Many new gardeners experience disappointment cherry planting. Having paid a significant amount for a unique variety, after some time they sadly observe the death of the fruit tree. There can be many reasons for this situation, ranging from the wrong location to violation of growing rules. To avoid such developments, it is important to know how to grow cherries and what rules must be followed.
Correct fit
The rules for planting cherries on a site are largely determined by the tree’s belonging to a specific variety.Most often, Russian gardeners choose the common variety for these purposes because of the versatility of using its fruits, suitable for fresh eating, making compotes, jams, juices and sweet products.
To successfully grow cherries, it is necessary to take into account the climate of the region and select a variety whose breeding qualities correspond to its conditions. In areas with cold climates, only winter-hardy cherry species can withstand difficult growing conditions.
It is important to determine when to plant cherries. The recommended time for planting a tree is spring and autumn.
When buying a seedling in the spring, parameters are important; the optimal standard is a two-year-old tree 60 cm high and 2.5 cm in diameter. Planting is carried out when the soil has warmed up, and the period of bud break has not yet begun.
Where to plant cherries:
- the soil must have neutral acidity and be of sandy type; loamy soil requires drainage;
- lowlands, areas with a damp climate are not suitable, cherries love illuminated, sunny places;
- the groundwater level must be more than 1.5 m;
- The place should be protected from gusty winds.
When asked whether and how to grow cherries in acidic soils, experienced gardeners will answer in the affirmative. Treatment with lime or dolomite flour will help reduce the indicators and bring them back to normal. At 1 m2 add 400 g of soil and dig it to the depth of a shovel. After this, after some time, organic fertilizers are applied, such as compost or manure per 1 m2 15 kg.
The distance between cherries should be at least 3 m. When planting a cross-pollinated variety, it is important to consider the likelihood of pollination.In this case, 4 types of cherries are taken and planted taking into account a pattern of 2.5 x 3 m for tall trees and 2.5 x 2 for short ones. Some gardeners prefer to plant trees in a checkerboard pattern.
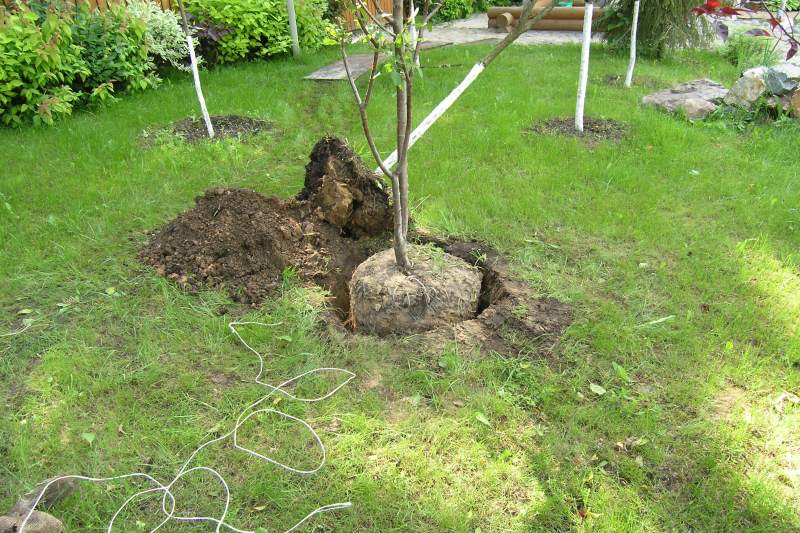
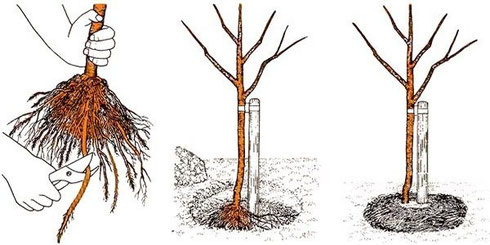
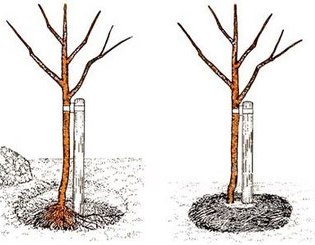
A hole for planting cherries is formed with a diameter of 80 cm and a depth of 50-60 cm. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers and lime are not added to the hole, otherwise the root system can be damaged. It is permissible to add ash, potassium chloride and superphosphate to it. The cherry root system should be healthy; damaged and dried shoots should be removed.
A wooden peg is driven into the center of the recess to facilitate the planting process. The seedling is buried, evenly distributing its root part. The neck should be 4 cm above the soil surface to prevent the seedling from rotting in the future. The roots are covered with soil and a small roll of soil is formed around the tree to better retain moisture. 10 liters of water are poured into the hole, after which the soil is mulched with humus or peat. For better protection, the seedling is provided with an additional support point by carefully tying it to a peg.
If you purchase a seedling in the fall, you need to dig it in before spring. The recommended time for carrying out work is October; there should be 20 to 30 days before the threat of frost. The following requirements are imposed on the height of the seedling:
- annuals - up to 80 cm;
- two-year-olds - up to 110 cm.
The root system of young shoots must be well formed and the wood must be mature. Before planting, dig a hole with a depth of 40 cm and a slope of 450. The roots are placed in a hole and watered generously. The tree is insulated with spruce branches, and in winter it is buried with snow. Immediately before planting, the tree is dug up for further rooting in the place of permanent cultivation.
Care
Cherry is undemanding to care; the main actions are related to watering, applying fertilizer and periodic loosening.
