Ferovit";
- "Raek";
- "Vectra";
- "Fludioxonil";
- "Phytoflavin".
The next treatment is carried out immediately after the apple trees bloom with the same means. Then again in July. After harvesting, it is advisable to spray the trees again with Bordeaux mixture, as it contains copper.
Selection of disease-resistant varieties
There are no fruit trees that are completely resistant to fungal diseases. There are varieties that are much less likely to be infected with moniliosis.
These varieties are:
- Mutsu;
- Jonathan;
- Idared;
- Ontario;
- Freiberg;
- Welsey.
Apple varieties with strong immunity against chlorosis:
- Andryushka;
- Day;
- Currency;
- Dialogue;
- Vasyugan;
- Moscow necklace.
Apple varieties that resist scab:
- Lungwort;
- Delight;
- Orlinka;
- Star;
- Moscow winter;
- Saffron pepin;
- Margo;
- Orpheus.
The following apple varieties are most protected from fly beetles:
- Manchurian;
- Blood red;
- Siebold;
- Abundantly flowering;
- Aldenham Purple.
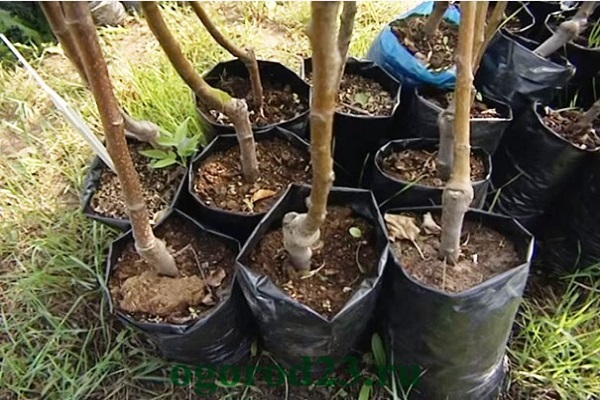
Proper tree planting
To protect trees from fungal diseases and pests, you need to know the rules for planting apple trees.
Important:
- Select pick up time.Early spring and mid-autumn are considered the most optimal.
- Maintain a distance between seedlings, which should be at least 3 meters, ideally 5.
- Purchase trees with a closed lump of soil. Then the apple trees are not injured, only the packaging is removed. The seedling is planted directly with the ground.
- Prepare the hole in advance: that is, for autumn planting it is dug in the spring, for spring planting - in the fall for applying fertilizers. It is dug up in a sunny area. Taking into account the passage of groundwater, at least 2 meters.
- The soil should be fertile, loose, slightly acidic.
Compliance with planting rules, knowledge of common diseases and measures to combat them will allow you to get a healthy harvest of apples.