The Marble variety pear can be found quite often in gardens in the middle zone, but with proper care, growing the crop will not be difficult in any region. The fruits are large in size, the pulp tastes sweet, with a high juice content. The variety is characterized by high productivity and good resistance to many unfavorable factors. Maintenance is simple and does not require much investment of time and effort.
- Description and characteristics of Marble pear
- Pros and cons of the variety
- Landing Features
- How to check the quality of a seedling?
- Choosing a place and time of landing
- Sequence of actions when landing
- How to properly care for a plant?
- How to water?
- When and with what to fertilize?
- How to whitewash?
- When and how to prune correctly?
- Crown formation
- Regulatory trimming
- Maintenance pruning
- Sanitary pruning
- Rules for trimming
- Preparing pears for winter
- Diseases and pests
- Typical diseases of the variety and methods of combating them
- Sooty fungus
- Moniliosis
- Scab
- Harmful insects and methods for their elimination
- Pear flower beetle
- Pear moth
- Aphid
- Harvest and storage
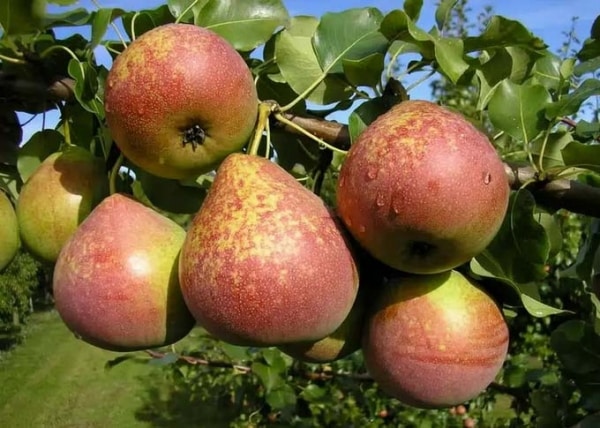
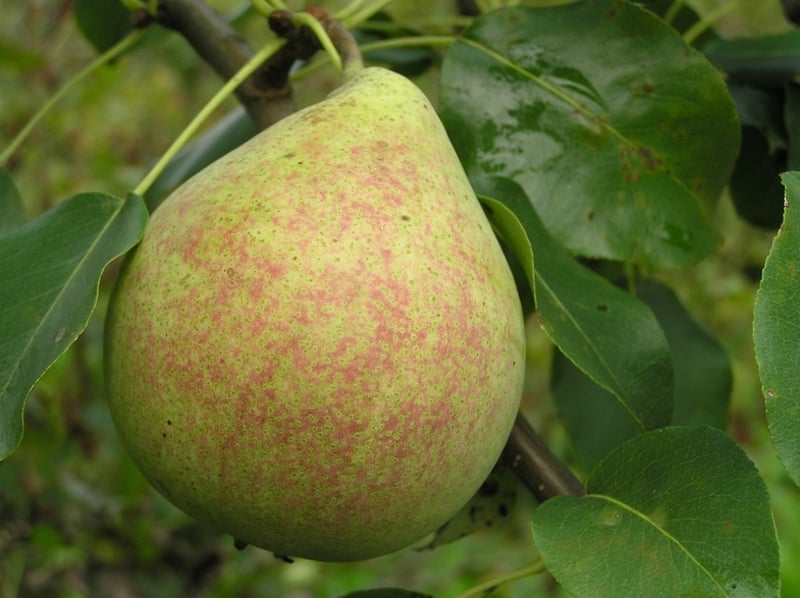
Description and characteristics of Marble pear
Marbled pear was developed in Russia. It is based on two varieties of pear: Bere Winter and Forest Beauty. The characteristics of the resulting culture have a large list of advantages.
The description indicates the following distinctive features of the pear:
- the height of the tree reaches 4 meters, a powerful crown of a pyramidal shape;
- leaves are dark green, large, slightly carved edges;
- The flowering period begins in early spring, the flowers are small and white;
- Fruit ripening begins in late summer;
- the dense skin of ripe fruits is yellow-greenish with dark yellow splashes, the flesh is cream-colored;
- grains are large;
- a young tree begins to bear fruit after 6 years;
- the pear becomes a pollinator for many other pear varieties;
- refers to self-pollinating crops, but the process is difficult.
