The use of drugs to protect plants from pests and diseases is one of the conditions for obtaining a good harvest. To do this, it is recommended to use the fungicide Zato. This product has a mesostemal effect, which provides plants with reliable protection even under the influence of unfavorable climatic factors. It also has low consumption compared to similar substances.
- Composition, release form and purpose of the drug Zato
- How does the product work?
- Advantages over analogues
- Consumption rates for different plants
- How to prepare a working solution
- How to use the product
- Safety regulations
- Toxicity
- Possibility of resistance
- Compatibility with other fungicides
- Storing the product
- What can be replaced?
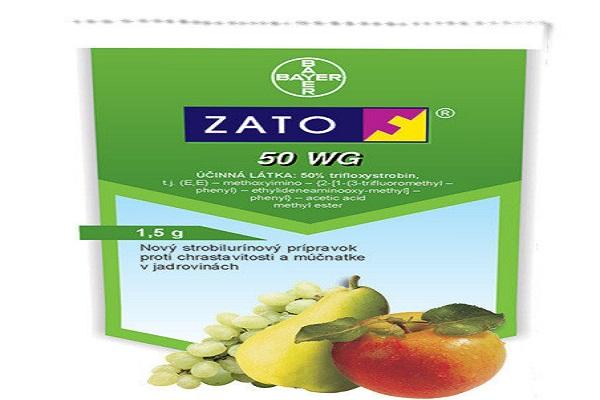
Composition, release form and purpose of the drug Zato
The main active ingredient of the drug is trifloxystrobin. It makes up 50% of the product. The product also contains many mineral additives based on magnesium, copper, nitrogen, potassium plus zinc.
The fungicide is available in the form of water-soluble granules. It is used to provide long-term protection of plant crops from diseases and harmful fungi.
How does the product work?
Fungicide But refers to mesostemal preparations, the effect of which is expressed in fixing the substance on the surface of plant crops due to binding to the wax layer. In addition, the drug has translaminar activity. This makes it possible to provide plants with reliable protection, which does not depend on meteorological conditions.
The main component of the drug is trifloxystrobin. It helps block mitochondrial respiration in fungi, which leads to impaired growth of the pest. Over time, this leads to his death.
The fungicide has a protective, therapeutic and prophylactic effect when treating fruit plants.
Advantages over analogues
The drug has a wide spectrum of action, including diseases during storage. Fungicide But it is resistant to rain and low temperatures. Thanks to the mesostem effect, plants can be treated at high air humidity.
Consumption rates for different plants
When spraying apple and pear trees against scab, powdery mildew, Alternaria blight, moniliosis, black spot and phyllostictosis, you need 140 grams of product per 1 hectare of plantings. The product is used in combination with other fungicides. Spraying is carried out during the growing season, before and after flowering. The total number of treatments does not exceed 2.The interval between them is 14 days. The consumption rate of the working solution is 800-1000 liters per 1 hectare.
In the case of treating fruits against diseases during storage, including the latent form of moniliosis, use 150 grams of the product per 800-1000 liters of water. Spraying should be carried out during the growing season. The total number of treatments is no more than 2. The interval between them is 14 days. They are carried out 14 and 28 days before harvest.
How to prepare a working solution
To prepare a working solution, you need to dilute 1 gram of the product in 6 liters of water. During this, 2 liters of warm water are poured into the sprayer tank, then the drug is added to it, and then the rest of the liquid is added. After this, the solution can be used to spray the fruits and leaves of fruit-bearing plants.
How to use the product
The drug But is used to treat the external parts of fruit plants. To do this, leaves, stems and fruits of crops are sprayed with a working solution using a special sprayer. Treatment can be carried out under any meteorological conditions.
Safety regulations
When processing plants, it is recommended to adhere to certain safety rules, thanks to which you can avoid intoxication of the body with a fungicide. These include:
- Use changeable clothing made from thick fabric. In addition, you need to have vacuum goggles, a hat, a respirator, rubber gloves and high shoes.
- Treatment should be carried out in the morning or evening, when the air outside is cool. Spraying can also be carried out during rain and gusty winds due to the mesostemic effect of the fungicide.
- When spraying fruit plants, do not eat, smoke or drink. This will prevent the drug from entering the digestive system and upper respiratory tract.
- Small children, pregnant and lactating women should not be near the person performing the treatment. This is also not recommended for people who are allergic to the components of the fungicide.
- After the procedure, the sprayer tank must be thoroughly washed with laundry soap or a 5% soda solution.
Toxicity
The fungicide belongs to hazard class 3. This means that the drug is moderately hazardous to human health, honey insects and the environment.
Possibility of resistance
There is no specific data on the development of fungicide resistance in fruit-bearing plants. However, to prevent the emergence of resistance, it is recommended to alternate the drug with other agents that belong to different chemical groups.
Compatibility with other fungicides
The product combines well with most insecticides and fungicides. The exception is acidic and highly alkaline substances.
Before treating plants, it is recommended to check drugs for compatibility.
Storing the product
The shelf life of the fungicide from the date of manufacture is 2 years. It is recommended to store the drug in a closed container, in a cool place out of reach of sunlight. After opening the package, the drug is good for no more than 6 months.
What can be replaced?
Alternatively, if it is not possible to purchase fungicide preparations Champion are used, Title Duo or Carbendazim. In addition, it is recommended to use Boxwood and Benomyl to treat plants against pests and various diseases.
Fungicide But is one of the most effective means in its group. Thanks to it, you can provide reliable protection to fruit and berry plants from harmful fungi. If you follow the instructions for use of the drug, the substance is not dangerous for people, honey insects and the environment, and also allows you to cope with the spread of diseases.