Since ancient times, the pear has been revered as one of the best plants in the garden, along with the apple tree. According to the description, these 2 crops are similar, but growing and caring for a pear differs from the agricultural technology of an apple tree. Pear is more thermophilic and does not tolerate low temperatures. But many plant varieties are parthenocarpic species, setting fruit without fertilization.
- Popular pear varieties
- Pear propagation
- Seminal
- Pear grafting
- Cuttings
- By layering
- Features of growing pears
- The importance of lighting
- Soil requirements
- How to plant a tree correctly
- Landing dates
- Selection and preparation of seedlings
- Choosing a landing site
- Preparing the planting hole
- Distance between seedlings
- Planting scheme
- Care after landing
- Watering
- Fertilizer application
- Trimming
- Protecting pears from pests and diseases
- Preventive actions
- Types of pear diseases and protective measures
- Using biological products to protect pears from pests
- Harvest and storage
- Is it possible to plant one pear on a plot?
Popular pear varieties
Choice for gardeners pear varieties depends on the purpose for which the fruit tree is grown and in what region. For fresh fruit consumption, early ripening pears are needed. Summer varieties ripen in July-August, among them it is preferable to plant:
- Limonka;
- Skorospelka;
- Rogneda;
- Duchess;
- Lada.
These types of crops have tasty fruits, sweet and juicy, but they are stored for no more than 1-2 weeks. Among the autumn varieties that ripen from August to October, the best are Otradnenskaya, Bere Moskovskaya, and Pamyati Yakovlev. In the pulp of the fruit, sweetness is combined with slight sourness. But fresh pears can be stored for up to 1.5 months. They are suitable for preparing preparations for the winter.
Winter varieties are given attention to those that try to preserve the harvest until next spring, feeding on a vitamin product all winter. 1-2 trees of late ripening varieties Conference, Saratovka, Curé are enough to provide yourself with fresh fruits for the whole winter.
Pear propagation
Methods of propagation of fruit crops can be either vegetative, seed or grafting. Their use depends on what they want to get as a result: a new plant with a set of positive qualities or to preserve the varietal characteristics of the old one.
Seminal
Pear for rootstock It grows better from seeds when frost-resistant varieties are chosen for propagation. Seeds taken from early plant species can be immediately placed in open ground. Winter ones can only appear through sowing seedlings.The seeds will finally be ready for planting in late autumn - early winter. They are soaked in warm water for 3 days, then mixed with wet sand and placed in a plastic bag. The material is stored at a temperature not lower than +5 degrees. As soon as the seedlings appear, reduce the storage temperature to 0 degrees. They try to preserve the sprouts in this form until spring.
Material is planted in the ground so that the sprouts reach a stem thickness of 1 centimeter. Then they are used for vaccination.
Pear grafting
You can graft a pear onto an apple, quince, or hawthorn tree. The operation requires certain skills. But even a novice gardener can master regular grafting. In this case, it is necessary that the scion and rootstock have the same thickness of cuttings. They should have at least 3-4 buds. Having made identical cuts on the scion and rootstock, they are connected so that their cadmium matches. All that remains is to tie a sponge around the joint and coat it with garden varnish on top. A regular adhesive plaster is suitable for fastening.
The butt is grafted when the thickness of the rootstock is 1.5-2.5 centimeters. The rootstock cut with bark and part of the wood must have a cut width equal to the thickness of the scion. Both cuttings are connected and tied. If the cuttings take root, then 2-3 shoots appear on them. The top one is saved, and the bottom one is pinched, leaving 2-3 leaves. They also use such methods of grafting as in the butt, by the bark, or by the kidney.
Cuttings
The preparation of material for reproduction begins in winter. Having broken off a young two-year-old branch without damaging the bark, leave it until April. Do not forget to tie a stick at the site of the break and wrap it with adhesive tape. In the spring, all devices are removed and the cuttings are cut off. Having placed the branches in water, wait for the bump to appear at the end of the cutting.In this case, the roots should reach 6 centimeters in length. Plant the rooted material into the ground.
