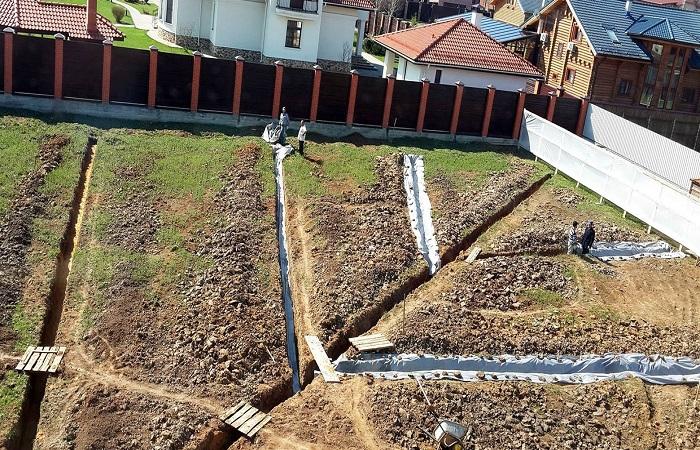
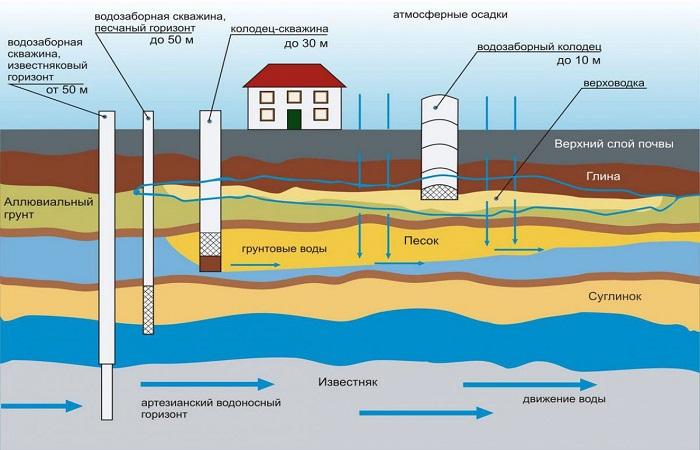
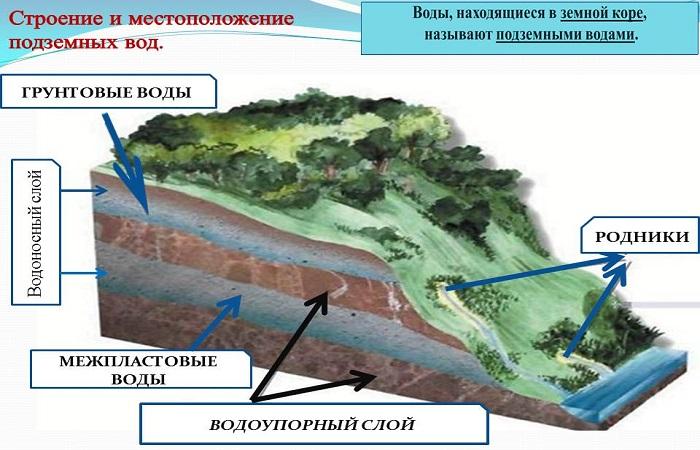
Groundwater is a liquid that accumulates in the upper structures of the soil. Its presence on the site can force a person to refuse to build permanent structures, since it spoils any work and provokes the destruction of structures. That is why it is so important to determine the presence of water and the depth of its occurrence. There are many types of water in soils. They are classified according to different criteria.
Types of groundwater
Sources of groundwater formation include precipitation - rain or snow.Also, the cause of their accumulation is considered to be condensation of water evaporation, which forms in the soil.
The depth of groundwater is influenced by the terrain and the presence of reservoirs near the site. In swampy places and lowlands, groundwater is located almost near the very surface of the earth - 1-2 meters. Sometimes this interval is only a few centimeters.
