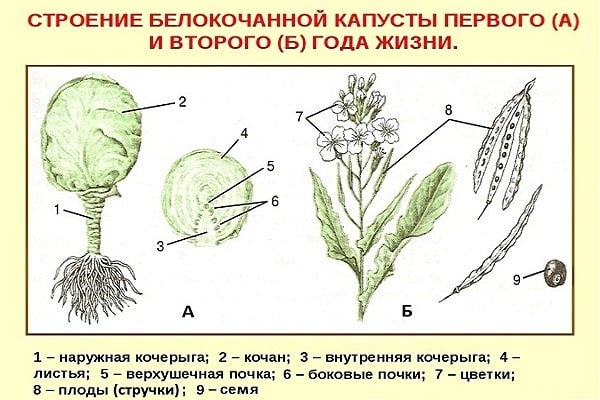
To figure out how to get cabbage seeds, you will have to study the botanical description of the plant.
Our usual and beloved vegetable is just an overgrown apical bud in which nutrients are deposited. From where, in the second year, a shoot with peduncles is formed.
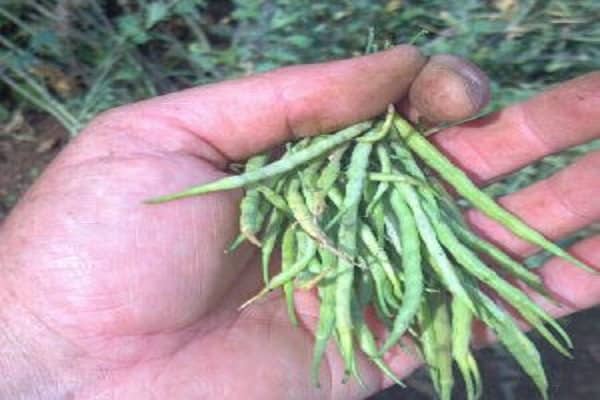
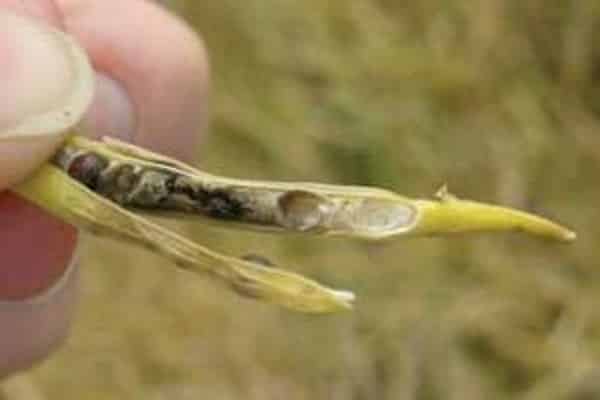
The real fruit of cabbage is a pod with 20-26 angular-rounded brown seeds.
Self-collecting cabbage seeds allows vegetable growers to provide themselves with a large amount of high-quality seed material and proven varieties.
Erroneous testis
Sometimes it happens that a plant of this crop in the first vegetative year suddenly takes and releases a shoot with flowers. Those who decide to collect such seeds from cabbage for further planting are usually extremely dissatisfied. The seeds show poor germination, the sprouts are weak, and most do not set heads.
Cabbage is a biennial plant and for normal fruiting it must go through all stages of development.
Therefore, a vegetable grower who decides to get cabbage seeds at home needs to:
- choose the right heads of cabbage;
- dig up queen cells in time and create conditions for vernalization;
- prepare overwintered heads of cabbage for planting;
- prepare the soil and plant stalks in the ground;
- care for the seed plant all season long, hill up, water, tie up and remove excess shoots;
- Collect mature pods in time.