Watering
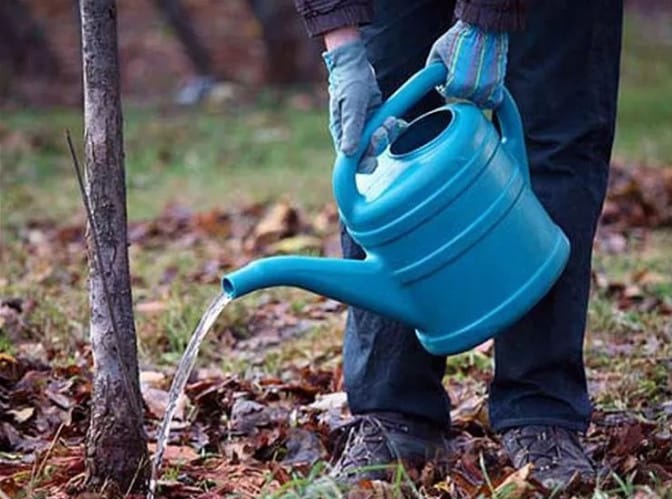
The first watering is carried out after flowering, which helps the berries fill with juice. The sufficiency of moisture supply is determined by how much the soil is saturated with water.. The optimal depth is considered to be from 45 to 55 cm. In the future, the need for watering is determined based on the sufficiency of natural precipitation.
Feeding
It is recommended to apply fertilizers at the moment when the cherry begins to form berries. Their rate depends on the condition of the seedling and its age characteristics. Compost or humus can be used as additives. In autumn, the soil should be enriched with fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium. If there is a lack of nitrogen in the soil, the deficiency is replenished in the spring.
The first fertilizing is carried out immediately at the end of flowering. The process is repeated after 14 days. For young seedlings, it is enough to add fertilizer to the circle near the trunk. Adding ash has a good effect when the soil is highly acidic.
Trimming
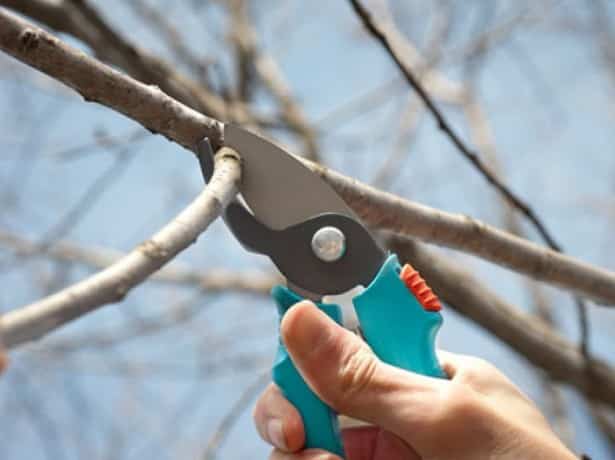
A distinctive feature of cherries is the rapid increase in the number of branches. As a result, the crown is able to grow and greatly increase in size; the formation of many shoots leads to thickening. In the absence of measures for pruning the plant, there is a problem of crushing the berries and reducing the number of bouquet branches on which the fruits are formed. The result is a decrease in yield and deterioration in the quality of cherry berries.
Branches with a shoot length of more than 50 cm must be pruned. It is recommended to carry out the procedure in early spring, 3 weeks before the buds begin to swell.The first work on crown formation must be carried out after planting. When the seedling height is 40 cm, you can begin to shape the shape of the crown, while removing excess branches and shoots.
On a tree with a height of slightly more than 40 cm, on average, 7 main branches are left as the basis of the skeleton. The shoots should be evenly spaced, 3 branches are enough on the lower tier, 2 on the second, 1 on the third. As the cherry matures, on average, 10 branches should remain. All processes that are directed inward must be removed.
To successfully grow cherries, it is important to prevent the growth from spreading throughout your garden plot. Excessive growth of young shoots weakens the plant and can lead to the death of the tree. To avoid this, it is necessary to promptly trim the shoots at a distance of 30 cm from the soil surface level. It is effective to dig a barrier made of slate, plastic or other material into the ground at a distance of 1.5 m that can limit the spread of growth.
Diseases and pests
In the spring, cherries can be susceptible to clasterosporia blight. The disease manifests itself in the form of the formation of brown spots with a red border on the leaves, which over time can reach a diameter of 2 cm. After 10 days, a hole can be observed in their place. When a large area is affected, the leaf blades dry out and fall off.
Formations due to clasterosporiosis can also form on berries, in which case their surface is covered with depressed purple spots. At the initial stage, their diameter is 1 mm, but in the absence of timely measures they can increase 4 times.To combat fungal disease, spray with a 1% solution of copper sulfate, dissolving 100 g of the product in 10 liters of water.
It is recommended to carry out treatment in order to prevent the appearance of kleasterosporiosis in early spring, when the buds have not yet begun to bloom. If the plant is sick, then spray with Bordeaux mixture, diluting 100 g of the drug per 10 liters of water.
It is recommended to do 4 procedures:
- before flowering or at the stage of bud formation;
- after flowering ends;
- 2 weeks after the 2nd spraying;
- 30 days before the planned harvest.
Cherries can develop coccomycosis, which manifests itself as the formation of red spots on the leaves. As it develops, the plates become yellow, dry out and fall off prematurely. The danger lies in the fact that fungal spores can spread over long distances and infect large areas of plantings in a short time. For control, spraying with a vitriol solution is used, preparing it from 100 g of the product and 10 liters of water, the procedure is carried out until flowering begins. For the same purposes, you can use the drug “Horus”, following the rules for preparing and using the working solution.
Among the most common cherry diseases include:
- scab;
- rust;
- moniliosis
Among the most common cherry pests includes aphids, mites, leaf rollers. Targeted drugs are used to combat diseases and pests. As a means of prevention, tree trunks are whitewashed in the spring, and foliage and affected tree branches are burned in the fall.