The pulp of the fruit contains a large amount of fructose, so the product is approved for use by patients with diabetes.
Pros and cons of the variety
The advantages of the Marble pear variety include a number of advantages:
- large fruits, weighing up to 180 g;
- high yield;
- The shelf life of collected fruits reaches two months;
- fruits tolerate transportation well;
- high resistance to infections and pests;
- The tree can withstand frosts down to -26 degrees.
The disadvantage of pears is considered to be poor tolerance to drought, so gardeners need to establish the correct watering regime. Young seedlings do not tolerate low temperatures well.
Landing Features
Marble pear does not make any special demands on the soil; it begins to bear fruit anywhere. But to obtain a high and high-quality harvest, you should try to create the most comfortable conditions for the crop.
How to check the quality of a seedling?
Particular attention should be paid to the quality of pear seedlings:
- For planting, it is better to choose two-year-old pears with 4 side branches.
- There should be 4-5 strong roots, up to 32 cm long.
- It is desirable to have an earthen clod along with roots.
- There should be no signs of cracking on the surface of the bark.
Choosing a place and time of landing
You can start planting pears in the spring or autumn months:
- Spring work begins only after stable warm weather has established, when the risk of return of frost has passed, approximately from May 1 to May 5.
- In the fall, you need to plant a pear before the onset of cold weather, since the root system needs time to adapt, in the first half of October.
The place for planting the pear must meet the following requirements:
- good lighting;
- protection from draft winds;
- fertile, loose soil with good aeration without stagnant moisture.
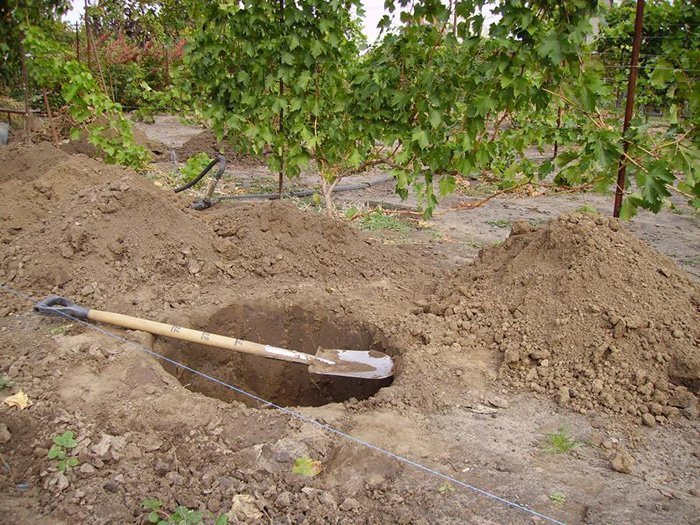
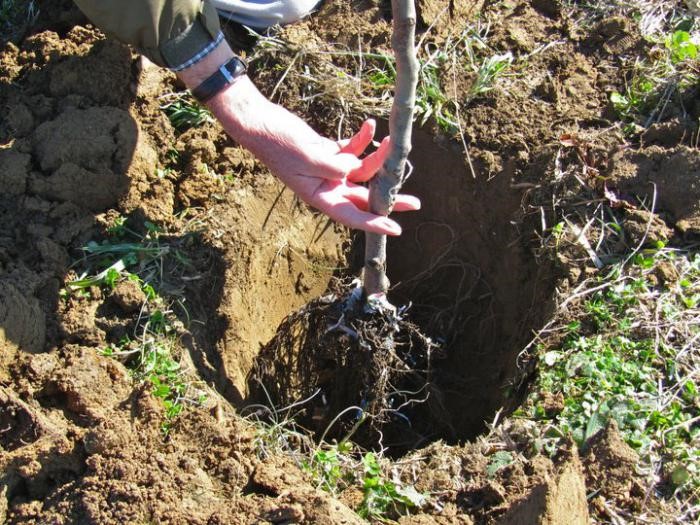
Sequence of actions when landing
Recommendations to help you plant pear seedlings correctly:
- 12 days before planting the seedling, dig a hole 75 cm deep.
