Pears have been cultivated in our country for a long time due to their many beneficial properties. From year to year, breeders work to improve known species and offer gardeners worthy new items. One of them is the early autumn pear of the Moskvichka variety, which has enormous advantages over its competitors.
- Description of Moskvichka pear
- Characteristics of trees and fruits
- History of selection and region of breeding
- Pros and cons of the variety
- Landing Features
- Choice of time and place
- Pit preparation
- Distance between seedlings
- Landing technology
- Tree care rules
- Watering and fertilizing
- Trimmings
- Shaping the crown of the Moskvichka pear
- Regulatory trimming
- Maintenance pruning
- Sanitary pruning
- Rules for pruning
- Diseases and pests of Moskvich pear
- Prevention measures
- Possible diseases
- Scab
- Sooty fungus
- Probable pests
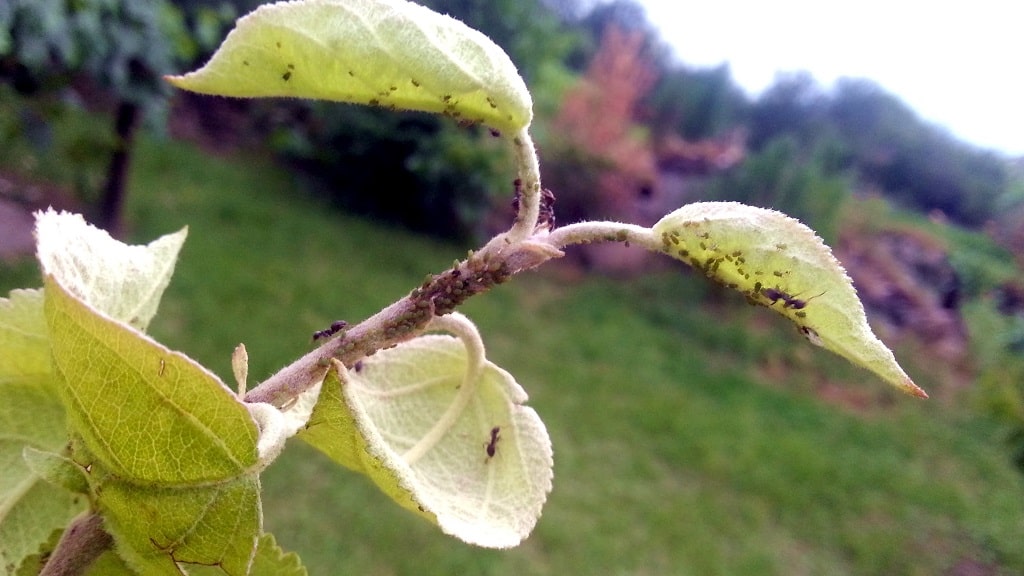
- Aphid
- Pear moth
- Pear flower beetle
- Collection, storage and use of crops
Description of Moskvichka pear
The Moskvichka pear variety is an early autumn variety and begins to ripen in September. It has good frost resistance and is successfully grown in all regions of our country. The tree bears fruit abundantly and annually. Muscovite is self-sterile, that is, for the formation of ovaries it is necessary to plant pollinators near it. The best varieties for this are recognized:
- Lada;
- Yakovlev's favorite;
- Moscow bergamot.
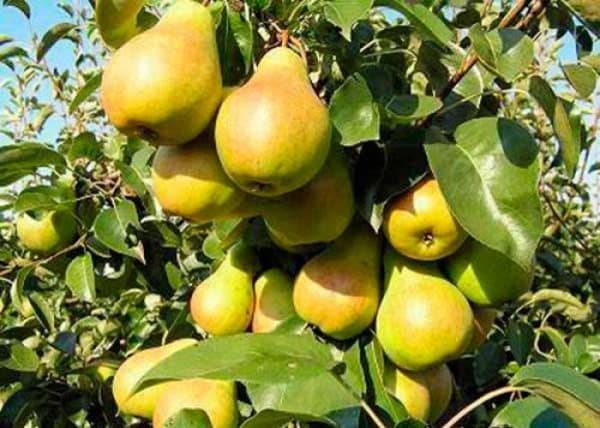
The first harvest is harvested 3 years after planting the seedling on the plot. An adult tree can produce up to 50 kg of fruit.