Today, quite a few types of groundwater are known. They are classified according to various criteria. In order to properly carry out planting work and erect various structures on the site, you need to determine the type of water.
By location
Based on the location of water in the ground, the following types are distinguished:
- strata - located in loose or weakly cemented rocks;
- pore - located in the pores of the rock;
- fissure – localized in cracks in well-cemented rocks.
A characteristic property of groundwater is its ease of accessibility. Therefore, you can use simple ways to access free water - for example, digging wells.
By aggressiveness
This term refers to the ability of water to destroy metal and concrete structures or structures made of other materials. This parameter is also used to evaluate the ability of water to influence the flora and fauna of water bodies. Aggressiveness is influenced by the presence of certain chemical compounds.
Depending on the variety and quantity, the following types of substances are distinguished:
- General acid. The pH level is used as an indicator of acidity. The most aggressive water is considered to be water whose pH is less than 4. This indicates that the environment is acidic. At the same time, water with pH parameters greater than 6.5 is considered the least aggressive.If the indicator is up to 6.5, they speak of general acidity.
- Leaching. They are characterized by a large amount of bicarbonates in their composition - more than 0.4-1.5 milligrams. These substances remove calcium hydroxide from concrete structures.
- Sulfate. They contain many sulfate ions. They provoke swelling of concrete and destroy the material.
- Carbon dioxide. They contain a lot of carbon dioxide, which leads to the dissolution of calcium bicarbonate. The substance can also provoke the destruction of concrete structures.
By mineralization
This parameter is used to determine the volume of compounds that are dissolved in water. It is evaluated by evaporating 1 liter of water to obtain a dry residue. Its size and composition help to establish mineralization parameters.
According to this indicator, water in the pores of the soil can have the following varieties:
- fresh;
- sulfate;
- slightly salty;
- salty.
By hardness
This parameter is determined by the presence of magnesium and calcium ions in the water. The following types of hardness exist:
- general;
- carbonate;
- non-carbonate.
There is also an additional classification based on overall hardness. Water can be very soft, soft, moderately hard or hard.
By pollution level
Groundwater becomes polluted by filtering harmful elements from the surface. The following types of pollution sources are distinguished:
- industrial sites that use elements that can migrate with groundwater;
- storage areas for industrial products and their waste;
- areas where household waste accumulates;
- fields for irrigation of agricultural products.
Pesticide storage areas, including those prohibited for use, are especially dangerous.This category also includes oil production and oil refining enterprises.
How to understand whether there is perched water or groundwater in the area?
Perched water refers to temporary accumulations of precipitation in the upper part of the soil. They are located above groundwater. This usually occurs after rain or snow melts. In this case, moisture is predominantly concentrated over soil that does not conduct water well - clay, dense rocks, loams. Subsequently, one part of the perched water evaporates, and the other enters the underlying structures.
The following signs are characteristic of perched water:
- Low power and minimal water layer area.
- The presence of clay or loam in the area - perched water does not accumulate in the sand.
- There is an obvious connection with seasonal factors - there is no high water in winter and summer. This phenomenon is typical for spring and autumn.
- Relationship with climate humidity parameters. High water is typical for the wet period. However, in dry times it disappears.
Increase or decrease in water level
The groundwater level can range from 2 to 30 meters. Its high placement provokes waterlogging of the soil, worsens the growth conditions of crops, and quickly destroys underground structures.
There are the following methods for lowering the groundwater level:
- drainage of the site;
- digging a reservoir.
The standard drainage scheme involves the construction of a ditch along the perimeter of the site. At the same time, it is necessary to lay pipes made of plastic or asbestos cement. After this, the ditch is filled with sand, soil and gravel.
It is usually not necessary to artificially raise the groundwater level. However, if such a need arises, reservoirs are built.
Groundwater is classified according to various criteria. This allows you to determine their characteristics and correctly construct various structures on the site.