By layering
A box with moist soil is placed under the lower shoot on the tree. At the junction with the ground, cuts are made on the branch and sprinkled with compost. Always ensure that the layering has enough moisture. For the winter they are covered with spruce branches. For the cuttings to take root, you must wait 2 years. Then they just transplant the shoot to a permanent place.
Features of growing pears
The choice of site in the garden for pears determines the growth, fruiting and durability of fruit plants. The basis for the longevity of a pear is laid at a young age of the tree, when the skeleton of the underground and above-ground parts of the plant is being formed.
The importance of lighting
The fruit crop bears fruit better in sunlit areas. Light is needed so that fruits contain more sugar. Trees located in the shade often suffer from scab and other infections. But not all varieties can tolerate extreme heat, so the best slopes will be northern, northeastern, northwestern and western.
To prevent flowers from being damaged by frost, you need to choose a site in a depression. It should be level or have a slight slope.
Soil requirements
The soil suitable for the plant is chernozem, slightly podzolized. But on sandy, heavy clay soils the culture develops worse. Swampy, rocky and saline soils will be unsuitable for pears. Before planting trees, check the depth of groundwater. They should be at a depth of 2 meters to the surface of the earth.
How to plant a tree correctly
To grow a pear, you need to pay special attention to planting the crop in the garden. The time of planting, the quality of planting material, and the condition of the soil on the site will also be important.
Landing dates
Both spring and autumn are suitable for the procedure. In April, as soon as the snow melts, you can plant pears in holes prepared in autumn. It is important that sap flow does not begin at this time and the buds do not prepare to bloom. Autumn planting will be successful until October 10 in areas with an early onset of winter. If the seedlings are acquired later, they are buried in a ditch half a meter deep. Covers roots especially well. Protect seedlings from frost and damage by rodents by covering them with brushwood or non-woven material. They are planted in the spring.
You can plant a pear in the summer, but with a closed root system, when the soil is preserved on the roots. The pear is in a container and spills well. They choose days for planting in July when it is cloudy and not hot.
Selection and preparation of seedlings
Suitable for growing are seedlings that must have moist, undamaged roots and an elastic trunk without flaws. Annual shoots may have 1-2 lateral shoots up to 12 centimeters long. You need to choose two-year-old seedlings with branches up to 30 centimeters and roots of the same length. Before planting, slightly dried roots are dipped into water. You can soak the roots in a solution of honey, mullein infusion. Rotten and damaged roots need to be trimmed.
If you need to replant a plant from a container, be sure to moisten the soil well. Carefully pull the shoot out of the pot, taking care not to damage the lump of earth on the roots.
Choosing a landing site
In addition to good lighting and levelness of the area for pears, it is necessary to allocate enough space for the tree. The accumulation of groundwater and shading of the plant will cause it to develop and bear fruit poorly.
The culture loves nutritious, loose, permeable soil with neutral acidity.
Preparing the planting hole
They dig holes for seedlings in advance, 2-3 weeks in advance, in the fall during spring planting. The top fertile layer is folded in one direction, and the bottom in the other. It is then scattered between the rows without being used for planting. The bottom is loosened, and then a place is determined for driving a planting stake. The optimal pit dimensions will be 50-70 centimeters deep and 75-100 wide.
Immediately before planting pears in open ground, mix 2-3 buckets of humus, 200-300 grams of mineral fertilizers with a nutrient layer and fill the hole to 3 quarters. On acidic soils, you need to add 200 grams of slaked lime. Then a bucket of humus is filled in to prepare a mound for planting.
Distance between seedlings
It is necessary to divide the area for pears taking into account how much space to leave between the trees. It is better to plant in rows with a distance of 4 to 5 meters; seedlings are also separated from each other. After all, the young garden will grow, and the trees will need plenty of light, nutrition and moisture.