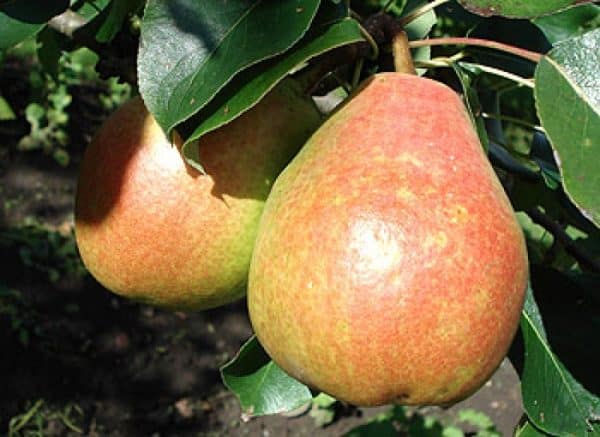
Characteristics of trees and fruits
The tree of the Moskvichka pear variety is standard, with an even and straight trunk. There are no side branches; a dense crown can be grafted or formed. The height of an adult pear reaches 3.5 meters. Skeletal branches are directed vertically.
Flowering begins late, so return frosts are not harmful to the future harvest.
The leaves of this variety are oval in shape, rich green in color and small in size. They are quite dense, but at the same time elastic. The flowers are cup-shaped, small, collected in inflorescences of 5 pieces.
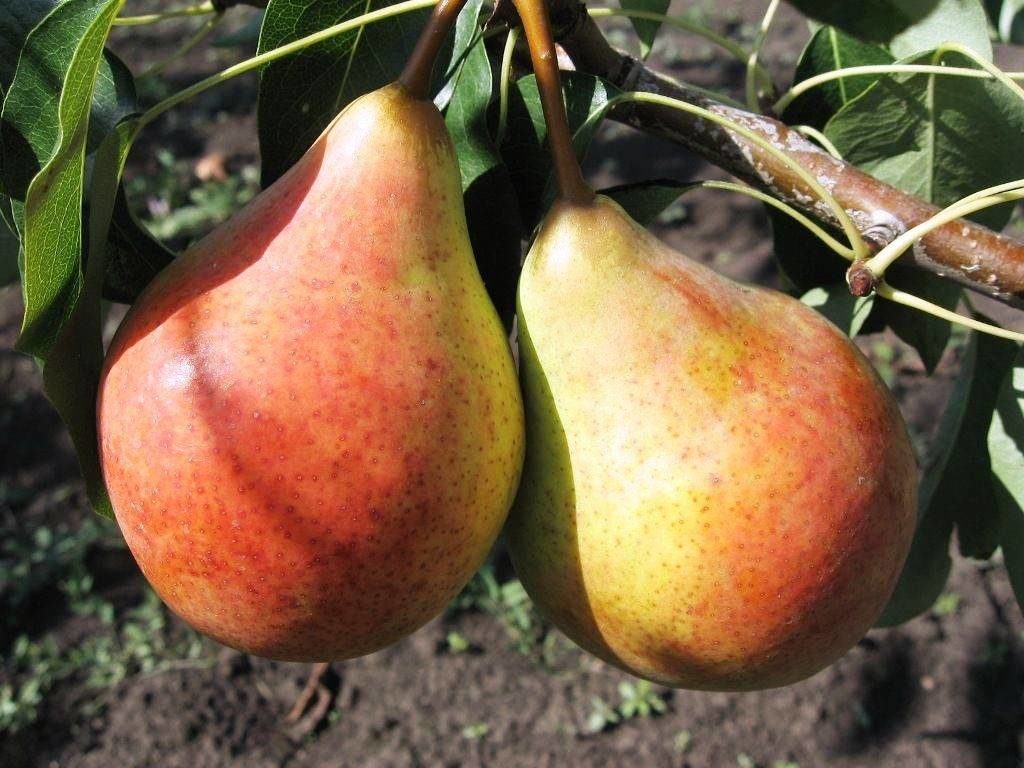
Moskvichka's fruits are medium-sized; the weight of one of them can reach 130 grams. Their shape is wide, classic pear-shaped. During technical ripeness, pears acquire a yellow-green color, and brown subcutaneous dots become noticeable. If the fruits are left on the tree for a little while, a slight blush will appear on them. The pulp is very juicy, tasty, sweet, white. The aroma is strong and classic.
