A microscopic gram-negative bacterium, having arrived in Europe along with seedlings of fruit crops or flowers, began to quickly spread throughout the environment, moving with the help of flagella. Erwinia does not form spores; entire colonies appear when it divides. The pathogen multiplies rapidly during warm and humid weather, which accelerates the onset of fire blight on pears and many fruit crops. Gardeners do not immediately notice the problem, and often it is no longer possible to save the tree.
- What is fire blight?
- Reasons for appearance
- Factors influencing the rate of spread of bacteria
- The first signs of illness
- Ways to combat fire blight
- Chemical method
- Radical method
- Use of antibiotics
- "Fitolavin"
- "Tetracycline"
- "Gentamicin"
- "Streptomycin"
- About folk and alternative methods
- Resistant varieties
- Preventive actions
- Competent selection of seedlings
- Pest Control
- Disinfection of garden tools
What is fire blight?
Erwinia, having made its way into the bark, heads to the cambium, where it begins to divide. During winter frosts, most bacteria die. In spring, along with the sap, surviving microbes appear on the surface of the shoots in the form of a white liquid. The exudate contains rods, which, with the help of insects, settle on the pistils of flowers and again infect the tree. In wet and dry weather, the bacteria multiplies every 20 or 30 minutes. Microorganisms are sent to the vessels, where they produce toxins that help reduce the plant’s immunity. Erwinia penetrates the flowers and ovaries, which leads to their death. Bacteriosis is the most dangerous for seedlings.
Reasons for appearance
The exudate, stretched into long threads, is transferred to other trees when pollinated by insects, wind, birds and enters cadmium through wounds and cracks. In humid and warm weather, bacteria are activated and, developing inside the flower, infect the branches and then the trunk.
Sometimes microbes fall on shoots or leaves along with splashes of water, and hide in a trunk for the winter; in the spring they appear on the shoots in the form of a milky liquid and begin to divide.
Factors influencing the rate of spread of bacteria
The presence of Erwinia during primary infection of a pear is difficult to recognize. And even when the disease moves to the next stage, it is very difficult to determine that it is a bacterial burn.
The rate at which anaerobic microorganisms attack a tree is affected by:
- type of soil in the garden;
- climate and weather;
- pear varietal characteristics;
- age of culture.
The disease begins at the top of the tree, causing gardeners to discover the problem when most of the shoots and trunk are infected. When the leaves wilt, people begin to water the tree much more often than before. Excess moisture promotes the growth of bacteria and the spread of disease.
The first signs of illness
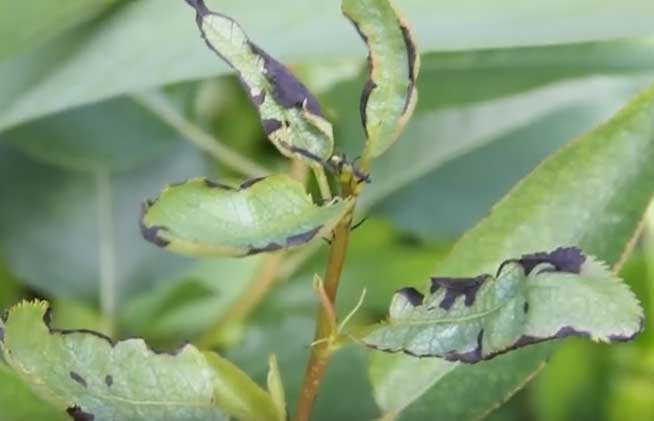
When infected with Erwinia in the spring, the buds on the pear do not open for a long time and gradually turn black, but do not fall off the branches. On an infected tree:
- Flowers wither and dry up.
- Leaves curl.
- The bark becomes covered with stains.
As the bacterial burn progresses, a viscous white liquid begins to leak from cracks and wounds. Once the wood peels off, the pear can no longer be saved. She looks like she's been on fire.
Ways to combat fire blight
To identify the causative agent of the disease and begin treatment, the tips of the branches and bark of the withering tree are taken to a special laboratory, where bacteriological seeding begins. To cope with an infection caused by Erwinia, not one, but several methods of eliminating it are used, each of which has its own advantages, but is not without its disadvantages.
Before using any of the methods, remove infected shoots by lubricating the cut area with copper sulfate. If the damage is extensive, the tree is dug up and burned.
Chemical method
If signs of bacterial burn are detected, when it appears, the pears are treated with fungicides that contain copper - “Oxychom”, “Skor”, “Rovral” or sprayed with vitriol, adding a 1% solution of the drug to milk made from quicklime .
The procedure begins:
- Before the buds swell.
- When leaves appear.
- After flowering.
- During the formation of the ovary.
The last processing is carried out in the fall, after collecting all the fruits. It is not always possible to cure a pear tree using this method, since Erwinia quickly gets used to the drugs.
Radical method
If fire blight is discovered on one plant, it is destroyed to preserve the garden. When only branches or 1/3 of the tree are infected, the infected shoots are removed, capturing up to 40 cm of healthy tissue. The sections are treated with copper sulfate, stirring half a glass of the substance in a bucket of water. Suitable for this purpose ferrous sulfate, 70 g of product is enough for 10 liters.
