Grading of cattle is a mandatory on-farm event. Includes an overall individual assessment of each individual from the herd. The purpose of the study is to establish breeding and quality values, features of the subsequent use of cattle. Permission to carry out grading is available to livestock breeders, researchers, and farmers with higher veterinary education.
Cattle grading: what is it?
This is an event that is held on a regular basis to identify the most productive cattle representatives in the herd. In the future, this will be needed to form breeding stock or offspring. It is important to carry out the procedure on a continuous basis, since there is a natural loss of livestock due to disease, infertility and similar phenomena. To compensate for the deficit, it is advisable to form a livestock of the best representatives of cattle.
Valuation allows you to accurately determine the qualitative value of individuals. The data obtained is the basis for the distribution of living creatures according to their intended purpose. Promising livestock are left for reproduction, the rest is left for production purposes (for meat, for milk production). The Ministry of Agriculture has developed the necessary instructions to regulate the specifics of valuation.
Grading classes
In total, 4 classes are distinguished in practice. The conformity of the animal is established after the assessment has been carried out. At the same time, cattle cannot always correspond to only one class. This is due to the fact that individuals grow and their indicators change every year.
Official classes:
- Elite record (ER) – the number of points scored exceeds 81.
- Elite (E) – score range from 71 to 80.
- 1st grade (1K) – 61-70.
- 2nd grade (2K) – 51-60.
The assessment has different scores in each category. For productivity, the possible maximum is 60, for constitution - 24, for genotype - only 16. Each individual can score up to 100 points, but with a number of less than 50 it is considered an extra-class variety. Such animals are not allowed to reproduce.
Most often, they are immediately sent to slaughter, since they do not provide any value to the farm.
How many times a year should it be done?
Valuation to identify breeding value is carried out once a year. Young animals, castrated animals, and oxen are not allowed to participate. Lactating cows are assessed after complete feeding. Young animals are examined at least 6 months after birth. Bulls - at the onset of sexual heat.
Criteria for assessing herd representatives
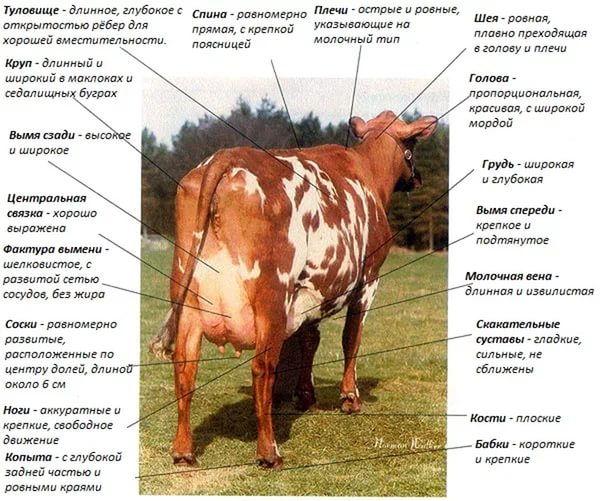
The first and main factors are gender and age. There are also several additional criteria for assessing individual individuals. They will differ depending on the direction of the breed. Common to all are genetic information, equipment and appearance or exterior.
Otherwise the criteria are different:
- For dairy cows - volumes and quality of products, milk production rate, readiness of the udder for automated milking.
- Bulls - the ability to reproduce healthy offspring.
- Young animals – quality of body development.
Additional criteria and explanations for scoring.
| Criterion | How is grading carried out? |
| Birth (for young animals) | Careful examination of documents, veterinary passports, and parents' pedigree. Conclusion - purebred individual or crossbreed. |
| Exterior of the body | In cows, attention is paid to the shape and size of the udder, the harmony of body composition.
In bulls - for the brightness of the breed, the structure of the hind limbs, the harmony of the exterior. “Excellent students” are individuals with developed withers in accordance with age, a wide sternum, absence of interception on the shoulder blades, and the correct shape of the legs. |
| Productivity (for cows) | The volume of milk yield, fat content of milk, and rate of return are taken into account. The data is verified in a specialized table. |
| Reproductive function | To evaluate bulls, the number of active sperm produced during the year is analyzed. The second option is the number of fertilized cows in one mating season.
Cows are graded based on the duration of the intercalving period and the course of calving itself. |
| Quality of offspring | In 12 month olds bulls are semen collected. The resulting seed material is frozen. An equal number of cows are then inseminated. The born offspring is registered and checked for defects and abnormalities. |
How to do it correctly?
It is important to prepare for the appraisal procedure. The preparatory stage includes checking the availability of inventory numbers, collecting information about the maintenance and feeding of the individual. It is necessary to summarize the information collected throughout the year. Enter data into individual cards. The appraisal itself takes place in 4 stages:
- Determination of the pedigree of an individual.
- Analysis of productivity or milk yield.
- Inspection of the correct body composition and exterior.
- The procedure is completed by counting points and the animal’s relationship to the class.
For meat direction
Appearance plays a decisive role. The first parameters are entered into a personal card immediately after birth. In young animals for meat production, they look at the structure of the skeleton, the structure of the chest and spine. When judging mature cows, muscle volume is important. Individuals are checked for combination with established standards for chest development, actual body weight, and the presence of adipose tissue.
For dairy breeds
The basis is milk yield for the past 3 lactations. Data for grading should be taken from accounting journals, which are required to be maintained on a farm. The fat content of dairy products and the level of protein content are calculated. The obtained data are compared with the performance of breeding cows.
For young animals
Only live weight at birth and at the time of valuation, as well as genetic background and body type are taken into account. Possible future productivity is also taken into account. Breed suitability is also determined. The first assessment is carried out when the young animals are 6 months old.
For the bulls
Individuals are considered for their purebredness and ability to reproduce breeding offspring. The quality of bulls is similar to determining the quality of cows. The point values are also identical. It is permissible to change the class and category of a bull, provided that the quality of its offspring increases.
Results of workover appraisal
After grading, the animal is given a general assessment and assigned to one of five classes. Based on the identified class, individuals are distributed into groups, the first of which is the main one (leading or breeding core). This includes the best cattle representatives in terms of productivity and breeding qualities, which ensure further reproducibility of the herd. The second group is animals for expanding the herd. The third is cattle without breeding value for culling.
Necessary for the formation of highly productive livestock. The study takes place according to a number of parameters. All individuals are subject to assessment starting from 6 months of age. Based on the data obtained, groups of animals are formed: to obtain offspring, to expand the herd, for speedy slaughter.