History of selection and region of breeding
Specialists from the Timiryazev Academy worked on breeding the Moskvich pear. They carried out open pollination of the no less famous variety Kieffer, and then grew seedlings based on the resulting material. It was these young plants that became the basis for obtaining Moskvichka. In the 80s of the last century, the new product had already begun to be adopted in the gardens of domestic summer residents. It was recommended for the Volga-Vyatka, Middle Volga and Central regions. However, most of all, Moskvichka was loved by residents of the Moscow region.
Pros and cons of the variety
Like any variety, Moskvichka has its own advantages and disadvantages that distinguish it from its competitors. Positive qualities include:
- early fruit ripening;
- dessert taste;
- precociousness;
- regular fruiting;
- high yield rates;
- fruits are not prone to shedding;
- excellent product characteristics;
- pleasant strong aroma;
- the crop is suitable for transportation over long distances;
- possibility of long-term storage of the harvested crop;
- increased resistance to common diseases;
- unpretentiousness.
The disadvantages are:
- self-sterility;
- average frost resistance;
- low resistance to prolonged drought.
Landing Features
The Moskvichka pear has planting features that you should familiarize yourself with before placing it on your site.
Choice of time and place
Moskvichka pear can be planted both in autumn and spring. In the fall, planting work is planned for October, and they try to meet the deadline from the 10th to the 20th. In spring, the tree is planted from April to May, but the best time for this is considered to be the last ten days of April.
The advantage of spring planting is that the young seedling has time to take root over the summer and tolerates winter cold well. When planted in autumn, the plant has greater frost resistance. Pears prefer loamy or sandy loam-chernozem soil. It should be loose, nutritious, with a sufficient amount of fertilizer. Choose a sunny, well-lit, dry place.
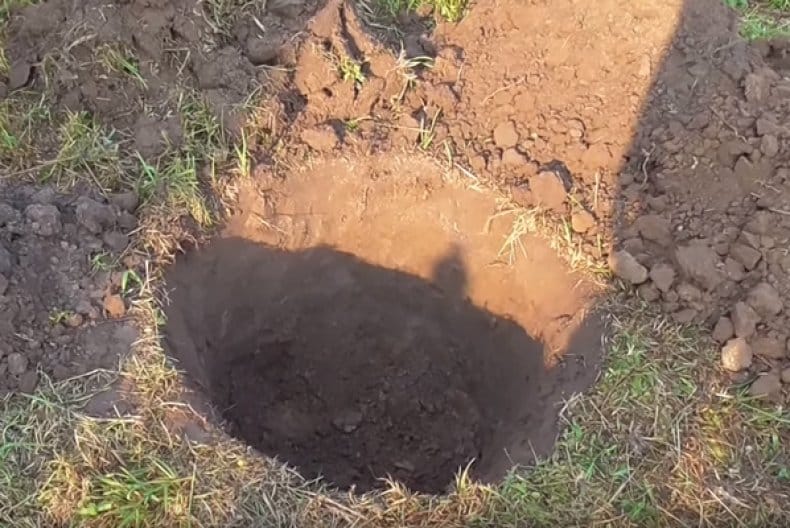
Pit preparation
Before planting a seedling, remove the top layer of soil 40 cm thick, after which they dig a hole 0.8-1 m deep and about 0.8 m wide. A nutritious soil mixture consisting of humus, sand, superphosphate, potassium sulfate, and any organic matter is added to it. Dolomite flour is poured into the prepared hole in a ratio of 0.3 kg per 10 liters of water, and then another 2 buckets of clean water are poured.
Distance between seedlings
Muscovite is considered to be of medium height, therefore the distance between seedlings is left at least 3-3.5 meters. The same amount must be retreated to the nearest fruit bushes or trees.
Landing technology
A wooden peg is driven into the prepared hole, which rises 0.5 m above the surface. At the bottom of the hole, a mound is formed from a nutrient soil mixture, placing the root of the seedling on it. The root neck of the pear should rise 5 cm above the ground surface. Gradually, the hole is filled with earth, compacting it a little and preventing the formation of voids. 3 buckets of water are poured under each seedling, the soil around the pear is mulched, and the tree itself is tied to a peg.
Tree care rules
In order for a planted plant to grow and develop normally, it must be properly cared for.
Watering and fertilizing
After planting, the Moskvichka pear requires watering once a week. 1 bucket of water is poured under 1 tree in the morning and evening hours.An adult plant during fruit formation requires irrigation up to 2 times a week. Water the pear before buds open, 2 weeks after flowering ends and 2 weeks before fruit formation begins. If the autumn is dry, then irrigation is carried out after harvesting.
