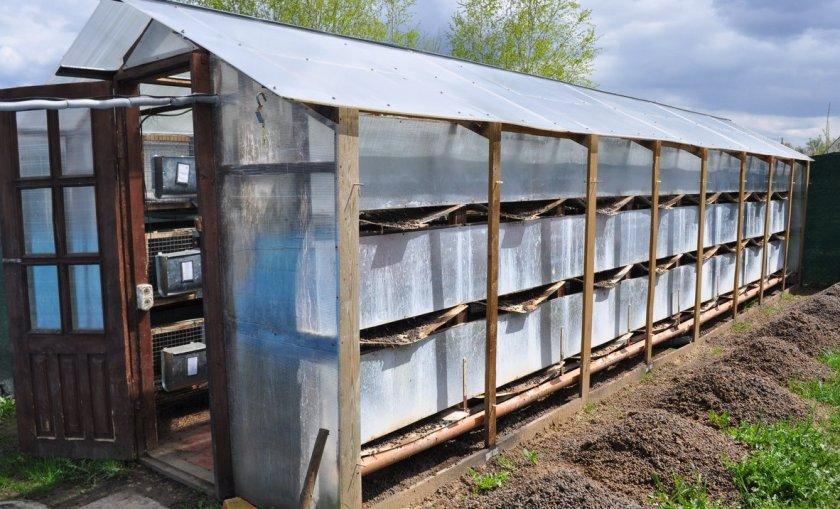
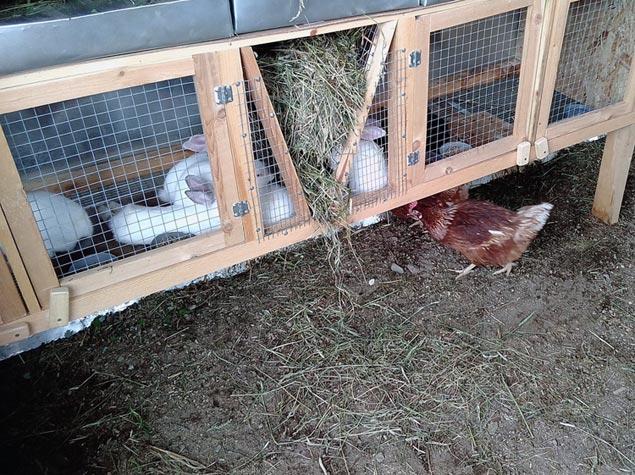
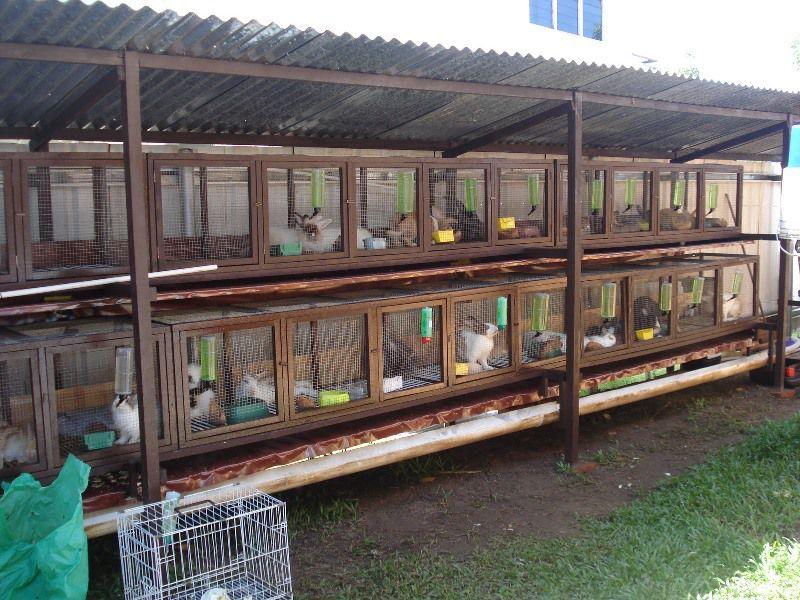
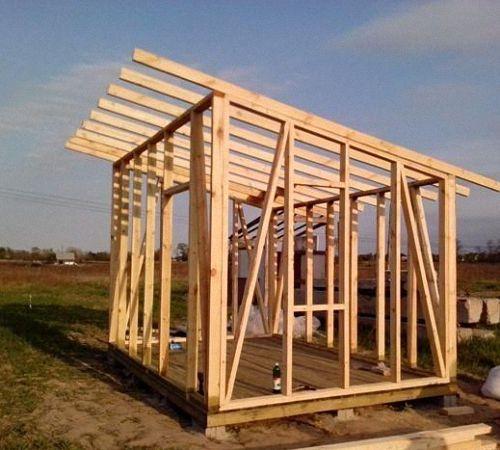
Raising pets requires a place to keep them. A barn is built for rabbits, which includes the installation of one-, two-, three-tier cages or free range. In such a room they can be looked after all year round. The structure has a simple design that is easy to build without the involvement of qualified specialists.