Infected parts of the pear are burned and cannot be stored or used as firewood. After the procedure, instruments are disinfected in potassium permanganate or dichloramine.
Use of antibiotics
Very often, treatment with fungicides in the fight against a disease caused by an anaerobic microorganism turns out to be ineffective, and it is necessary to use antibacterial drugs that are sprayed on the entire tree, not missing healthy areas.
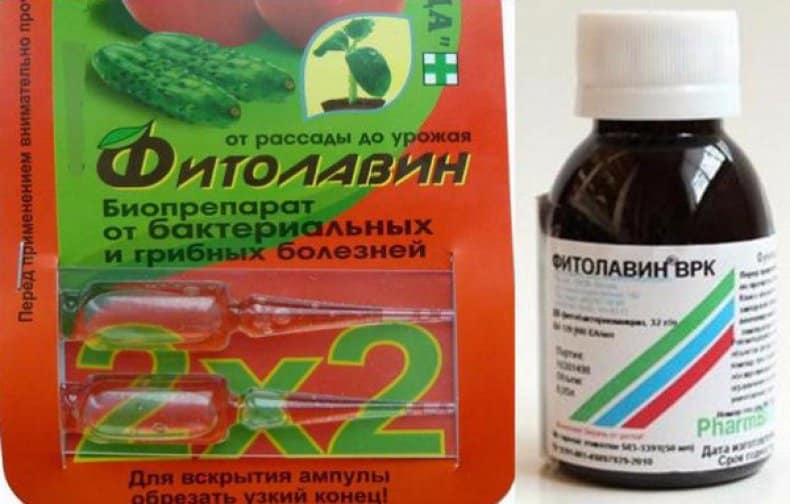
"Fitolavin"
This product is a waste product of actinomycetes and combines the functions of a biological fungicide with the action of an antibacterial drug. Penetrating into the tissues of the tree, “Fitolavin” spreads through their vessels, but does not accumulate in the ground, and helps strengthen the root system of the pear. After treating the plant with the drug, beneficial microorganisms also die.
To prepare the solution, add 20 ml of “Fitolavina” to a bucket of settled water, spray the leaves with the composition, and water the tree trunk. The product quickly loses its properties; pears must be treated within 2–3 hours.
"Tetracycline"
When the first signs of bacterial burn infection appear, a tablet of this antibiotic containing 100 g of the active ingredient is mixed with water.Spray the tree once.
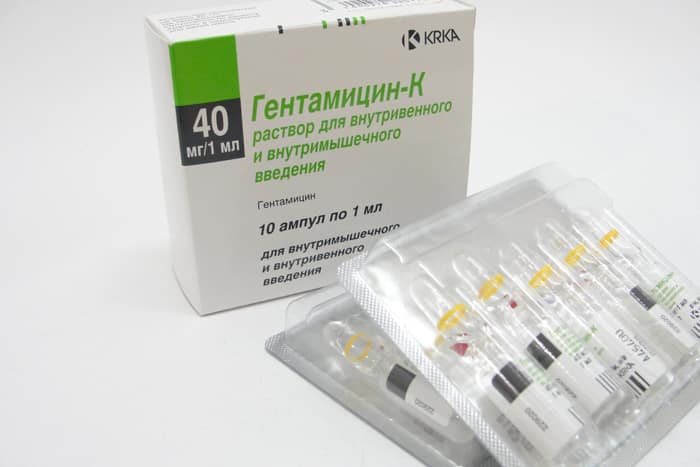
"Gentamicin"
A drug from the aminoglycoside group destroys gram-negative bacteria and is active against Erwinia amylovora. To prepare a composition for treating pears, combine 2 ampoules of Gentamicin with 1 liter of water. The tree is sprayed three times, maintaining an interval of 5 days after the procedure.
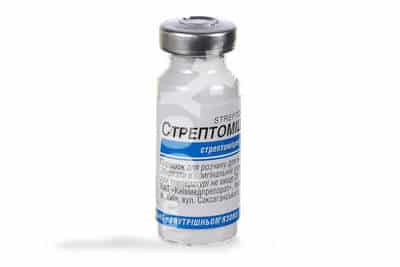
"Streptomycin"
This antibiotic is used to treat industrial plantings because it is inexpensive. In order to spray 10 plants, 5 liters of a composition prepared from water and an ampoule of Streptomycin is enough.
The product cannot be used for 2 or 3 years in a row; it is better to alternate it with Gentamicin, since Erwinia gets used to the active component and it stops helping. How to dilute the preparation for spraying pears is indicated in the annotation, if you buy such antibacterial agents not in a pharmacy, but in specialized gardening centers.
About folk and alternative methods
Infection of a tree with a bacterial burn can lead to its death. It is impossible to destroy the causative agent of the disease by spraying the plant with decoctions of celandine or infusion of garlic and other folk remedies. Agronomists advise first destroying harmful microorganisms, and then restoring beneficial microflora in the garden.
