Ferns and mosses belong to the group of higher spore plants. At one time they completely captured the Earth. Somewhat later, such crops gave way to the leading positions to angiosperms and gymnosperms. At the same time, not everyone knows exactly how ferns differ from mosses. These types of cultures are characterized by differences that concern many nuances.
What kind of plants are these
Mosses belong to the highest crops. This department includes more than a hundred families. It includes 700 genera and about 10 thousand varieties. This species is considered one of the oldest. Its appearance dates back to the Carboniferous period.In this case, several classes of mosses are distinguished. These include deciduous, anthocerotaceae. In addition to this, there are hepatic varieties. The most common are leafy mosses, also called true mosses. Today they are called “cuckoo flax” and “sphagnum”.
Fern-like crops are considered the oldest of the plants that have survived on Earth. Their appearance dates back to the Devonian period. It existed about 400 million years ago. Such plants have different shapes, dimensions, and life expectancy. Although crops are characterized by a number of visual characteristics, they number more than 10 thousand varieties.
Main differences
The differences between cultures concern a number of characteristic features. These include size, structure, reproduction.
In sizes
The key difference between the varieties under consideration is their dimensions. Mosses are small plants. They are devoid of mechanical tissues, which are characterized by good development. Therefore, such species cannot maintain the structure. Large dimensions would provoke a fall.
Ferns can reach impressive sizes. This is due to the fact that they have good root development. Such cultures are characterized by obvious tissue differentiation. This makes it possible to develop a powerful mechanical structure that interacts with other plant elements. Due to this, ferns can grow to gigantic sizes.
What makes their structures special?
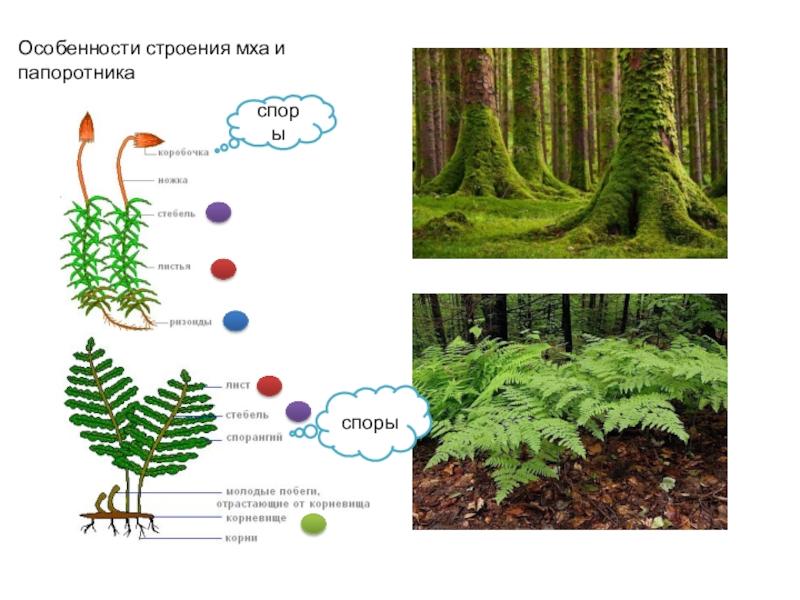
Ferns are crops that can be herbaceous or woody. They are characterized by modified shoots. Fronds, which are considered pseudo-leaves, are attached to them using petioles.This is the initial stage of evolution towards the formation of true leaves in crops. The fronds have two important functions. They take part in photosynthesis and are responsible for the formation of spores.
Mosses are also characterized by the presence of a stem and leaves. But they differ in visual characteristics. The leaves are small in size and contain chlorophyll. Many representatives of this category are characterized by yellowish-brown lower leaves. This is due to damage to the pigment due to lack of light. However, such plants are rootless. They are attached to the ground by rhizoids, which are multicellular hair-like shoots.
By reproduction
Fern-like plants spread in different ways - by vegetative means or through spores. In the first case, buds and roots are involved. Reproduction of mosses occurs by spores, the maturation of which occurs in the sporangium of the sporophyte. It, in turn, is a leg that has a box.
The sporophyte is characterized by a short lifespan and dries quickly. After this, the box opens and spores spill out of it. From them a culture emerges, which is characterized by a haploid set of chromosomes.
Other differences
Other cultural differences include the following:
- Ferns are old crops. They occupied a leading position during the Mesozoic.
- Ferns are dioecious crops, and mosses are monoecious.
- Gas, oil, and coal were formed from fern-like cultures. Mosses were the basis for the formation of peat accumulations.
- Moss leaves produce exclusively chlorophyll. Fern foliage takes part in photosynthesis and spore production.
- Mosses are equipped with rhizoids, and ferns are equipped with rhizomes.
What could happen after the extinction of ferns and mosses?
After the extinction of ferns, significant accumulations of valuable minerals formed in the soil. Among them it is worth highlighting oil, gas, and coal. Mosses formed the basis for the formation of peat extracted from peat bogs. It is used as an organic fertilizer and a raw material base for the production of paints, plastic, alcohol and other materials.
Bryophytic and fern-like plants are characterized by a number of nuances. The difference concerns structure, visual signs, life expectancy and other features.