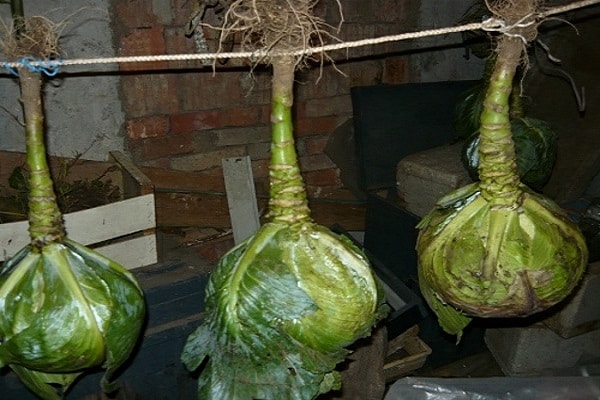
Queen cell
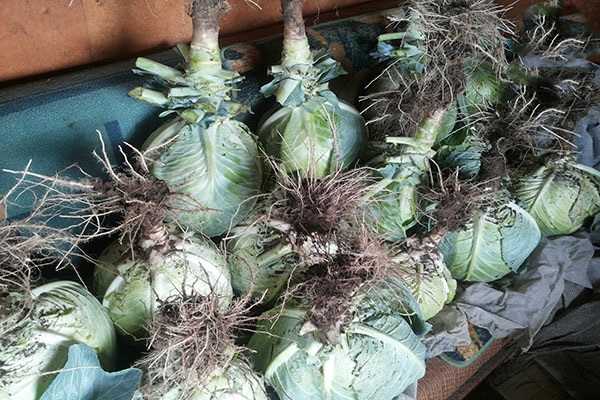
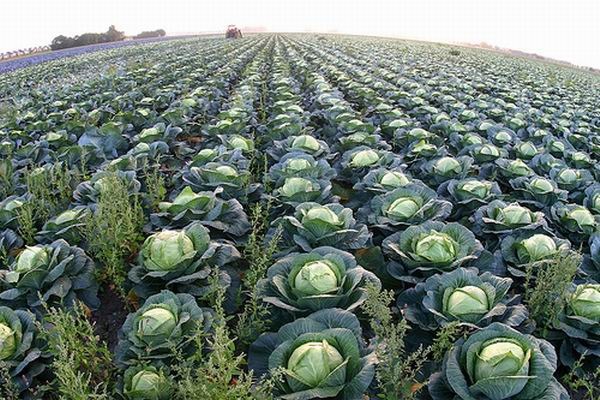
Before growing cabbage seeds, you need to select and properly winterize the queen cells. Among the harvest ready for harvest, you should notice the most beautiful healthy heads of cabbage with the following characteristics:
- not overgrown;
- most consistent with the description of the variety being grown;
- not overfed with nitrogen;
- the strongest;
- on a thin outer stalk;
- the heaviest relative to the weight of the rest of the plant.
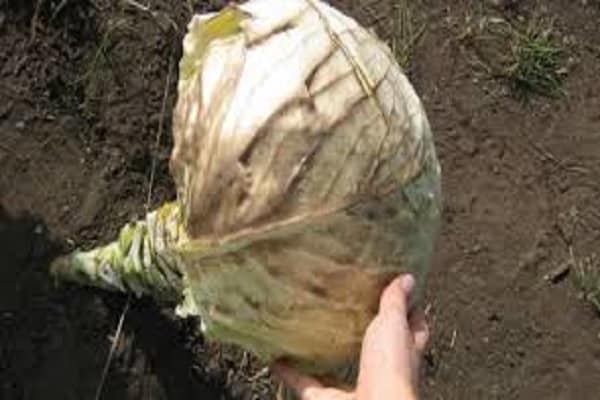
The selected heads of cabbage are carefully dug up along with the roots before the first frost. Cabbage leaves are cut off, leaving 2-3 near the head of cabbage and sprinkled with wood ash or chalk. It is advisable to dip the rhizome in a clay mash to avoid drying out.
Important! If the plants are caught in an early frost, they are left in the ground for another week to recover.