Types of rabbitries
The choice of method for raising animals depends on their number, the purpose of raising (for meat, fur, breeding), and the climatic conditions of the region. Animals are kept in cages or free range. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
There are 3 placement options for keeping rabbits:
- open (in the shed);
- closed (in a barn);
- Yamnoe
The first and last type of rabbitry is suitable for regions with warm winters. An enclosure is made in the shad or cages are installed. The canopy protects the rabbits from direct sunlight and rain/snow and wind.
The closed type is a barn, cold or insulated. The room must be provided with lighting and ventilation. Rabbits are kept on free grazing or in multi-tiered cages.
Requirements for the conditions of keeping rabbits and care features
The room should be comfortable for rabbits and convenient for caring for them. Regardless of the breed, animals cannot withstand dampness, drafts, or sudden temperature changes. Animals get colds and get sick. Lighting is natural, through windows, supplemented with artificial lighting in winter. The total area of window openings should be up to 10% of the floor area. The duration of daylight in the rabbitry is from 8 to 10 hours, the maximum is 16 hours.
Temperature and humidity
Optimum temperature for keeping rabbits: +5 to +15 degrees. Air humidity should not be higher than 75% and lower than 50%. Adults, when kept in a cold barn without cages, can withstand temperatures down to -30 degrees, if there is enough hay in the barn for them, in which the animals hide and warm up on frosty days.When kept in cages, the barn must be insulated so that the air temperature does not fall below 5 degrees Celsius.
Overheating is no less harmful for animals, so the barn needs good ventilation and thermal insulation of the roof. But at the same time, the movement of air in the room should not create a draft.
Hygiene
Fresh air is essential for the healthy development of animals. The concentration of harmful fumes (hydrogen sulfide and ammonia) from decomposing manure cannot exceed 0.015 and 0.01%. In a barn where animals are kept on free grazing, daily manure removal and regular bedding changes are necessary. The floor covering is made continuous and sloped towards the door so that rabbits cannot dig a hole and leave the room outside.
When keeping cages, a mesh is attached to the floor or a slope is made to the rear wall to facilitate maintenance. The basic rule for arranging cages is that manure from the upper cages should not fall into the lower tier. The frequency of cleaning in enclosures and cages depends on the arrangement. If manure is spontaneously removed through the mesh or holes in the floor, then cleaning is done 1-2 times a week. Feeders and drinkers are washed daily. Uneaten food (compound feed, vegetable mash) is removed, and the feeder is thoroughly washed.
Nutrition
The diet of rabbits should have a balanced content of dry food (oats, wheat, corn), mixed feed, vegetables (fresh and boiled), fresh grass/hay. In the summer, fresh grass and seasonal vegetables should predominate in the feed. Animals should not be given contaminated grass. It should be washed and slightly dried. In autumn and winter they provide hay, mixed feed, and vegetable mash.
Rabbits need something to chew on.Branches of aspen, birch, and willow will act as a food supplement and provide an opportunity to satisfy the natural instinct. When kept in an enclosure, hay is laid out on the floor for constant access for several days. The water should always be fresh. In an unheated barn in autumn and winter, water is provided in the morning and evening in a heated state.
Subtleties of maintenance in summer and winter
In summer, animals must be protected from overheating and bright sunlight. Cages placed outdoors should be covered with hay or straw on top. The canopy over the shad or enclosure should protrude 20-30 centimeters.
In the barn in the warm season, a mesh door is used to increase the flow of fresh air. The second door is kept open.
With the onset of cold weather, the barn is filled with hay for warmth during free grazing. When keeping cages in the barn, there must be heaters. In unheated premises, the number of rabbits is reduced to a minimum, leaving adults for breeding in the warm season. Birthing at low temperatures in a rabbitry can cause the death of offspring.
What should a barn be like for keeping rabbits?
Before construction begins, the premises for the animals are determined with its location. The north side, under the canopy of large trees, is considered favorable for breeding. The distance from housing and other outbuildings is 10-15 meters.
Materials for construction:
- board;
- logs;
- brick.
The choice depends on the capabilities and desires of the rabbit breeder. A cold shed is built from boards, and a warm one from bricks and logs.The area of the room depends on the method of keeping: with free range, 1 square meter is enough for 1 rabbit; with a cell – no less than 1.5 square meters (1.5 meters long, 1 meter wide).
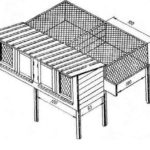
The roof of the rabbitry is made pitched to be used for drying hay. A hay storage facility (attic or deck) is installed between the roof and the room. When calculating the area, queen cells are taken into account: cages for rabbits for littering. When keeping rabbits in cages, an enclosure under a canopy for walking is attached to the back wall of the barn.
