Using the lunar calendar, you can calculate all the favorable days for planting garlic in 2024. The influence of the satellite on most processes in nature has been proven by scientists and is beyond doubt. Vegetable crops respond differently to planting and care on different days of the moon cycle. For root crops and bulbous plants, all growth processes are accelerated during the waning moon. Garlic can be planted in autumn and spring; the technology of planting and growing will be slightly different.
When to plant winter garlic?
According to the calendar, several favorable periods for planting winter garlic can be identified in 2024.
The moon is waning:
- in September: 1–8, 26–30;
- in October: 1–8; 25–31;
- in November: 1–6, 24–30.
On the days of the full and new moon, it is not recommended to plant any plants:
- in September: 9 new moon, 25 full moon;
- in October: 9th new moon, 24th full moon;
- in November: 7th new moon, 23rd full moon.
Select date in 2024, When is the best time to plant winter garlic? according to the lunar calendar, will depend on the growing region. The bulbs should have time to take root in the soil, but not germinate. This usually takes 2-3 weeks before the first frost.
When to plant spring garlic?
Spring planting of garlic according to the lunar calendar in 2024 is possible:
- in March: 3–16;
- in April: 1–15;
- in May: May 1–14, 30–31.
Unfavorable days for planting:
- March 2 and 31 are full moon, March 17 is new moon;
- April 16 new moon, April 30 full moon;
- May 15th is the new moon, May 29th is the full moon.
Selecting the appropriate date depends on the growing region. For rooting of bulbs, the soil temperature should be 5–6 ⁰C. In the central zone this is usually the end of April-beginning of May. A good signal for planting can be the opening of buds on a birch tree. If by this time the water has subsided from the site and the soil has dried out sufficiently, you can begin planting.
Too warm (above 12-15 ⁰С) soil inhibits the development of the root system and the yield decreases. Therefore, it is better not to delay planting this crop.
Differences between spring garlic and winter garlic
There are several significant differences spring garlic from winter:
- Winter garlic is larger and consists of 4-10 large cloves arranged around a thick stem. The spring onion contains many segments of different sizes, arranged in a spiral.
- Spring garlic (except for the Gulliver variety) does not form shoots with airy bulbs. Therefore, it is propagated only by cloves. Winter varieties usually bolt and can be propagated by growing from bulbs.
- The spring crop lasts longer and remains viable for up to 2 years.
The soil
Garlic prefers loose, neutral soil with a high organic content. The root system of this crop is not very developed; it is enough to prepare beds 30 cm deep. Humus, compost, peat and ash are added to the garden soil.
The planting site is changed annually with a possible return in 4–5 years. It is desirable that last season this area be occupied by green manure, legumes, young cabbage, cucumbers, and zucchini.
You can form high beds to prevent water stagnation. This is especially important for winter planting.
Light frosts will not harm garlic if you take care of high-quality mulching of the beds. Peat, straw or sawdust are used for these purposes. A loose organic layer will help keep the soil moist and prevent the formation of a hard crust.
Winter plantings are additionally covered with branches for the winter to trap more snow.
Landing
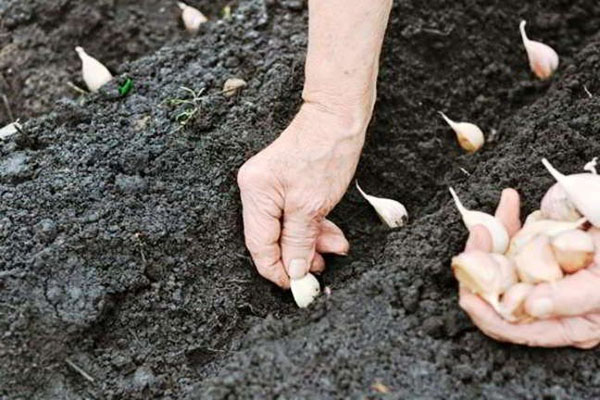
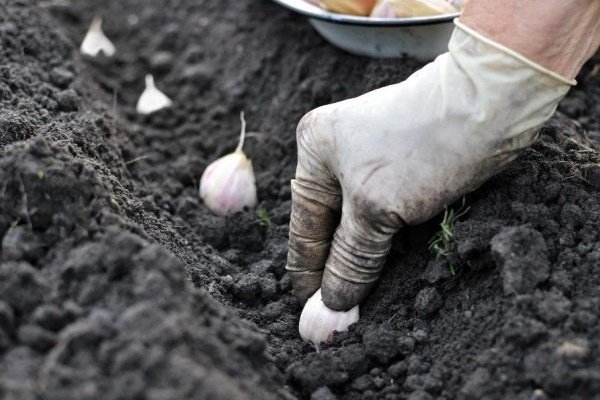
The planting cloves are chosen to be the largest and without damage. For sowing spring garlic, only the outer cloves are usually selected.