In the spring, ammonium nitrate is applied to the tree trunk circle, and in the fall, superphosphate, compost, humus, and potassium sulfate are applied.
Trimmings
Pears require pruning throughout the growing season. As a rule, work is carried out before the buds begin to bloom.
Shaping the crown of the Moskvichka pear
When pruning, it is imperative to maintain the position of the central shoot. Only skeletal branches are left, all others must be removed. The length of the main trunk is shortened by a quarter of the original.
Regulatory trimming
In the second year after formative pruning, the main trunk is shortened by another 25 cm. The length of skeletal shoots is removed by 5 cm. Work can be carried out in autumn and spring.
Maintenance pruning
Supportive pear pruning Muscovite involves removing all growing new shoots that contribute to thickening of the crown. Only a few fruiting shoots should remain on each skeletal shoot. Cut off all branches growing in a strictly vertical position.
Sanitary pruning
Sanitary pruning of pears is carried out both in autumn and spring. It involves removing all dry, damaged, diseased and broken branches.
The shoots growing inside the tree are also pruned.
Rules for pruning
You should not remove too many branches at one time, as the pear may not tolerate such stress. This is especially true for anti-aging trimmings.All cutting areas must be treated with garden varnish.
Diseases and pests of Moskvich pear
Muscovite has increased resistance to major diseases and pests, but preventive measures will not hurt it.
Prevention measures
As a preventative measure pear diseases and pests Muscovites ration watering, do timely pruning, and treat the tree with preparations specially designed for this purpose.
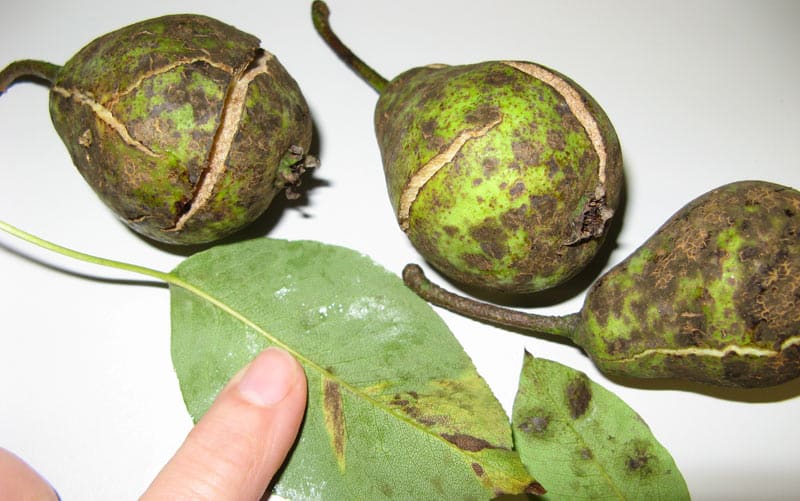
Possible diseases
Muscovite has good immunity to fungal diseases, but some infections still carry a certain risk of damage.
Scab
To prevent scab, the pear is sprayed several times with Bordeaux mixture, iron or copper sulfate. Leaves and weeds must be removed under trees in a timely manner.
Sooty fungus
Another pear pest that can cause trouble. To prevent its appearance, Moskvichka is sprayed with colloidal sulfur and copper sulfate. In especially severe cases, they resort to the use of drugs “Skor”, “Azofos”, “Delan”.
Probable pests
Pears can also become a treat for some pests. If measures are not taken in time, you may be left without a harvest.
Aphid
The drugs “Kinmiks”, “Iskra”, “Agravertin” help to resist aphids. Folk remedies are also effective: chamomile decoction and green soap.
Pear moth
To prevent the codling moth from spoiling the fruit, treat the pear with Karbofos or Cyanox. Folk remedies include infusions of tobacco dust and dandelion.
Pear flower beetle
They fight against this pest by treating Muscovites with colloidal sulfur. Also used against the pear flower beetle is an infusion of yarrow, chamomile, and tobacco dust.
Collection, storage and use of crops
Moskvichka pears are harvested in September. They have a universal purpose, are suitable for transportation over long distances, have good commercial qualities and shelf life. This makes it possible to grow Moskvichka for commercial purposes.
For long-term fresh storage, the collected pears are sorted, placed in wooden boxes, layered with newspaper, and sent to a cool, dark place.