The barn is built without a foundation. There should be no gaps in the walls. This will protect the room from drafts, mice, ferrets and weasels. The rabbitry should have 2 doors: a mesh door and a solid door that closes tightly.
Step-by-step instructions for creating a rabbitry with your own hands
Construction of a rabbitry consists of 4 stages:
- design;
- choosing a location;
- preparation of material;
- construction sites
Designing means drawing a plan for the shed.
The area of the room is calculated based on:
- from the number of adult livestock;
- females for breeding;
- places for rabbits;
- placement of inventory;
- Sennikov;
- drinking bowl;
- feeders.
The drawing indicates the dimensions for one tier of cages along the walls or for free range. The width of the passage between them must be at least 1 meter. The height of the room is 1.8-2 meters. It must take into account human height and the number of tiers of cells. When multi-tiered, the upper cells should be located no higher than 1.5 meters, the lower ones - from 0.4 meters. The distance from the roof of the upper cage to the attic or attic flooring is at least 45 centimeters, so that the rabbits on the upper “floor” do not overheat due to poor air circulation.
Then the location of the rabbitry is determined, and the site is marked according to the plan.The side should be leeward, not flooded by spring floods, far from housing, a chicken coop, a cowshed, or a pigsty.
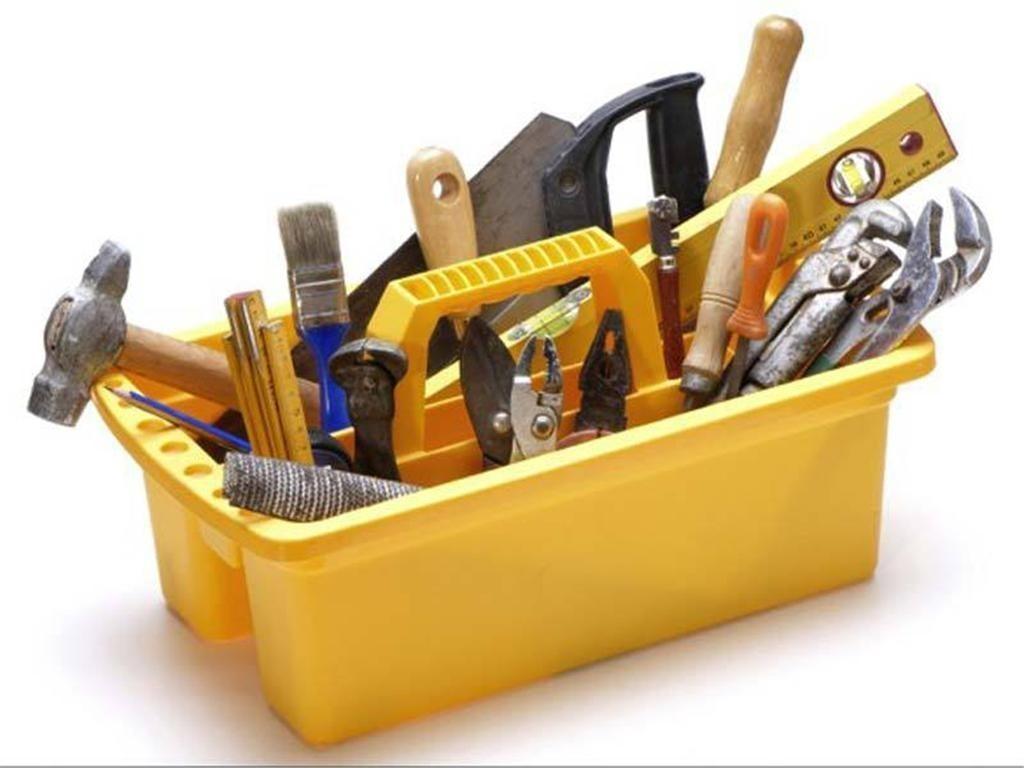
Main tool for work:
- level;
- roulette;
- hammer;
- hacksaw/power saw;
- hammer;
- metal scissors;
- ticks.
The most economical option is to make a shed out of wood. But, if desired, it can be built from brick or foam concrete.
The following materials are also taken into account:
- roofing felt or slate for the roof;
- cement and sand for screed;
- galvanized metal for upholstery corners;
- mesh for cages and internal doors (if kept in cages);
- hinges for hanging doors and doors;
- insulation (for a warm barn);
- glass (for windows);
- lighting equipment.
Construction begins with marking and leveling the site. The strip foundation is made under brickwork or polystyrene foam. A frame made of timber (for a wooden building) is installed at the corners of the site. A cement-sand screed is made over the entire site. Walls are being built. A pitched roof is installed. Doors are hung. Internal work is being carried out according to plan.