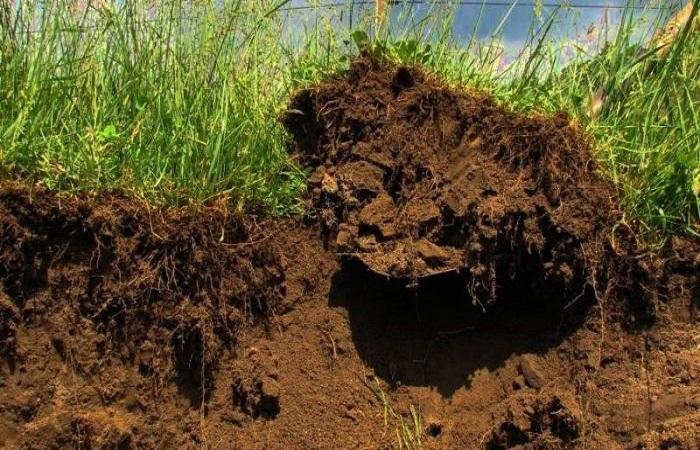
Good soil is necessary for the growth and development of plants so that they produce a rich harvest. This is a support for roots, a source of nutrition and water. Complex organic substances are converted into simple mineral substances, which are absorbed by plants. Let's consider what is in the soil, what layers it consists of, and how it is formed. What are soil microorganisms needed for?
What is soil made of?
It contains several components: organic and mineral nature, moisture and air.
Mineral base
It is considered one of the main characteristics of soil.This is its solid part, represented by minerals, it was formed as a result of the processes of weathering of rocks and their transformation. The soil cover was formed under the influence of physical and chemical factors and microorganisms. The main component of the mineral part of the soil is silicon-oxygen compounds, for example, silicon oxide. Iron and aluminum are found in large quantities in ferrosilicate and aluminosilicate soils.
The mineral part contains primary and secondary minerals. Primary ones predominate in sandy and sandy loam soils, in loamy soils – both, and in clayey soils – secondary ones.
The earth also contains mineral salts: carbonates, sulfates, phosphates, nitrates and chlorides of various elements. They are soluble in water, and their quantity is greater in saline soils than in normal soils. There are also insoluble or difficultly soluble salts. Their main source is also mountain soil-forming rocks.
Organic
Located in the surface layer of the earth. These are the remains of organic matter (plant and animal tissues that have partially retained their structure and shape) that entered the soil; they are found in the form of organic or organomineral compounds. Humus is also a component of this part of the soil. Humus is the result of the formation of nitrogen-containing compounds that have a complex structure.
Humus makes up the fertile part of the soil, consisting of humic and fulvic acids and their salts. Humic acids are poorly soluble in water and are black or dark brown in color. Fulvic acids are highly soluble in water, give the soil a yellowish color, and participate in the soil-forming process of podzols.Humus also contains nonspecific substances: proteins, amino acids, carbohydrates, monosaccharides, peptides, purines, resins, lipids, lignin, organic acids and tannins, aldehydes, alcohols.
What other layers does soil consist of?
The liquid part of the soil is represented by the soil solution; it is the most active and mobile. From it, plants extract water and nutrients dissolved in it. The composition and concentration of the soil solution varies depending on the physicochemical and biological processes occurring in the soil. Air is present in the pores; it contains more carbon dioxide and less oxygen than atmospheric air. Its composition is also variable and depends on gas exchange between the soil and the atmosphere.
All components of the soil are interconnected and mutually influence each other; a mobile equilibrium is established between them. The entry of salts into the soil solution depends on the weathering and destruction of minerals, the transformation of organic residues, and the supply of mineral fertilizers from outside. A diagram of the soil profile shows that it consists of several layers, with more moisture and air present in the upper ones than in the lower ones.
How is it formed?
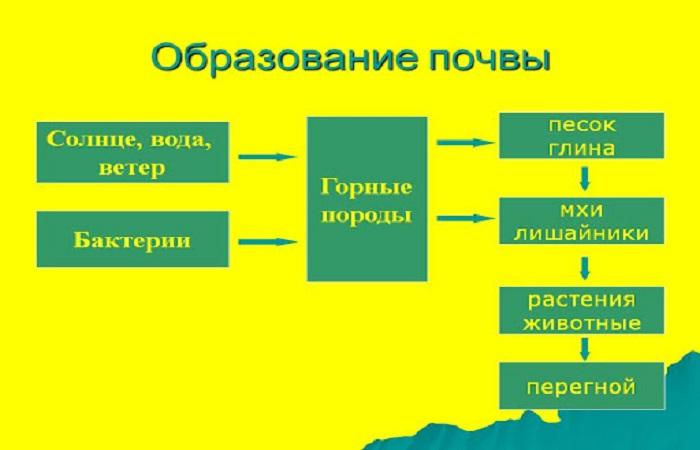
Soil formation is a long process and occurs continuously. Minerals are formed from rocks, which are gradually destroyed under the influence of water, air, heat, and microorganisms. All these components themselves are part of the soil.
The main source of organic matter is plants and their residues, which are processed by bacteria. Insects, worms, and small animals living in the soil take an active part in the formation of soil. They process organic particles, mix them with the soil, and loosen it.
Different types of soils differ in structure, physical properties, humus and nutrient content, which determines their fertility.
The role of microorganisms in soil formation
Bacteria, fungi and other representatives of microorganisms perform an important function - they regulate metabolism and process plant particles into mineral ones. This occurs as a result of aerobic or anaerobic reactions. In the first case, organic matter is completely converted into simple substances: salts, carbon dioxide, water. In the second, incomplete decomposition of organic matter occurs with the formation of alcohols and acids.
What does the term “fertile soils” mean?
Soils are considered fertile if they satisfy the needs of plants for water, heat, air and nutrients in the quantities they need. They should be light in composition, loose, well heated, allow air to pass through, and contain nutrients and substances in the upper horizon.
All processes that occur in the soil are interconnected. If something is disrupted, it affects the entire system. The deterioration of the soil entails a deterioration in the condition of plants and a decrease in productivity. To determine fertility, you need to pay attention to the chemical composition, acidity, air and moisture permeability.
The composition of the soil affects its characteristics; the main components are the mineral part, organic, liquid and air. Microorganisms and small soil animals play a major role in soil formation.