Vernalization
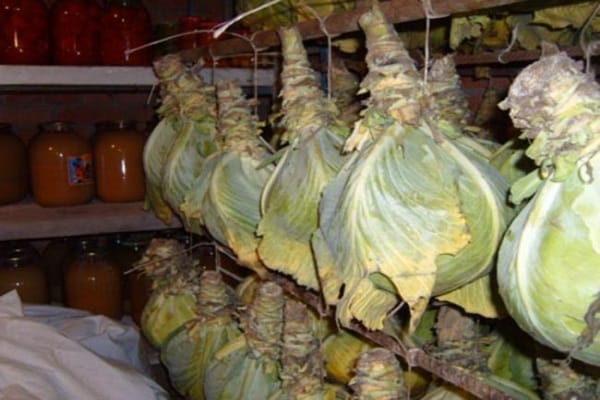
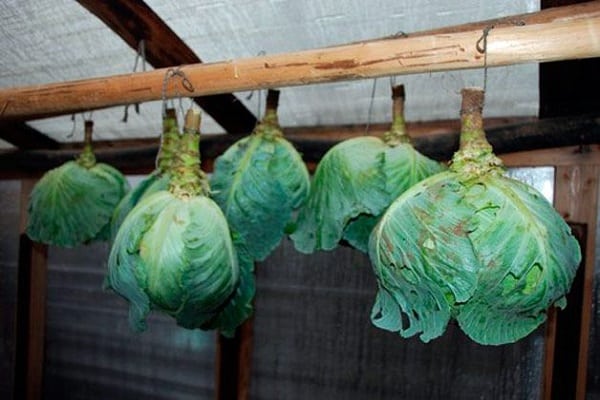
Queen cells are laid out or hung in a dark basement with a temperature of 1-2 ℃ throughout the winter. Cabbage, for normal fruiting, must undergo vernalization. If the temperature is above 6-8 ℃, the metabolism in the head of cabbage will not slow down and the process of formation of generative organs will not start.
When planted further, the plant will simply produce a large number of leaves instead of flower stalks. In winter, it is better not to disturb the heads of cabbage and minimize exposure to light. A month before the planned planting, the temperature in the storage is slightly increased to +5-6 ℃.
Preparing the queen cell for planting
At the end of March, the queen cells are taken out and the stalk is cut into a cone. Leave a base of 15-20 cm at the bottom and point upward. Inspect the rhizome and remove rotten areas.
Then the future seeds need to be “awakened” and germinate:
- the roots of the cut stalks are dipped in slurry;
- stacked with the roots down;
- sprinkle with peat or humus;
- leave in the fresh air for 2-3 weeks, protecting from frost.
Landing
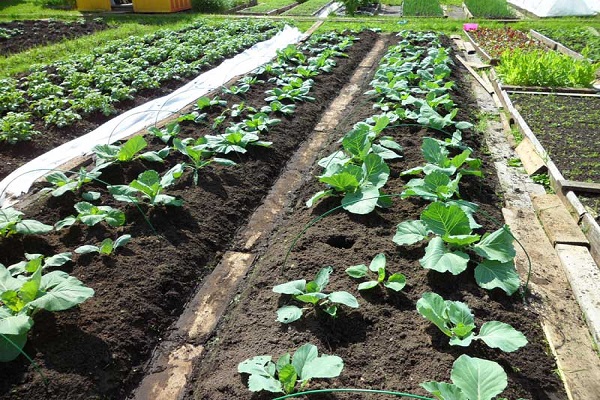
The time for planting queen cells varies between late April and early May. And it’s better not to be late, otherwise the flowering time will occur in weather that is too hot for cabbage. The optimal temperature for pollen germination of this crop is 15-21 ℃. Therefore, the sooner the stalks begin to take root and sprout, the better.
Cabbage easily tolerates cold snaps and, if covered in a timely manner with straw and non-woven fabric, can easily tolerate light frosts.