For the prevention and treatment of bacterial and fungal diseases, the following is used:
- "Trichodermin." The mycelial spores present in it germinate into the soil. By releasing toxic substances during their life processes, they destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
- “Pseudobacterin,” which is produced on the basis of a live culture of a microbe, has a negative effect on harmful flora and accelerates the growth of trees.
- “Mycoplant” performs the functions of a fungicide and improves the formation of vermicompost in the soil.
Some gardeners water pears in the spring with Previkur Energy, although the product is intended to protect vegetable crops from diseases, it strengthens the trees’ immunity and prevents the proliferation of microbes.
Resistant varieties
Among the hundreds of types of pears, there are those that are less likely to become infected with fire blight. In regions where the disease has begun to actively spread, it is recommended to plant the autumn early-fruiting Potomac variety, bred in the USA.
The pear of the Ukrainian selection Yablunivskaya is resistant to fungal diseases; it is practically not affected by scab and fire blight.
Late varieties Maria and Noyabrskaya have good immunity to Erwinia amylovora infection.
Preventive actions
It is very difficult to cure a pear from a bacterial burn, and this can only be done in the early stages. If the entire tree is blackened, the struggle does not guarantee a positive result.
Prevention helps reduce the risk of infection with Erwinia, which includes:
- uprooting wild bushes in the garden;
- weed removal;
- spraying pears with copper preparations.
Blackened trees must be disposed of immediately so that the infection does not spread to other crops. Don’t get carried away with watering; bacteria and fungi love damp soil. Do not overfeed pears with organic matter or mineral complexes. Regular sanitary pruning reduces the likelihood of contracting the disease.
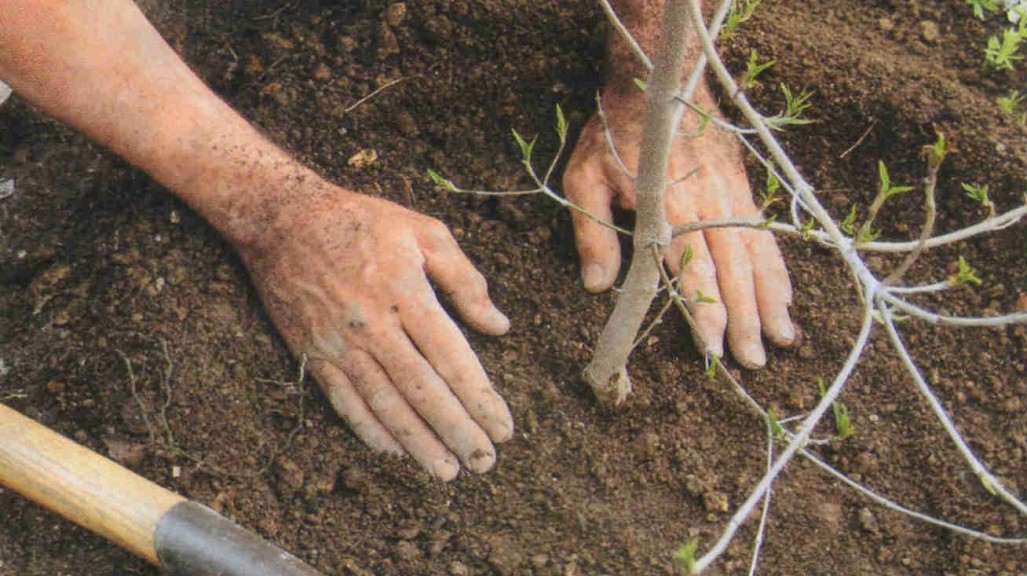
Competent selection of seedlings
A tree for growing on a country plot or cottage must be purchased from a nursery. It is advisable to find out which region it was brought from and find out if there are cases of bacterial burn infection there. You should not take risks buying seedlings from Belarus, Tambov and Saratov regions.A healthy young tree has no scratches on the stem, the roots are not damaged, and the pear itself has an even light brown color.
When choosing seedlings, you should give preference to varieties that are resistant to bacterial blight infection:
- Maria;
- Potomac;
- Williams;
- Carmen.
We must not forget that when trees are treated with the same compounds, pathogenic microorganisms can get used to them, and even worse, mutate. Fungicides need to be changed more often.
In early spring, pears are sprayed with Bordeaux mixture, dried and diseased shoots are removed, and the cuts are lubricated with garden varnish. In summer, in order to stimulate the plant’s defenses, biological products such as “Zircon” are used. In regions where fire blight occurs, pears are sprayed with antibiotics as a preventive measure.
Pest Control
Caterpillars, butterflies, and beetles carry the infection, affecting leaves and branches, and help reduce the defenses of trees. When aphids, fruit beetles, and spider mites appear, both the pears and the soil on which they grow are treated with insecticides, since some pests lay eggs in the tree trunk and larvae hatch in the soil.
Disinfection of garden tools
When shortening shoots, a pruning shear or a sharp knife is used; when uprooting diseased pears, you cannot do without a saw. Mycelial spores and bacteria remain on the tools and are then transferred to healthy trees. To prevent this from happening, the cutting parts are disinfected in a solution of potassium permanganate, alcohol, and kerosene.