- The soil dug out of the hole is mixed with fertilizers.
- If the soil is heavy, then crushed stone is poured into the bottom of the hole.
- A pole is installed in the center of the pit, which will serve as a support for the trunk.
- Place the seedling and bury it with earth. The root collar of the seedling should protrude 6 cm above ground level.
- The trunk is tied to a support, the soil is lightly compacted and a groove is made for irrigation.
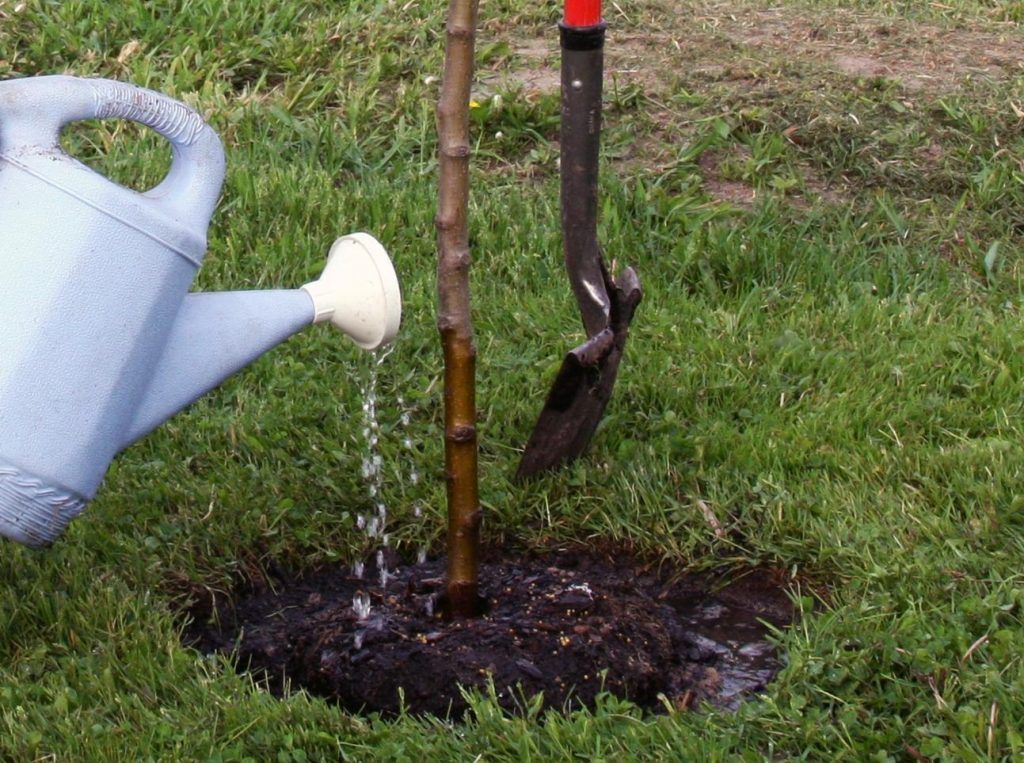
Immediately after planting, the pear is watered with settled water. Up to 25 liters of water are consumed per root. Then the soil is mulched. Straw, sawdust, and dry leaves are chosen as mulch.
How to properly care for a plant?
Caring for the Marble pear variety is simple. It is necessary to water the soil on time, add nutrients, prune, and treat against infections and pests.
How to water?
The variety needs frequent watering. When there is a lack of moisture, unripe fruits and leaves begin to fall off. As a result, productivity decreases. The first month after planting, you need to water the pear once every 7 days.
In the future, the pear needs additional watering in spring and autumn, especially if the weather is dry.
The ideal method of watering is sprinkling. If it is not possible to carry out this type of watering, then dig a ditch 15 cm deep around the tree. The ground must be periodically loosened and weeded from weeds.