Garlic is planted in rows every 30 cm, retreating 8–10 cm between cloves. The cloves are placed in the holes vertically on the bottom with the sprout facing up. The layer of soil above the top of the clove should not exceed 2–3 cm for spring and 5–6 cm for winter. A layer of mulch of 2–3 cm is laid on top.
Spring planting material can be germinated before planting; to do this, it is soaked in composition of potassium humate and ash (2 tbsp per 1 liter).Then the cloves are wrapped in a damp cloth and placed in the refrigerator in the vegetable compartment for 5–6 days. Soaking and sprouting will help the slices restore their water balance and get off to a quick start in the garden.
Winter garlic from bulbs
Growing winter garlic perhaps not only with teeth, but also with bulbs. In the first year after planting, small bulbs without separated cloves grow. The set is edible, but it is usually replanted to obtain full-sized bulbs. Such cultivation is useful for renewing seed material, as it eliminates the transmission of diseases from the soil. Bulbs from sets are larger because they contain more nutrients to start growing.
In the garden bed, the bulbs are placed at a distance of 3–4 cm, maintaining 8–10 cm between rows, planting depth is 1–2 cm. Seeds are planted in the same way as cloves.
Watering
High yields of this crop can only be achieved with regular watering. Lack of moisture inhibits the growth of bulbs, even to the point of death of the roots. Yellow and dry tips of the leaves are a signal that the soil is drying out. After the formation of 5–6 leaves, watering can be slightly reduced, since the bulb has already formed by this time. Garlic does not need watering 2-3 weeks before harvesting.
Feeding
Garlic is fed 3-4 times per season. A week after germination, plants need nitrogen-containing fertilizers. An infusion of mullein, bird droppings or complex mineral compositions are suitable for this.
After 2–3 weeks, fertilizing is repeated. After the formation of 5–6 leaves, phosphorus-potassium fertilizer compositions are suitable.
Additional care
Winter plantings require timely removal of shoots (10 cm long), since the formation of aerial bulbs takes a large amount of nutrients.
The spring crop often does not have time to ripen sufficiently due to the short growing season. Therefore, you can tie the leaves into a knot in mid-August. This will force the plants to stop growing the green part, and all the energy will go to ripening the bulb.
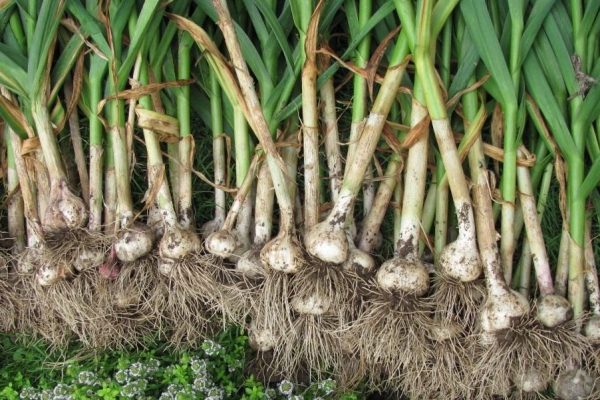
Harvesting and storage
Signal to harvesting winter garlic serves:
- cracking of inflorescences with bulblets;
- thin, durable and dried scales;
- the foliage of mature garlic turns yellow and falls off;
- The teeth are easily separated from the shaft.
Most often this happens in mid-July.
Spring garlic ripens by the end of August or early September.
A harvest that is not harvested in time falls apart into individual cloves and is poorly stored. Some bulbs may regrow.
The day for cleaning is chosen to be dry and sunny. The dug up garlic is left for 1–2 hours on the surface of the beds. Then it is scattered in a warm, dry place to dry. After two weeks, the foliage and roots are cut off, and all the bulbs are sorted. Bulbs that are damaged or show signs of disease are separated for quick use.
You can store the harvest in cardboard boxes with slots, in linen bags, or simply hang bunches on the walls.