Planting scheme
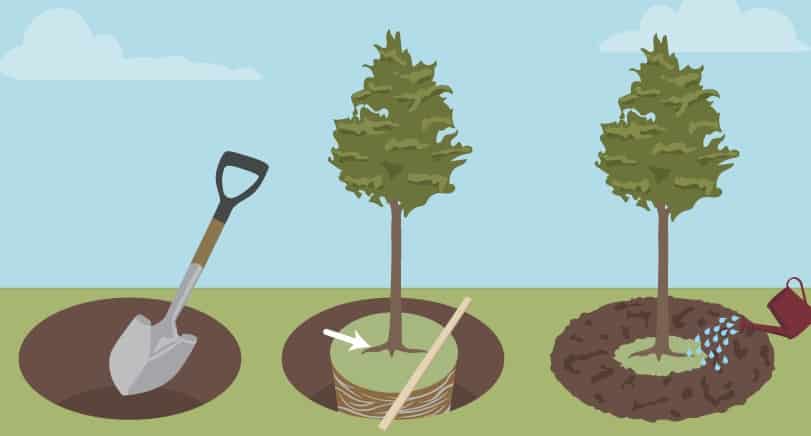
According to the step-by-step instructions, planting begins by placing the seedling in a hole, determining the position of the root collar. The plant should be planted so that the neck is 1-2 centimeters above the surface of the loose soil. In dense soil - at surface level. After this, they begin to fill the hole with earth, spreading the roots of the tree along the mound at the bottom. When planting, the seedling is constantly shaken so that the clods of earth are distributed between the roots.
Then, around the tree, the soil is crushed by moving the sole from the edge of the hole to the tree trunk. You need to make a roller around the seedling to mark the boundaries of the hole. Moisten the soil with water from a watering can, distributing the moisture evenly. One pit requires up to 3-5 buckets of water. Fruit crops should be planted on a cloudy day or evening.
Care after landing
To create a strong and powerful tree skeleton, you need to properly care for the fruit crop. This includes not only the usual activities - watering, fertilizing, but also the formation of the tree crown, protection from pests and diseases. The rules of pear farming are simple, but they must be followed regularly.
Watering
Pears need moisture especially during dry periods. Starting from planting, water no more than 2-3 times per season. During the fruiting period, the need for hydration increases. In order not to water the pears often, a layer of mulch is placed in the circle around the trunk.
The soil around the tree is kept in this condition constantly during dry periods, and for 1 year during wet seasons. It is better to lay mulch over the snow to retain moisture. In the fall, after digging up the tree trunk, the plants are fertilized. Do not dig deeply to avoid damaging the roots. The mulch should not lie close to the tree trunk.
Fertilizer application
In addition to basic fertilizers, proper care also includes fertilizing with mullein diluted with water in a ratio of 1:5, or bird droppings - 1:12. It is useful to first dilute organic fertilizers with water at a concentration of 1:3, keep them in a barrel for 3-5 days, and then bring them to the desired proportion and water the fruit trees.
The first time fertilizing is done in May, when the buds open, and then after flowering. Furrows are made under the tree into which mineral fertilizers are applied. They can be replaced with wood ash, 50 grams per bucket of water. For 2-3 linear meters of furrow you will need 1 bucket of nutrient solution.
Trimming
To obtain rich harvests, sanitary, formative pruning of the tree crown is carried out annually.In the spring, the shoots located on the trunk 40 centimeters from the ground are pruned. 1 peephole is left at the border, and 2 above, with a distance of 25 centimeters between them. First-order branches are also trimmed regularly by 20-30 centimeters. Every year the degree of pruning must be reduced. When the growth is at the level of 25-30 centimeters, do not shorten the branches.
Guidelines for crown formation should take into account the age of the tree. In 4-5 year old crops that are beginning to bear fruit, annual shoots are not shortened. Otherwise, you may lose fruit. All that remains is the work of thinning the crown. To do this, remove those branches that go inside the crown, cross, and hang down. By removing part of the wood from two-year-old shoots, a stronger growth of the tree is caused.