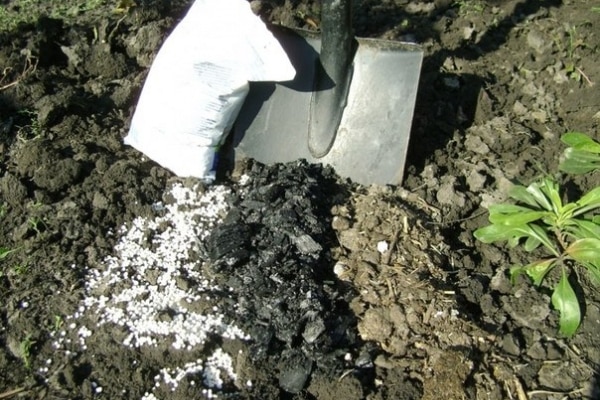
When and with what to fertilize?
During different growing seasons, pears need fertilizer. It is important to correctly calculate the dosage, since not only a deficiency, but also an excess of nutritional components can lead to poor development of the crop:
- During the flowering period, nitrogen fertilizers are applied to pear trees.
- Two weeks after flowering, the tree is treated with a urea solution.
- In June, urea is added.
- In July, feed the soil with potassium sulfate.
- In the autumn, when fruiting ends, it is advisable to add organic matter. Manure, compost or bird droppings are suitable.
As the pear grows, the need for additional fertilizer may arise:
- If the leaves develop poorly, and the lower leaves even fall off, a lack of phosphorus is detected.
- If spots appear on the leaves, calcium deficiency cannot be ruled out.
- With a lack of potassium, the leaves turn brown and fall off.
- When fruits do not ripen well, too much nitrogen may be applied.
- Small leaves with a pale color due to lack of nitrogen.
The first five years after planting pear feeding You can’t apply it to the very root. It is better to distribute nutritional components around the perimeter of the tree trunk zone.
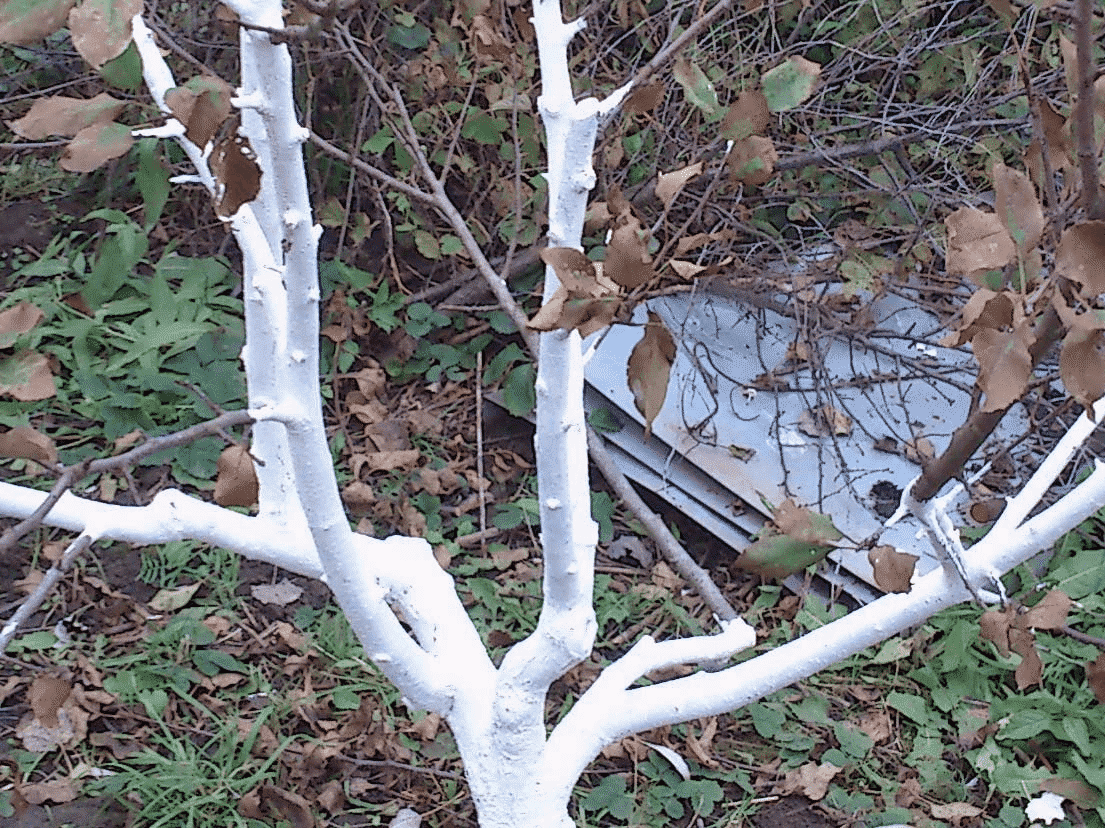
How to whitewash?