In one small area you can plant the seeds of only one variety of cabbage. Otherwise, all plants will be pollinated by bees. There should be at least 500 meters between plantings of different varieties.
The soil is prepared nutritiously, filled with organic matter and mineral fertilizers.
The “awakened” stalks are planted a little deeper than the heads of cabbage grew in the fall. The plant will produce new lateral roots.The cabbage is watered generously and covered for a couple of weeks under a layer of straw or light non-woven fabric.
After two weeks, the protection can be removed and the plants can be fed with organic (1:10 slurry solution, 3 liters per seed) or mineral fertilizers (nitroammophoska, nitrophoska).
Repeat feeding before flowering begins. The plants require standard care, like ordinary cabbage seedlings: hilling, weeding, watering, loosening.
Another way to preserve queen cells
Save queen cells from varieties early cabbage the usual way is almost impossible. But experienced gardeners have found a way:
- cut out the whole stalk and store it in the basement;
- in the fall they are planted in pots with nutritious soil mixture;
- The seedlings are stored in a dark basement at 1-2℃, just like regular queen cells.
With this method, the stalks take root well over the winter, and the apical bud remains healthy. In the spring, carefully transship it into open ground without disturbing the earthen coma.
Plants must be shaded at first.
This cultivation of queen cells is also well suited for the northern regions of the central zone of our country. Too long a period of winter cold makes it difficult to preserve healthy heads of cabbage in the usual way.
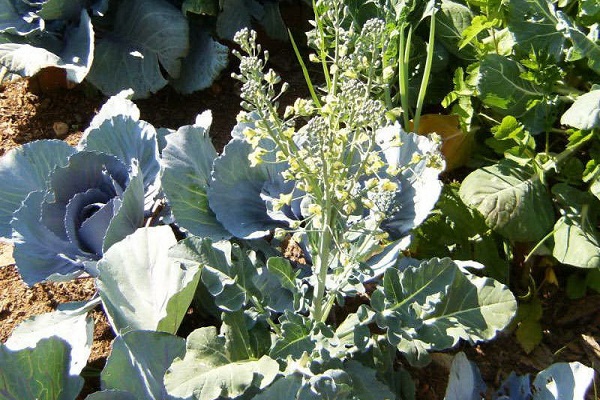
Flowering and seed collection
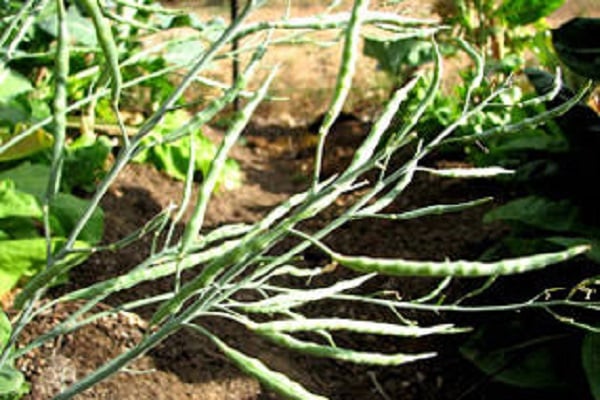
After planting, a properly overwintered mother plant begins to form long shoots, on which flowers then bloom. Such a plant is called a seed plant.
The healthiest seed material can be obtained from the central shoots grown from the apical bud. Side shoots are cut off, leaving only the strongest ones if necessary. The plant may not be able to handle too much ovary. Therefore, weak and too late shoots are also removed.To prevent long stems from breaking off and dying, it is advisable to tie them up.
The pods ripen at different times over a period of 30-50 days. It is important not to miss the moment and not let the very first seeds fall to the ground. They will produce the strongest and healthiest seedlings in the future.
Before collecting the seeds from the pods, they are tied into small sheaves and hung to dry. During the season, you can get 30-50 g of healthy seed from one plant. The collected seeds are stored in paper or fabric bags for 3-4 years.