Protecting pears from pests and diseases
In the care of fruit crops, protection from diseases and pests occupies one of the main places. Although varieties of pears have been bred that are not afraid of infections, it is necessary to be able to carry out preventive measures to protect plants from the effects of pathogenic microorganisms.
Preventive actions
To prevent the development of diseases in pears, you must:
- Apply fertilizers, water, and trim trees on time.
- Regularly weed and loosen the tree trunk circle.
- After harvesting, remove fallen fruits, leaves, pruned branches, burning them.
- Whiten tree trunks to protect against sunburn in winter and spring.
- Spray with a 3% solution of copper sulfate before buds open and after leaf fall.
The likelihood of fruit crop diseases and pest damage is reduced when the plant is properly cared for.
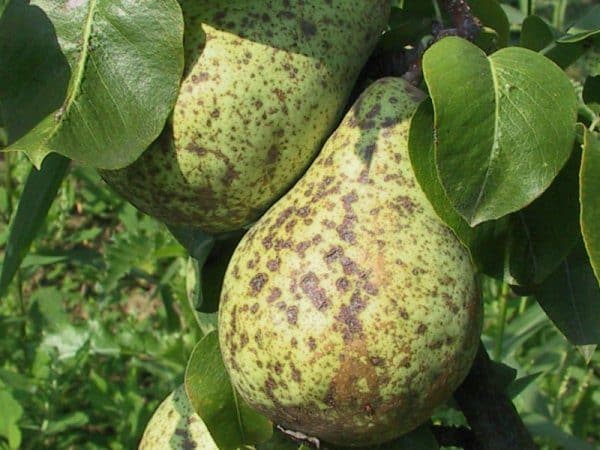
Types of pear diseases and protective measures
Pear trees require protection from:
- scab;
- moniliosis;
- septoria;
- Cytosporosis.
These fungal infections affect the stems, fruits, and leaves of the plant. They must be controlled with fungicidal drugs. In this case, parts of the tree affected by the disease are cut off and burned. Worse than pathogenic fungi is bacterial cancer, which can completely destroy a pear plantation. Cutting out areas of the tree damaged by cancer, treat them with fungicides and fill them with garden varnish.
Using biological products to protect pears from pests
To combat fruit crop pests - aphids, spider mites, codling moths, you can use biological products. Throughout May, trees are sprayed with tobacco infusion. For 5 liters of water take 1 kilogram of shag waste or tobacco dust. Let it sit for a day, then put it on the fire and boil for an hour. After filtering, the settled solution must be diluted. You need 0.5 liters per bucket of water. Add another 100 grams of laundry soap and process the pears.
In good, calm weather, treatment with Fitosporin M, Novosil, and green soap is effective.
Harvest and storage
Pears are harvested when they reach technical maturity. It depends on the period of fruit ripening. Trees often do not begin to produce pear crops immediately after planting. You need to know what year the variety bears fruit in order to expect a harvest. Winter crop varieties are stored for storage. The fruits are sorted, removing rotten and damaged ones. They can be used for harvesting. The remaining fruits are placed in boxes, which are placed in basements and cellars, where the air temperature will be within +1...-2 degrees. Every year, pear fruiting will decrease.
Therefore, it is necessary to choose for planting those crops that are known for how many years they will produce rich harvests and what is the duration of their life.
Is it possible to plant one pear on a plot?
In a small dacha you can’t plant many pears, but you definitely need two. If the varieties are not self-pollinating, then one pear will not produce a harvest. She needs pollinators nearby. Parthenocarpic species are found among the culture. This is Bere Zimnaya, In Memory of Yakovlev, Chizhovskaya. Such a tree alone will produce good harvests of tasty pears. Most varieties need trees nearby that will help the fruits appear.