To prevent the tree bark from being damaged by exposure to sunlight, the trunk is whitewashed in the spring. The solution can be purchased at the store or made independently. Clay and lime are mixed in water.
If you add copper sulfate to the solution, this whitewash will protect not only from the sun, but also from pests and diseases.
Whitewashing begins to be applied from the lower branches of the pear to the very bottom of the trunk. All branches of a young seedling are additionally whitened.
When and how to prune correctly?
Pruning promotes the formation of young buds. As a result, the yield and quality of the fruit increases. Every season there is a different type pear trimmings.
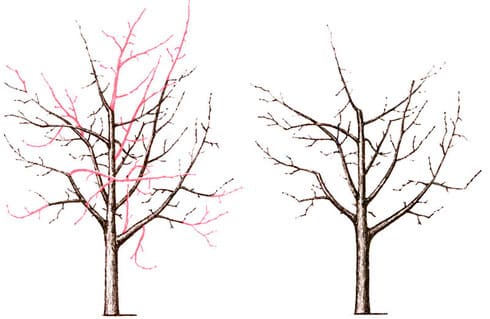
Crown formation
In most cases, the crown of the Marble pear is formed in the form of a bowl. With this method, all parts of the plant receive enough air and light. The procedure is carried out in early spring, before sap flow begins:
- A year after planting, the main branches of the tree begin to be identified. There can be 3 or 4 of them. Take into account that the distance between the branches should be 18 cm. Selected branches are shortened by 25%.
- The remaining branches are removed completely, leaving no stumps on the trunk.
- Two years later, on each remaining branch, two more shoots are identified, which are shortened by half. The distance between the branches is 55 cm.
- All other branches are completely cut out.
- In subsequent years, selected branches are pruned, maintaining a constant length.
The work is carried out with clean, disinfected garden tools to prevent infection.
Regulatory trimming
This type of pruning is in most cases carried out in early spring. The need for it arises only in case of excessive crown density. During the work, branches that grow inside the tree crown are removed.
Maintenance pruning
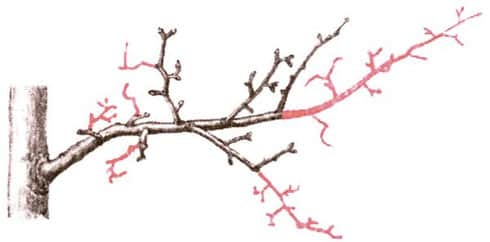
In the summer months, when active growth of young shoots is observed, this pruning method is carried out. The Marble pear variety is not prone to forming a large number of shoots, so the branching of young branches is increased by chasing. The procedure involves cutting young branches to 11 cm.
Sanitary pruning
In the fall, during the preparation of pears for winter, sanitary pruning is carried out. Remove dry and damaged branches. Sometimes the procedure is required in early spring.
Rules for trimming
Pear pruning is carried out following some rules:
- the work is carried out with sharply sharpened garden tools;
- instruments are disinfected;
- during pruning, do not leave stumps so as not to provoke the spread of infection;
- Large cuts are covered with garden varnish.
If you follow simple rules, you will be able to increase the yield and improve the development of the crop.
Preparing pears for winter
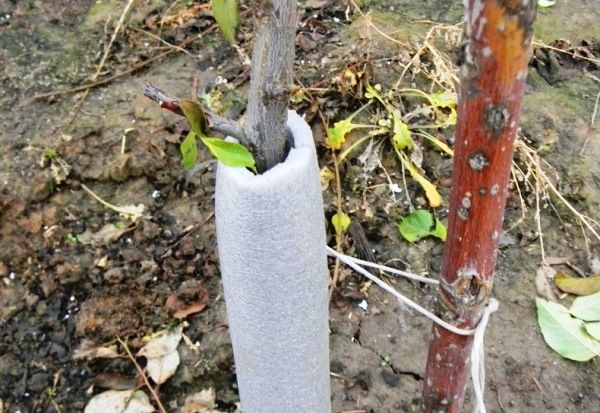
An adult tree can withstand frosts down to -26 degrees. Young seedlings are damaged at temperatures of -9 degrees. Therefore, every autumn they carry out insulation with various covering materials.
