When growing crops, you often have to deal with problems such as the appearance of insects and diseases. At the first signs, you should immediately resort to fungicides. For example, by studying the instructions for use of the fungicide “Polyram”, you can quickly deal with the causes of diseases.
- Composition, purpose and release form
- How does the fungicide "Poliram" work?
- Advantages and disadvantages of the product
- How to prepare a working solution and its further use
- Potato
- Tomatoes
- Grape
- Fruit trees
- Safety rules when working with the product
- Degree of toxicity
- Compatibility with other drugs
- Shelf life and storage conditions
- Analogues of "Polyram"
Composition, purpose and release form
"Poliram" refers to contact fungicides, which are used for fungal diseases in agricultural crops. The chemical is produced in the form of water-soluble granules.
For what diseases is it used:
- late blight;
- mildew;
- anthracnose;
- rust;
- scab;
- various types of leaf spot;
- powdery mildew.
Belongs to the group of dithiocarbamates. The active substance is methiram.
How does the fungicide "Poliram" work?
The substance metiram is an inhibitor of several fungal enzymes; as a result of treatment, spore germination is prevented.
Thanks to this property, fungi do not develop resistance to the drug.
During the season, it is recommended to carry out no more than 4 treatments with breaks of 10 days. The first spraying is carried out before the beginning of the growing season, when there are no signs of disease yet.
Advantages and disadvantages of the product
The benefits of use include:
- Prevention of fungal diseases.
- The chemical is non-toxic to plants and insects.
- It is allowed to be used during flowering.
- The granules dissolve well in water.
- Fungi are not susceptible to the chemical.
The disadvantages include the strong toxicity of Polyram for humans.
How to prepare a working solution and its further use
Before using the fungicide "Poliram", you must read the instructions for use. The dosage of the drug may vary depending on the crop being treated.
Potato
To prepare the solution, 40 g of powder is diluted in 10 liters of water. The first time the potatoes are processed until the tops close. The second is during budding. The third is after flowering ends, and the last when the berries appear. During the growing season, 3 treatments are carried out with breaks of 20 days.
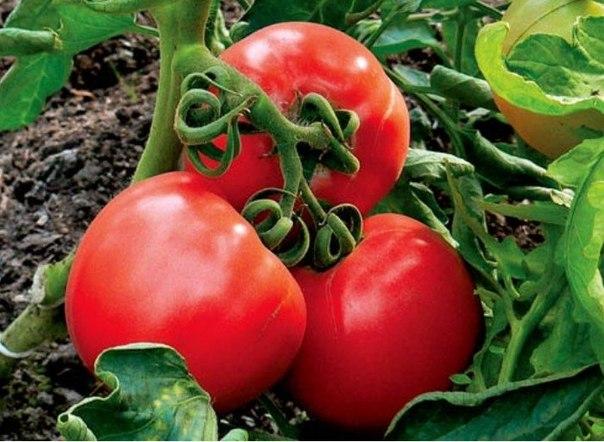
Tomatoes
It is very difficult to cure already infected tomato bushes. Most of the bushes will most likely die even during treatment, so in this case preventive treatments are important. To prepare the solution you will need 40 g of chemical and 10 liters of water. Dissolve the powder in water and spray the bushes. Treatments are carried out on a sunny, windless day.
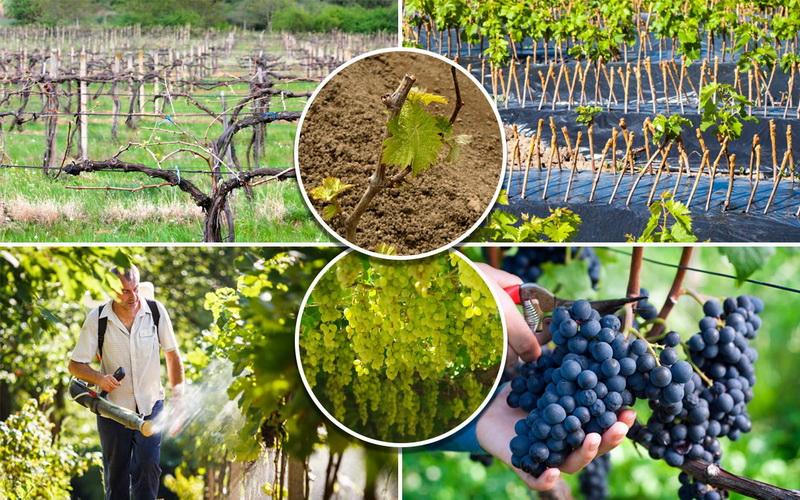
Grape
In spring, preventive treatments are carried out against powdery mildew and anthracnose. They are carried out before the buds open. 25 g of powder are diluted in 10 liters of warm water. During the growing season, 4 treatments are carried out.
The first time the grapevine is sprayed is during the formation of inflorescences.
Then after flowering. The third treatment is carried out during the formation of berries and the last one - when the berries reach a weight of 50 g. The protective effect of the drug lasts about 20 days after the procedure.
Fruit trees
The first treatment of fruit trees is carried out before the leaves bloom. The second - after the appearance of buds. The plants are treated the third time after flowering. And the last one - when the fruits reach a length of 4 cm. 20 g of the chemical are diluted in 10 liters of water. Stir until completely dissolved and then spray the trees.
Safety rules when working with the product
Before processing, you should wear a protective suit, hat, gloves and goggles. After spraying, be sure to take a shower and wash your hair thoroughly.
Also, during the procedure, animals should not be allowed nearby.
When spraying the plant, it is better to choose windless days so that during the procedure the liquid does not splash in all directions and does not fall on a person.
Degree of toxicity
The chemical is unsafe for humans and has a 2nd degree of toxicity, so when using Polyram you should first think about protective equipment. It is prohibited to eat the fruits for some time after processing.
Compatibility with other drugs
Combining Polyram with drugs that have a strong acid reaction is contraindicated. The chemical can be used together with the fungicides Acrobat MC and Fastak. It is advisable to conduct a compatibility test first.
Shelf life and storage conditions
The chemical must be stored out of the reach of animals and children. A cool and well-ventilated room, where open sunlight does not penetrate, is best suited for this. After use, open packaging must be packed in a strong bag. The shelf life of the fungicide "Poliram" is 3 years.
Analogues of "Polyram"
Analogs of "Polyram" include the following fungicides:
- "Polycarbacin";
- copper oxychloride;
- "Mancozeb".
Using these drugs instead of Polyram will help prevent the occurrence of diseases no less effectively.