They begin preparing for the winter cold as early as September. The tree trunk soil is dug up, watered with warm water and covered with a thick layer of horse manure, tree bark or humus. In winter, a large snowdrift is thrown onto the trunk.
Some gardeners wrap the trunk with warm, breathable material. Pine and reed branches are suitable. You can use newspaper, corrugated cardboard, or cotton fabric.
Diseases and pests
The Marble pear variety is characterized by high immunity and good resistance to pests. But it doesn’t hurt to know about the first signs of a problem in order to take control measures in time.
Typical diseases of the variety and methods of combating them
Most often, pears are affected by fungal infections. They are usually controlled with fungicides.
Sooty fungus
A black coating in the form of soot becomes noticeable on the leaves and branches. The carriers of infection are insects: aphids, whiteflies. The disease is provoked by a lack of lighting and air, and a dense crown. All affected branches and leaves should be removed from the tree, then the crown should be treated with Fitoverm. In advanced cases, chemical preparations are used: “Skor”, “Chorus”.
Moniliosis
The fungus affects any part of the plant. Flowers, leaves, fruits, young shoots first wither and dry out, and then turn black and fall off. The affected parts of the pear must be cut out, including the adjacent healthy area, and burned.
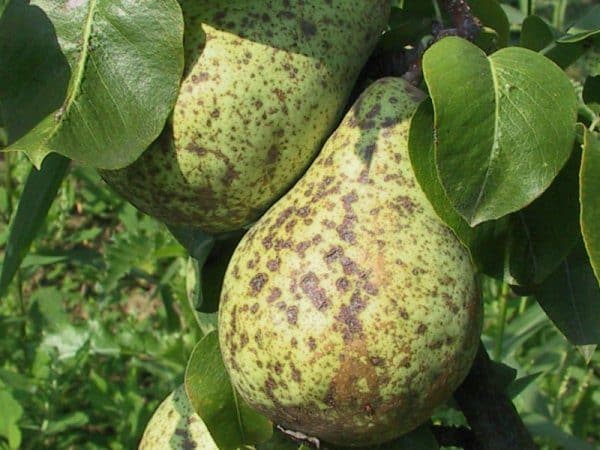
Scab
Dark burgundy spots appear on the inside of the leaves. The fruits begin to rot and cracks form on the skin. Rainy weather provokes the spread of fungus. Trees are treated with fungicides: “Poliram”, “Horus”, “Merpan”. Among folk recipes, compositions based on mustard, salt, potassium permanganate, and horsetail infusion are effective.
Harmful insects and methods for their elimination
Sometimes the pear tree is attacked by pests. They are combated with insecticides (Decis, Iskra, Diazonin).
Pear flower beetle
The pest becomes active in the spring; it eats buds, flowers, and young leaves. In May, the beetle returns to the soil and lays eggs. The eggs hatch into larvae that eat the roots. The beetle overwinters in the soil, around a tree trunk.
Pear moth
A small gray butterfly lays eggs in the soil. The eggs hatch into caterpillars that feed on the fruits. The caterpillars climb up the trunk and penetrate into the fruit. You can escape from the pest by whitewashing the trunk.
Aphid
Ants spread aphids. Installing trapping belts and luring ladybugs that feed on aphids to the area will help prevent the appearance of pests.
Harvest and storage
Full ripening of pears occurs in mid-October, but harvesting begins in September. Harvesting should be done in the morning, in dry, clear weather. The allods are torn off along with the stalk.
Only fruits that are dense and without signs of damage or cracking are selected for storage. Selected pears are placed in cardboard boxes, wooden boxes or wicker baskets. Fruits should be stored in a cool, dry place with good ventilation. The air temperature should be between 0 and +2 degrees.